1. Understand the fundamentals of Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD).
2. Learn how to create and configure a GitLab CI/CD pipeline step-by-step.
3. Explore how GitLab automates builds, tests, and deployments efficiently.
4. Recognize GitLab’s limitations when scaling to Kubernetes environments.
5. See how Devtron unifies and simplifies Kubernetes operations with one platform for complete control.
In the modern world of software development, Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment have become essential practices.
CI/CD is a continuous software development method involving ongoing building, testing, deploying, and monitoring of iterative code changes. Learning GitLab CI/CD is invaluable for catching bugs early in development and ensuring adherence to established code standards in production deployments.
In this blog, we'll guide you through a hands-on and step by step demo on “How to create a CI/CD pipeline in the Gitlab”.
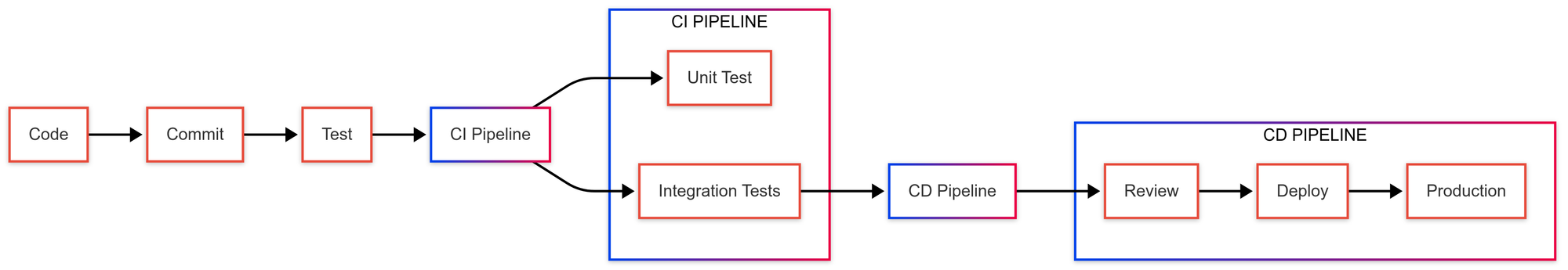
Why Gitlab CI/CD Pipeline?
Now you might be wondering, or a question comes into your mind that there are so many tools like CircleCI, Github Actions, Jenkins, etc available in the market, then what makes Gitlab CI special?
- Gitlab CI provides great issue tracking and issue shuffling features, and it also allows you to parallel test pull requests and branches.
- GitLab simplifies monitoring by displaying test results directly within its user-friendly interface.
- Compared to Jenkins, GitLab offers a more intuitive experience, making it easier to navigate and work with during testing workflows.
Prerequisites
Before creating the CI/CD Pipeline in Gitlab, make sure that you have followed :
- A GitLab account
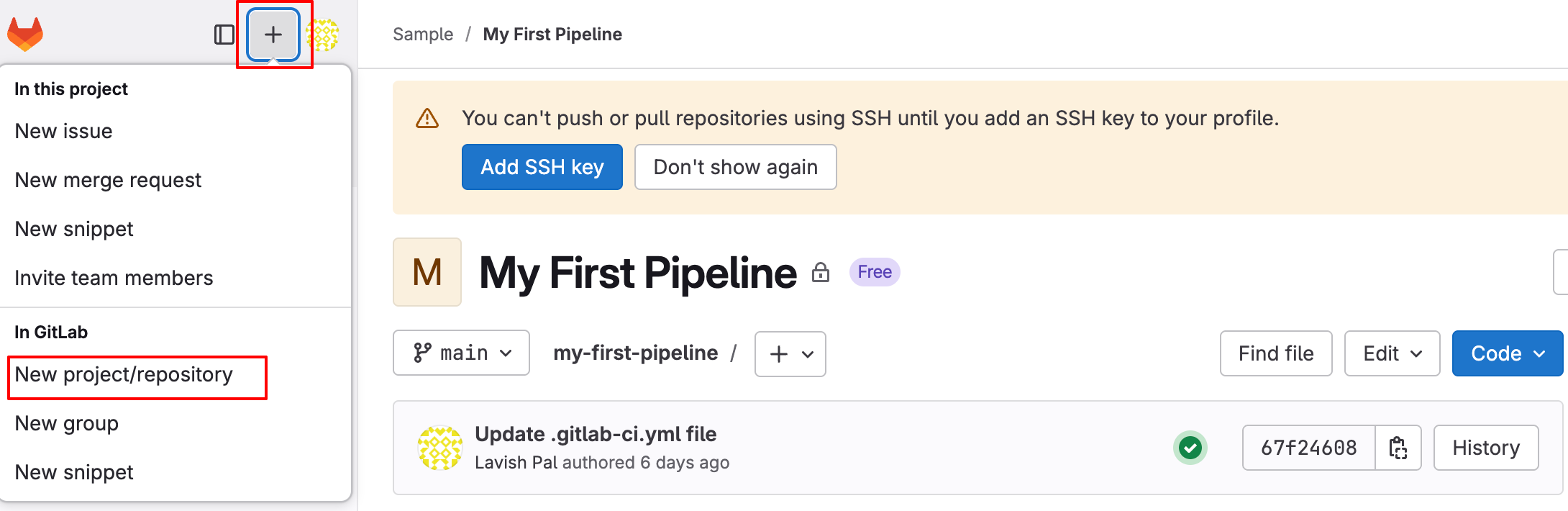
- Create a Blank Project
- On the left sidebar, at the top, select Create new (+) and New project/repository.
- Select Create Blank Project.
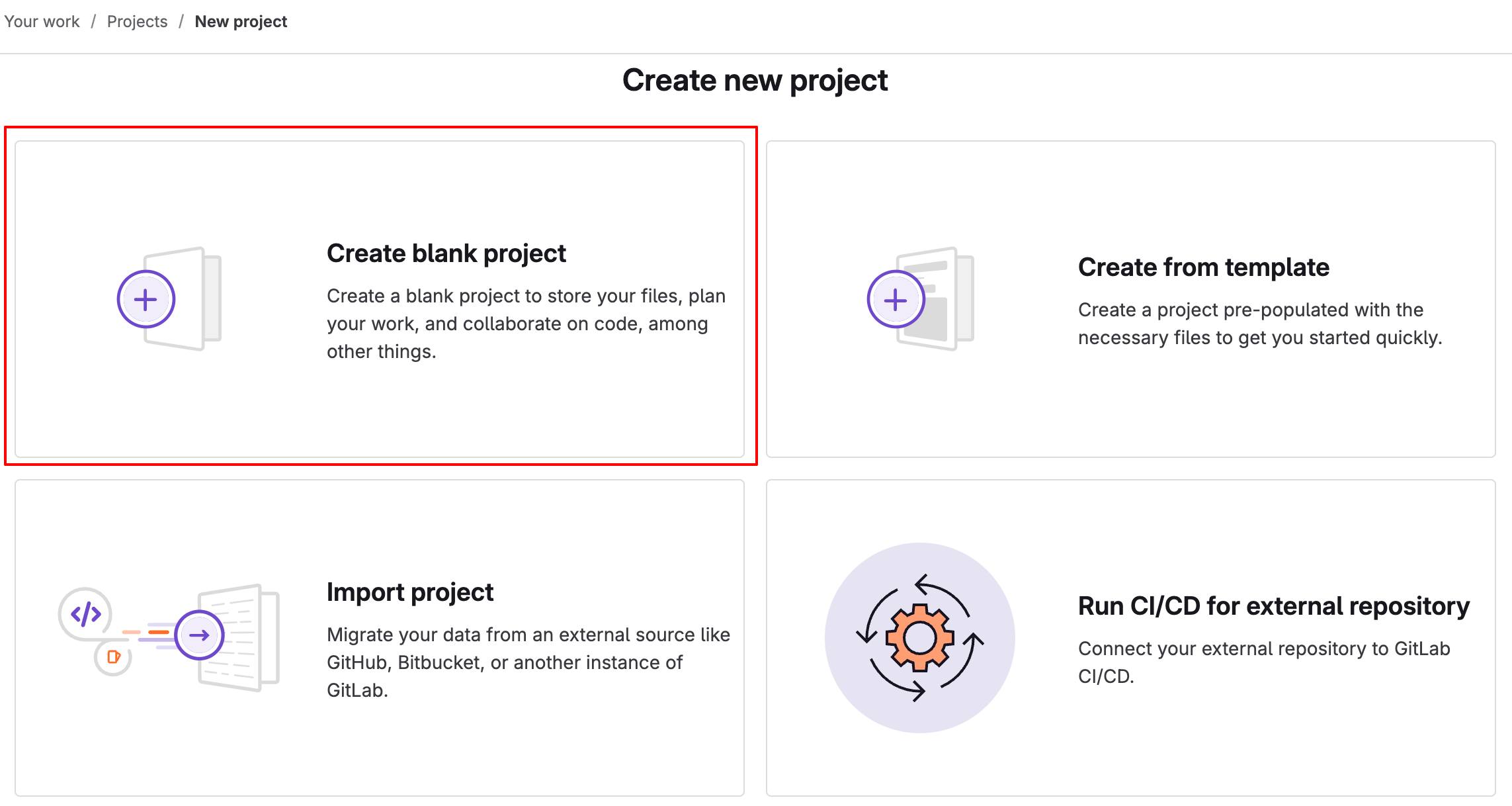
- Enter the project details as per your requirements.
- Select Create project.
So, now you’ve set up your Gitlab account and created a project in Gitlab. Let’s keep the momentum going and follow the next steps.
Step-by-Step guide to build a Gitlab CI/CD pipeline
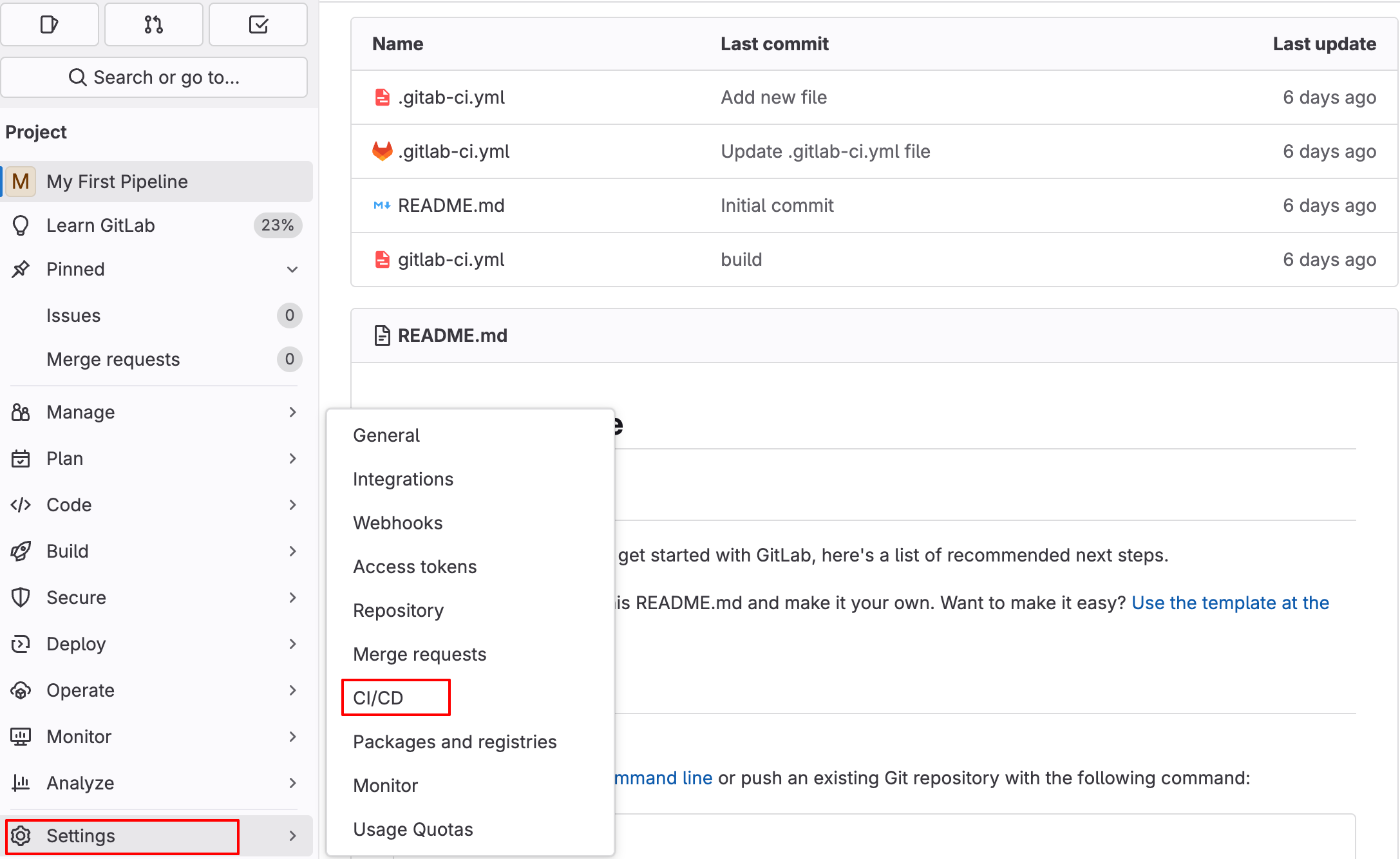
Step 1: Ensure you have all runners available:
- In GitLab CI/CD pipelines,GitLab manually, as GitLab provides them by default.
- To check and ensure that you have all runners available and running.
- Go to your project in Gitlab.
- Navigate to Settings > CI/CD > Runners.
Step 2: Navigate to the root directory:
In your local git repository, make sure you are in the root directory.
Step 3: Create a Gitlab YAML file:
- Create a Gitlab YAML file named
.gitlab-ci.ymlfile. .gitlab-ci.ymlis a YAML file in which you define the instructions for the CI/CD pipeline or what jobs you want to perform by defining all the stages like building, testing and deploying.- For creating a
.gitlab-ci.ymlfile in your project
- Navigate to the project’s main page in GitLab.
- Navigate to the project and click on the (+) icon on the right-hand side of the project name.
- From the drop-down menu, select the “New File”.
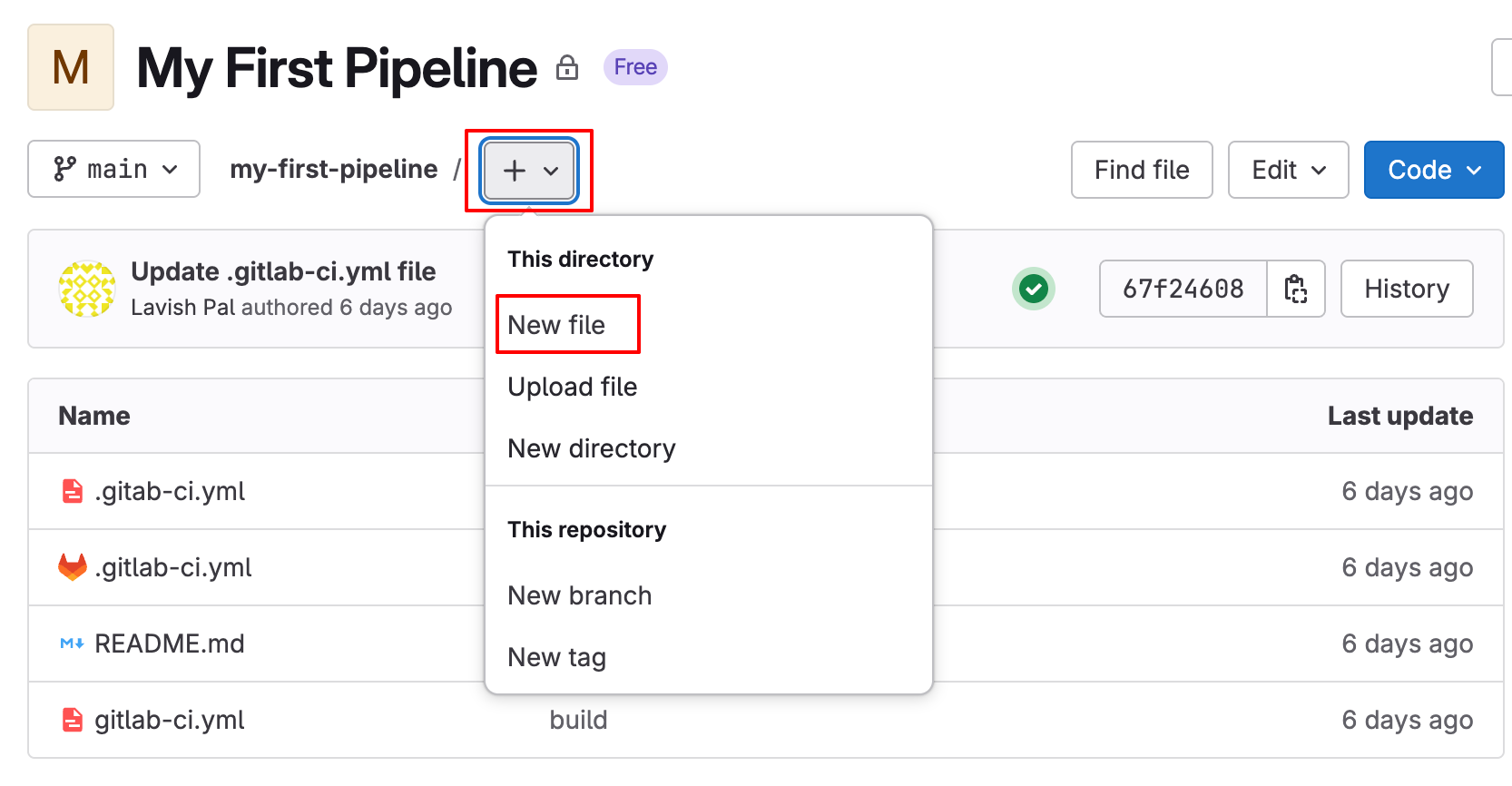
- In the filename, enter
.giltlab-ci.yml. - Define the pipeline stages and jobs within this file.
stages:
- build
- test
- deploy
build-job:
stage: build
script:
- echo "Building the project..."
test-job:
stage: test
script:
- echo "Running tests..."
deploy-job:
stage: deploy
script:
- echo "Deploying the application..."
- Now commit to the main branch to automatically trigger and start executing the defined stages.
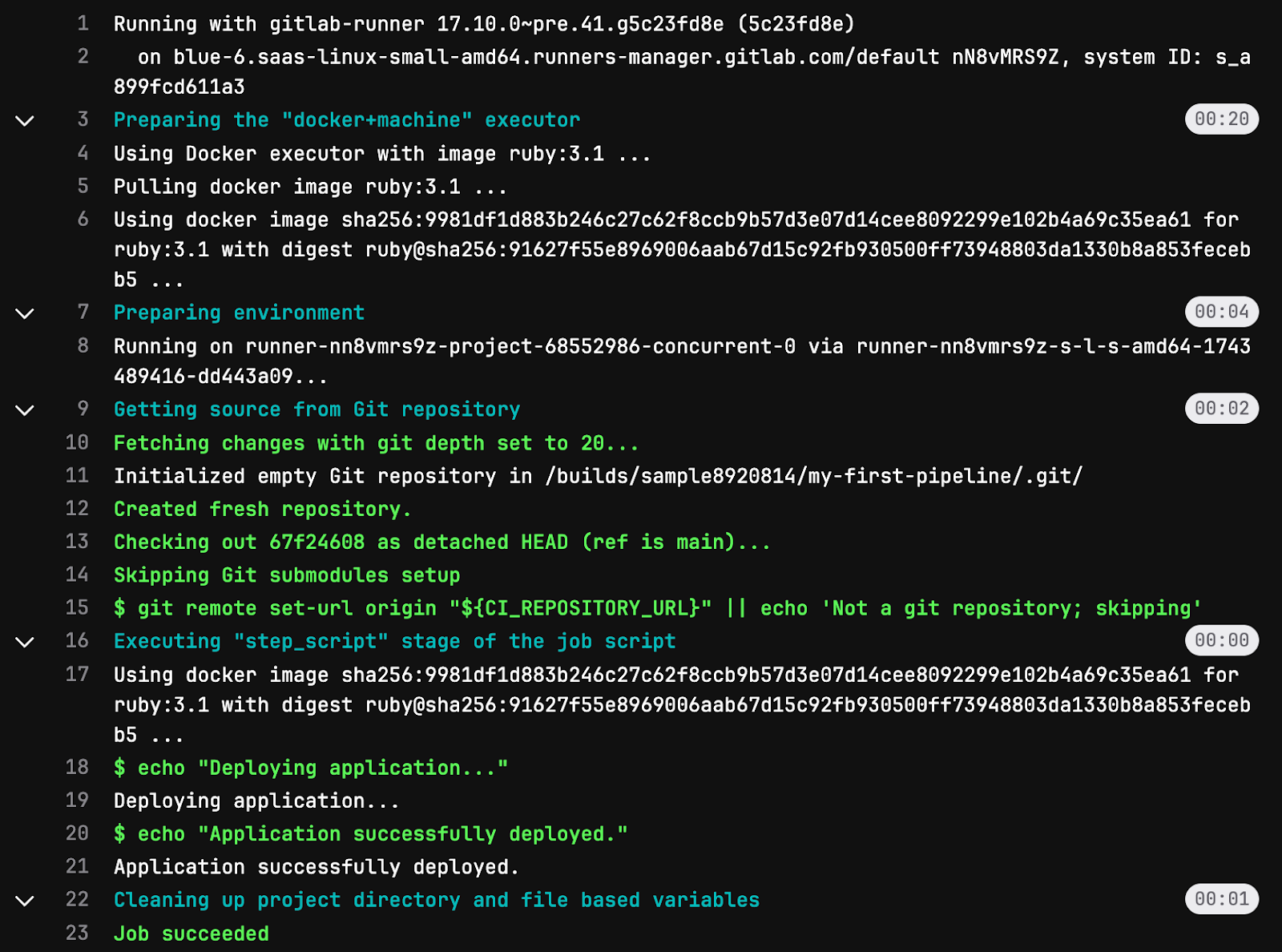
Step 4: Monitor the status and result of the CI/CD Pipeline
Once the .gitlab-ci.yml The file is committed, and Gitlab automatically triggers the pipeline as defined in the configuration file.
To view the status of the Gitlab CI/CD pipeline:
- Navigate to the project main page and go to Build > Pipelines.
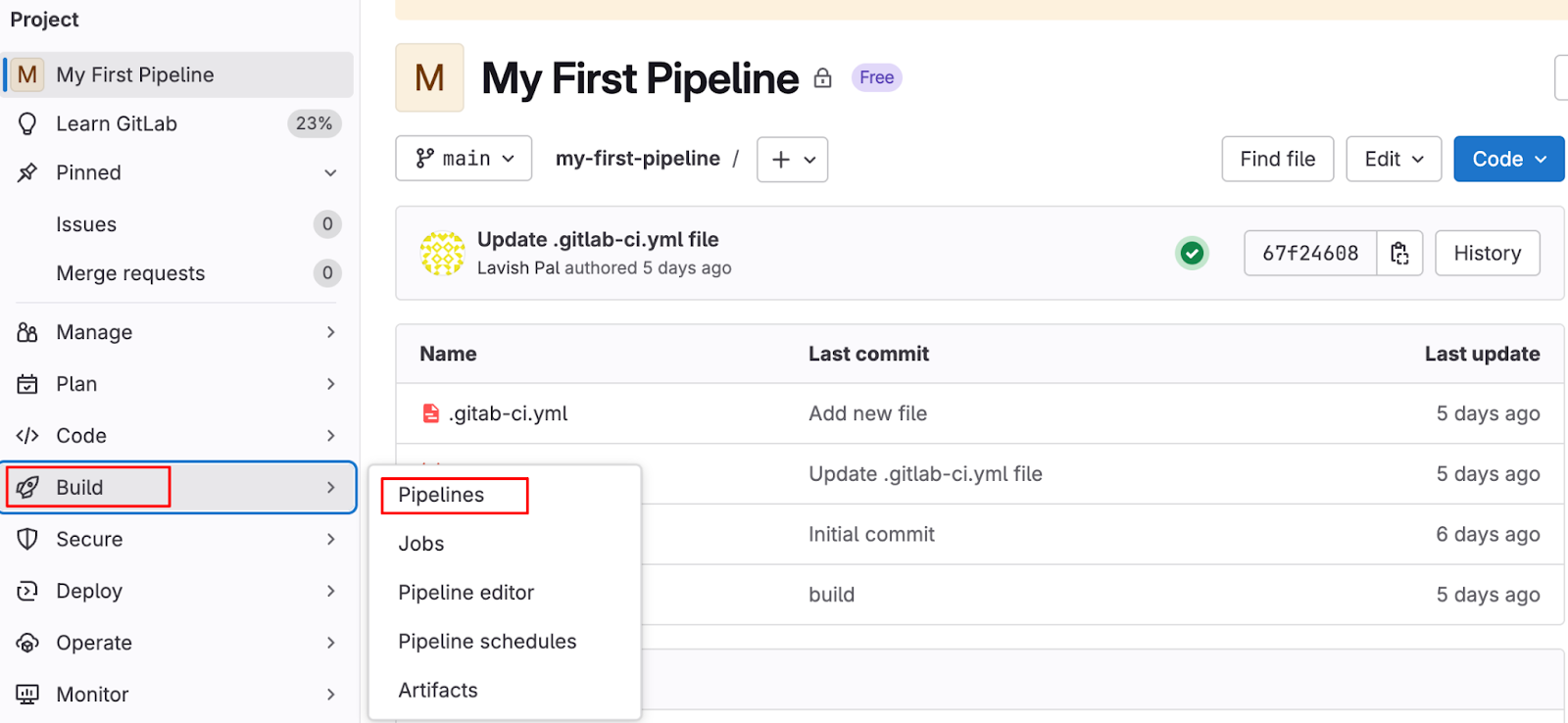
- Click on the pipeline to inspect. This will open a visual representation of your pipeline, showing all the stages like
build,test,deployIn what order do you define the.gitlab-ci.ymlfile.
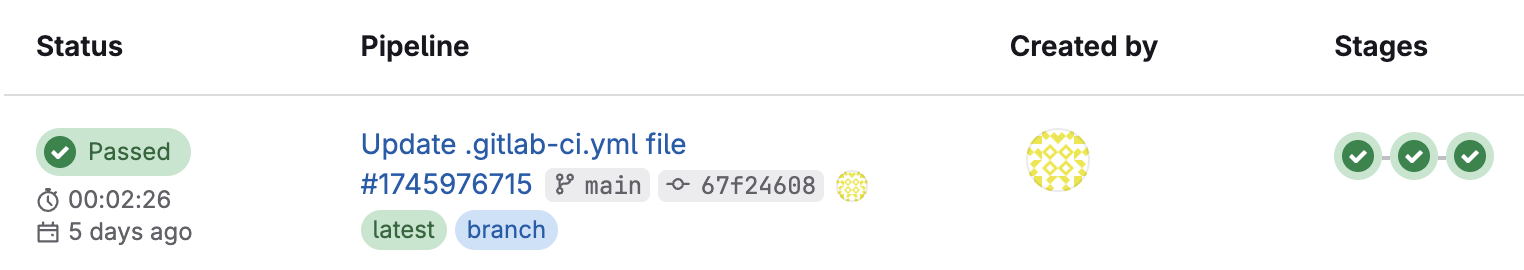
- Navigate to the jobs section to view the particular jobs in the pipeline.
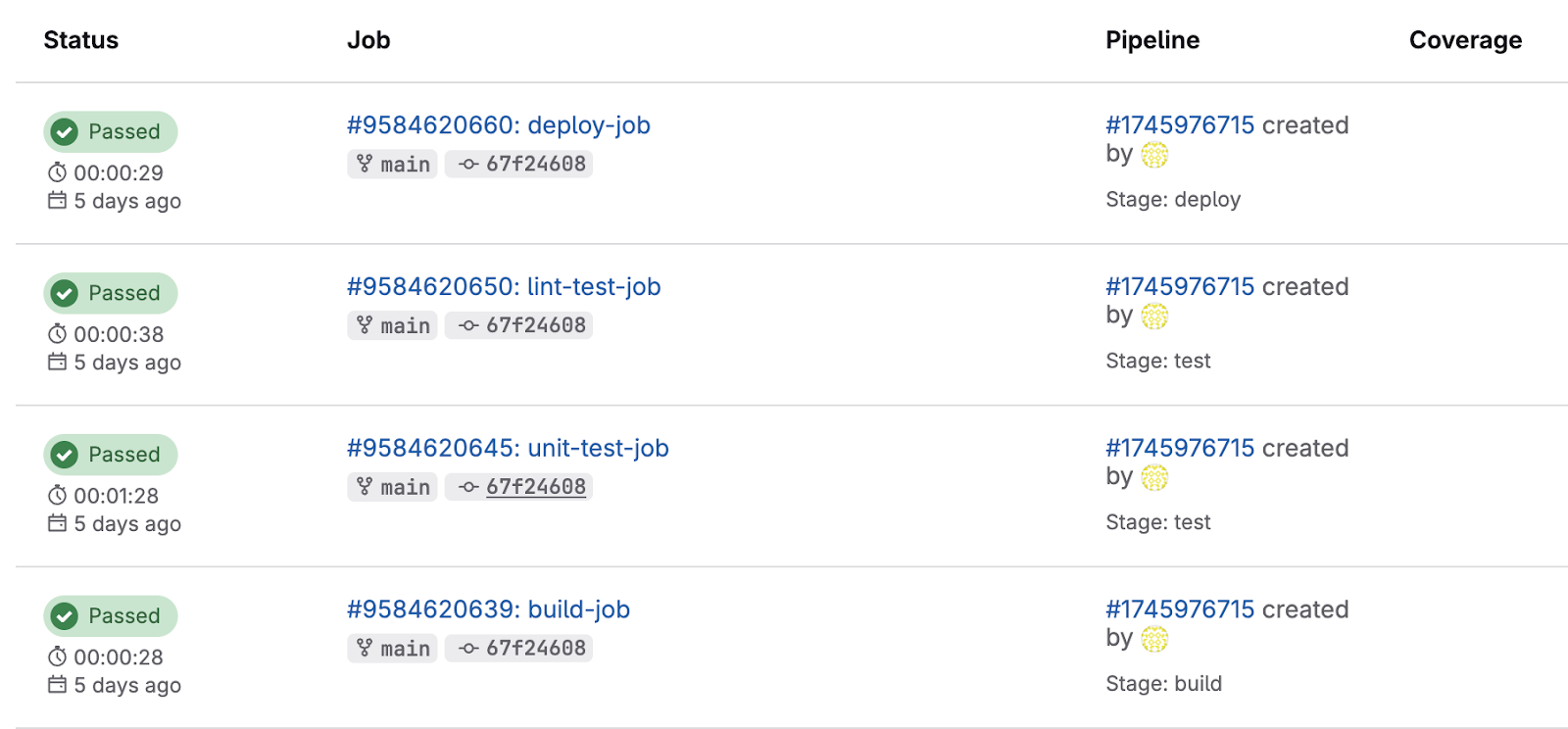
- Click on the job for a detailed view of how the execution of that particular job is done.
Limitations of GitLab CI/CD Pipeline
While GitLab CI/CD simplifies the automation of builds and deployments, it’s not built for the full operational complexity of Kubernetes.
When teams scale to dozens of microservices or hybrid environments (across AWS, Azure, GCP, or on-premise), challenges emerge:
- No native GitOps integration for Kubernetes,
- Limited infrastructure visibility,
- Fragmentation across multiple monitoring and deployment tools,
- Growing operational chaos as clusters and environments multiply.
That’s where platforms like Devtron come in.
Automate CI/CD using Devtron
Devtron is the Enterprise Kubernetes management platform that eliminates operational chaos through unified control and AI-powered operations across all clusters and clouds.
While GitLab CI/CD streamlines builds and deployments, Devtron extends automation to the entire Kubernetes lifecycle from your first migration to managing hundreds of microservices.
How Devtron Transforms CI/CD Workflows
- Unified Operations: Manage CI/CD, GitOps, observability, and cost optimization from one control plane — no more switching between 15+ tools.
- Native GitOps: Automate continuous, declarative deployments through integrated GitOps and Argo CD.
- AI Operations: Devtron’s Agentic SRE will autonomously identify and resolve app–infrastructure app-infrastructure.
- Multi-Cloud Ready: Operate consistently across AWS, Azure, GCP, or on-prem — with no vendor lock-in.
With Devtron, platform teams move from tool sprawl and firefighting to unified visibility and control, transforming Kubernetes operations from chaos to clarity.
Explore more Devtron Features and explore how you can build a Kubernetes CI/CD pipeline with Jenkins (CI) and ArgoCD (GitOps CD), then check out this blog: Kubernetes CI/CD Pipelines with Jenkins and ArgoCD.
Conclusion
GitLab CI/CD pipelines provide automation and streamline the entire software delivery process from development to deployment. Whether building a new pipeline or improving an existing pipeline, GitLab becomes a reliable partner that helps you move faster, catch issues early, and build.
FAQ
What is GitLab CI/CD used for?
GitLab CI/CD can identify the bugs early in the software development lifecycle through automates testing and continuous integration.
What is the difference between Jenkins and GitLab CI/CD?
GitLab is an integrated DevOps platform that offers version control, CI/CD, issue tracking, and code review. Jenkins is an automation server primarily focused on CI/CD, automating tasks like building, testing, and deploying code changes.
What are GitLab CI file?
GitLab CI file named as .gitlab-ci.yml is the file in which you define the instructions for the CI/CD pipeline, or what jobs you want to perform by defining all the stages, like building, testing, and deploying
What are the GitLab runners?
GitLab runners are the agents responsible for running the jobs in a GitLab CI/CD pipeline and are also used for building, test, deploy the project.










