
A web-based interface for monitoring and managing Kubernetes cluster resources.

Kubernetes provides a command line (CLI) component called “kubectl” for carrying out core operations like managing application deployments, releasing updates, managing traffic provisioning storage, and much more. But there are two significant hurdles to using CLI enterprise-wide:
The high learning curve for developers to adopt Kubernetes for deployment.
Time-consuming and frustrating work for SREs and Ops team to monitor and troubleshoot multiple clusters at scale.
Dashboard by Kubernetes ( also known as Kubernetes Dashboard) is a web-based user interface to deploy applications into the Kubernetes cluster, monitor the health of all the resources, and troubleshoot them in case of any issues. The application is helpful for DevOps, Ops, and SRE teams to manage Kubernetes resources such as Deployments vs Statefulsets, Jobs, etc. One can quickly deploy an application using manifest files and update the help from the UI itself.
Features of Kubernetes Dashboard
Kubernetes Dashboard is compelling for the DevOps team because of two primary features:Cluster-wide visibility and troubleshooting.UI-based deployment.
Cluster-wide visibility and troubleshooting
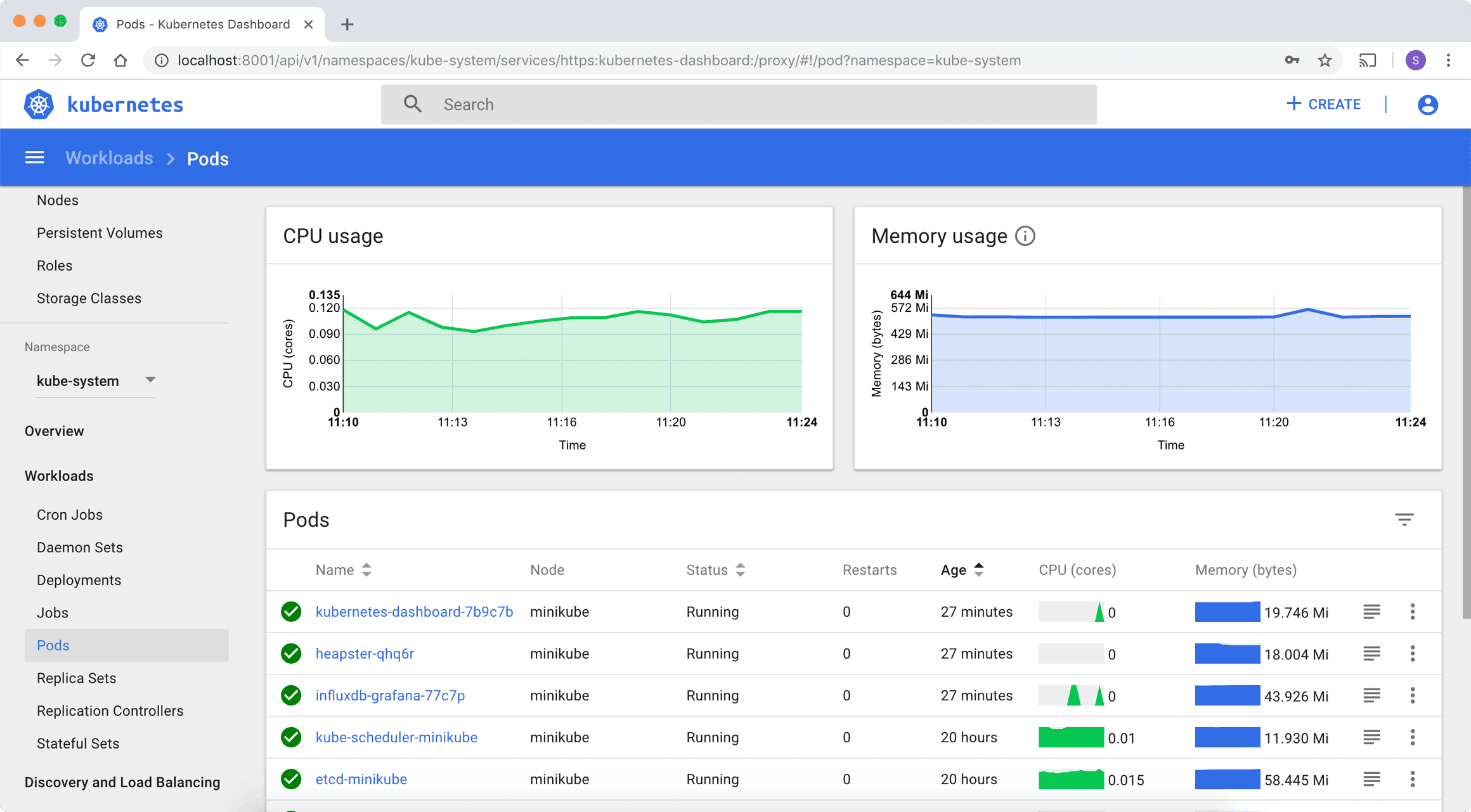
The Kubernetes Dashboard will provide a view of various running workloads and their total count. DevOps engineers will get the visibility of workloads, services, configurations and storage, and cluster view.
Workload view
Under the workload view, users will get the details of workload resources such as Deployments, Pods, ReplicaSets, DaemonSets, Job, and StatefulSet running in all the namespaces of a cluster. One can also perform a granular search based on a particular namespace in a cluster. Getting a visual representation of these different workloads helps in managing various applications deployed on the cluster.
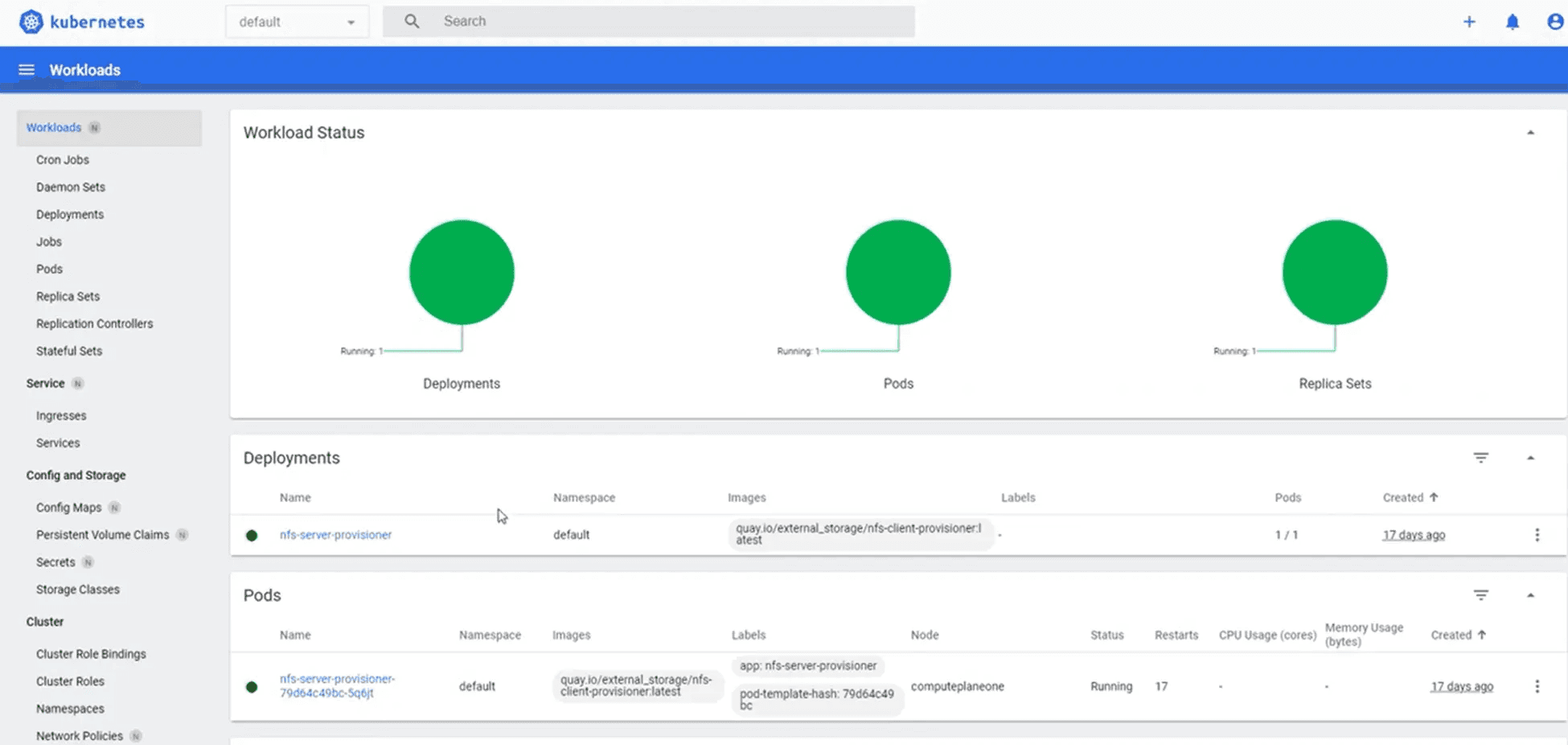
Pods view
One of the most important aspects of workloads can be the number of pods running in a specific node and its respective namespace.
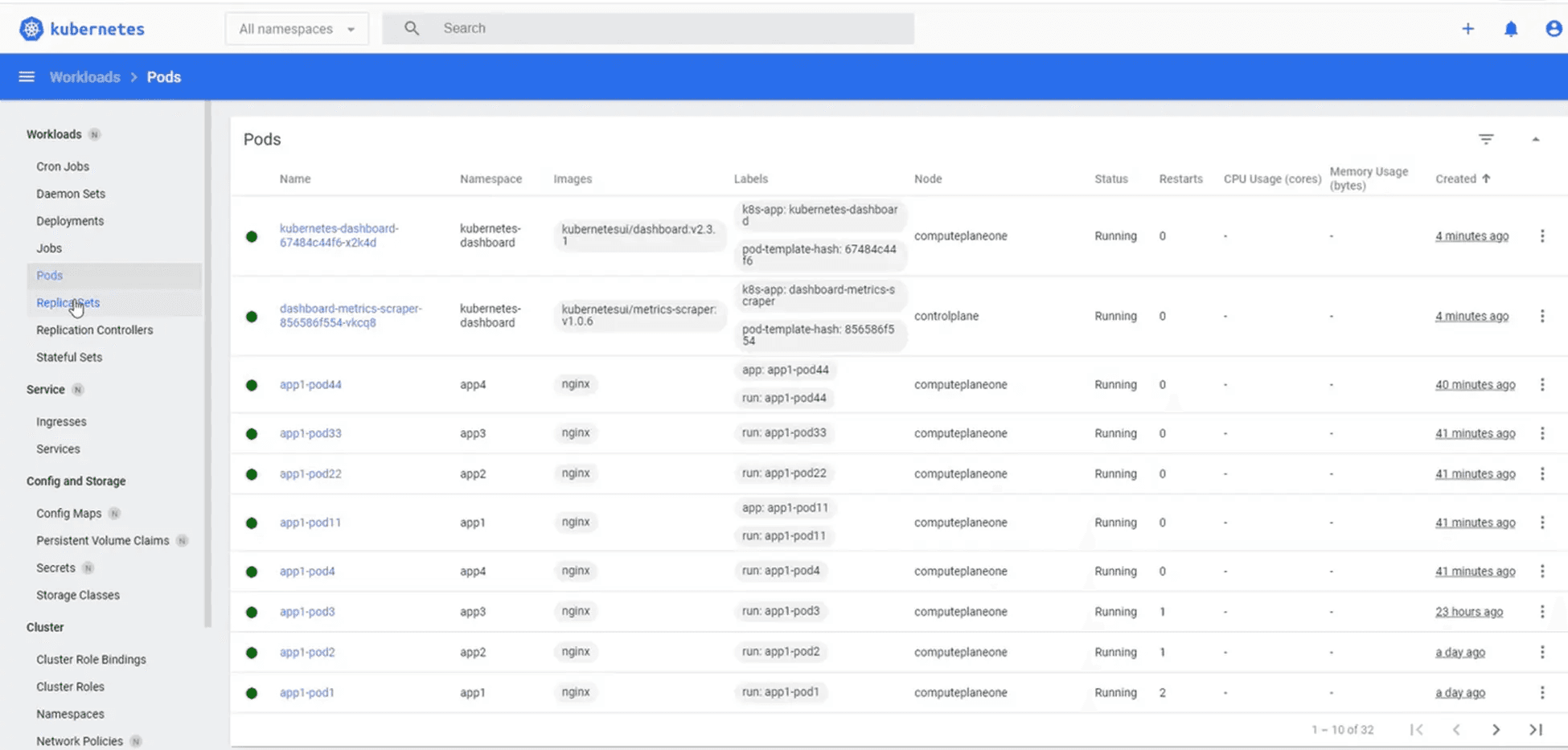
Users will get drilled-down information about a pod, such as:
Metadata about labels and annotations.
Resource consumption – CPU and memory utilization.
Date of creation and number of restarts.Events logs and persistent volume claim.
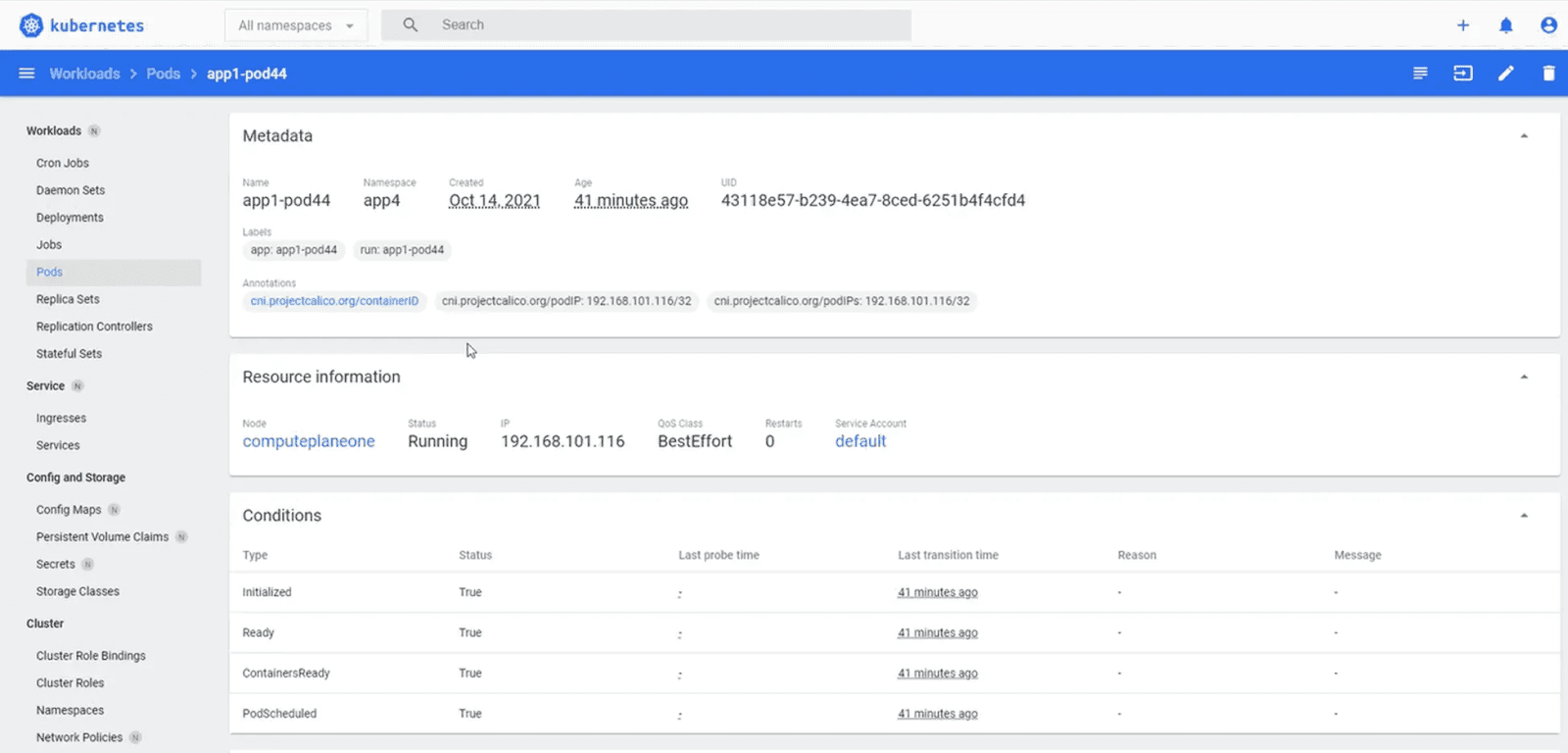
Similarly, Kubernetes Dashboard also provides an aggregated view of namespaces and a detailed view of services & ingress objects, configmaps, network policies, secrets, and persistent volume claims in a namespace. Visibility into these resources can help with cluster management.
Service and Ingress view
Kubernetes Dashboard provides visibility about running Services and Ingress objects, including the namespace each Service or ingress belongs to, their labels, and Cluster IP. Users can get far more drilled-down information about each Service, such as labels, pods, endpoints, etc.
Configuration and storage view
Kubernetes Dashboard provides visibility about running Services and Ingress objects, including the namespace each Service or ingress belongs to, their labels, and Cluster IP. Users can get far more drilled-down information about each Service, such as labels, pods, endpoints, etc.
UI-based Deployment
The Kubernetes Dashboard allows you to deploy any (workload) resources from the UI. You can create manifest files in the browser, or you can upload your manifest files from a source such as Git. And the Kubernetes Dashboard will directly communicate with the Kubernetes controller to get an object of a resource created for you. In the below example, we have created a manifest file to create a pod with NGINX 1.19.0 image to create a pod.

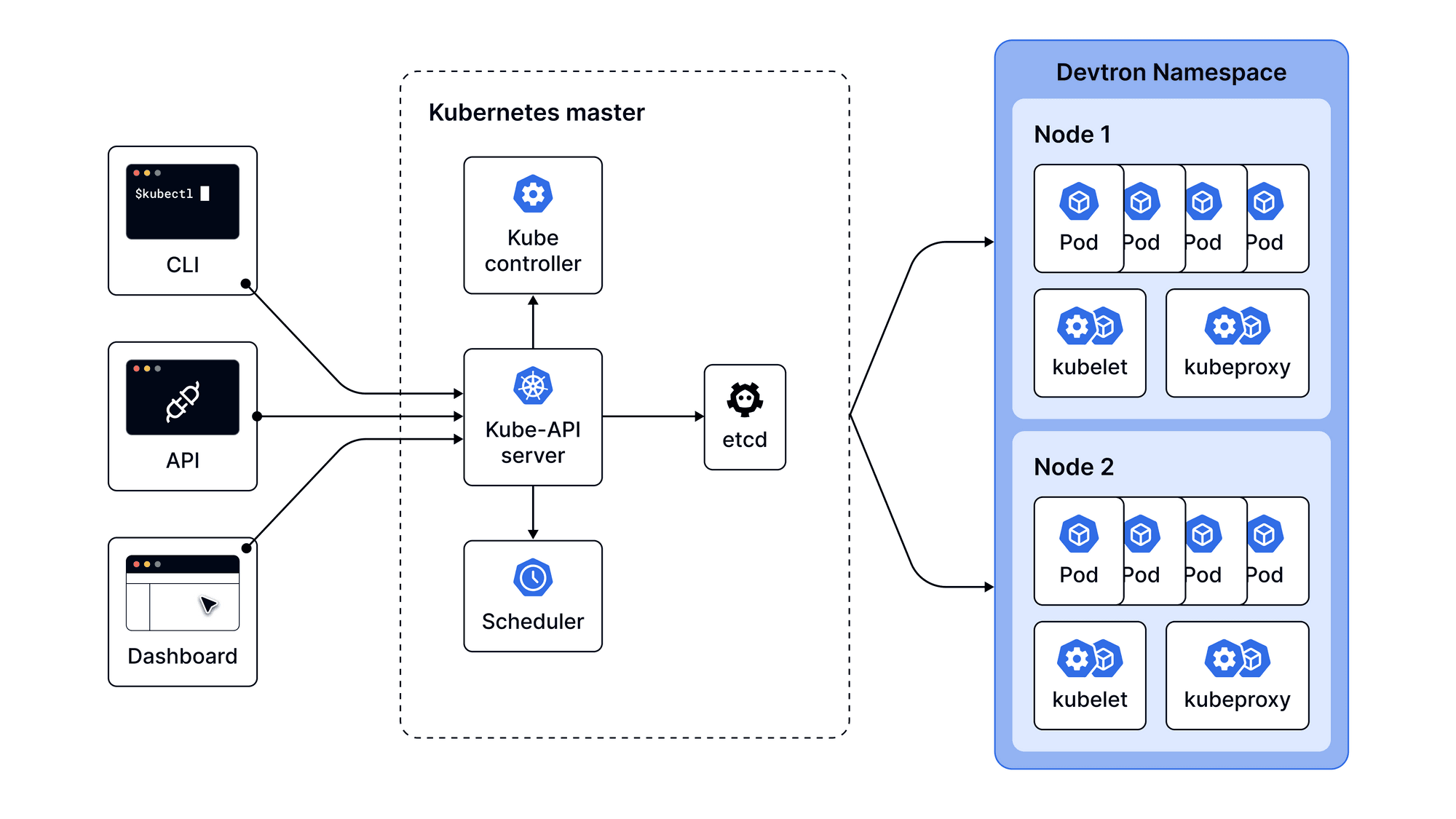
Kubernetes Dashboard Architecture
Kubernetes Dashboard is an external service developed on top of Kubernetes architecture. Under the hood, the Dashboard uses APIs to read all cluster-wide information for visibility into a single pane. It also uses the APIs to deploy resources and applications into a cluster. Both CLI and Kubernetes Dashboards depend on the kube-API-server to process the requests. To get started with the CLI, the Ops team must deploy the Kubernetes Dashboard in the same cluster (similar to Kubectl deployment).
Getting started with Kubernetes Dashboard
To get started with Kubernetes Dashboard, you need to run the following commands in your cluster.
Step 1: Deploy Kubernetes Dashboard
The Kubernetes dashboard can only be installed with Helm. Please ensure that you have Helm installed and run the below commands:
To access the Kubernetes Dashboard from the local machine, one can create a secure channel to access the K8s cluster by running the following command:
You can access your Dashboard using the following URL: http://localhost:8001/api/v1/namespaces/kubernetes-dashboard/services/https:kubernetes-dashboard:/proxy/
Step 2: Create a Service Account
The Kubernetes Dashboard is installed with minimal RBAC permissions, so you can access the Dashboard using a bearer token. So you can create a service account and bind it to a cluster with admin rights. You can use the following service account yaml file:
Make service resources by using the command:
You can use the following ClusterRoleBinding.YAML to make the service account as cluster-admin:
Similarly, apply the YAML file to create a ClusterRoleBinding resource in your cluster.
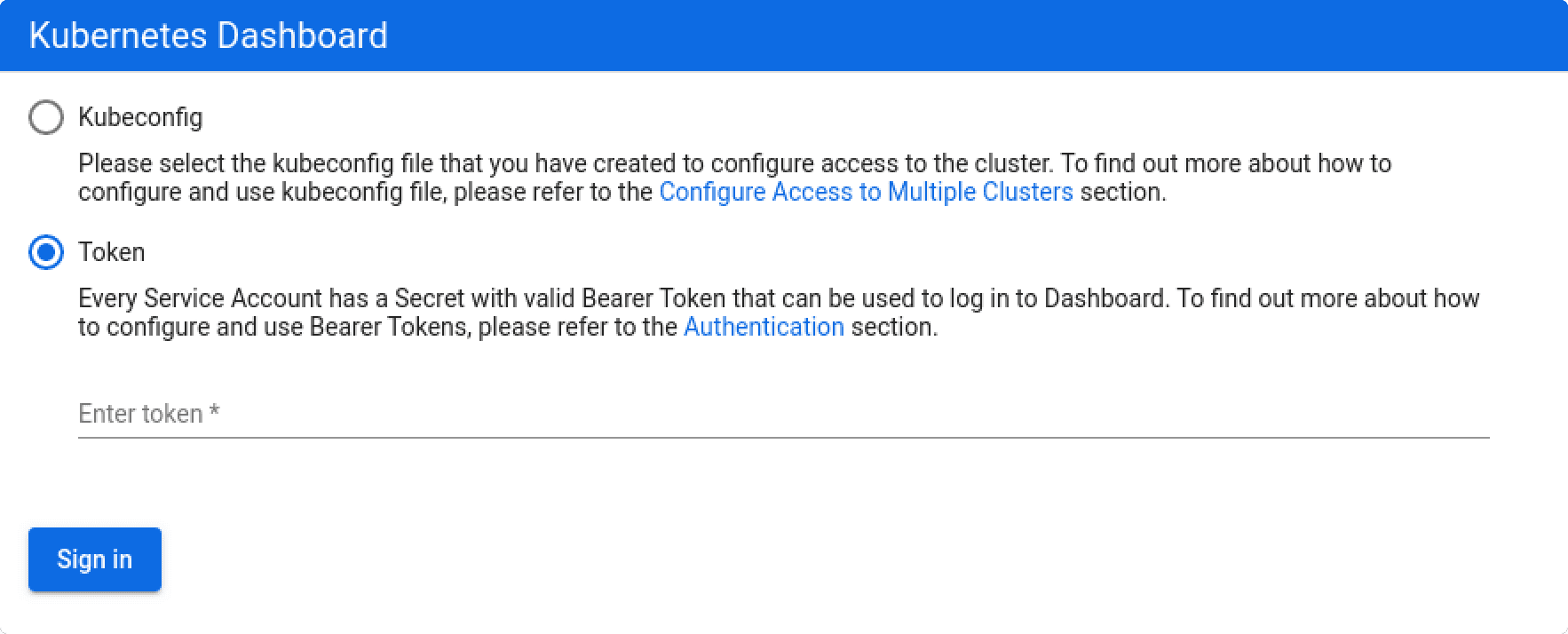
Step 3: Generate Bearer Token
Use the command to generate the bearer token
Step 4: Use the token and get started with the Dashboard
You can paste the bearer token to get started with Kubernetes Dashboard.
Limitations of Kubernetes Dashboard
Using a UI-based Kubernetes Dashboard to replace CLI is undoubtedly good. However, there are a few limitations that restrict its use cases to only small startups:
Lack of multi-cluster view
Kubernetes Dashboard provides the view pertinent to namespaces in a single cluster. It does not offer a view of multiple clusters.Minimal RBAC
Kubernetes does not provide granular access control for various users. One has to be dependent on token or kubeconfig files.Lack of Single Sign On(SSO)
Kubernetes Dashboard does not provide SSO login services. SSO is essential for mid and large enterprises to secure resources and applications in Kubernetes.No Node management
Kubernetes Dashboard DevOps team to view the node information such as status, labels, limits, and memory/CPU requests, machine ID, addresses, allocated resources, pods, etc. But does not allow any provision to edit nodes and manage nodes. This is essential because if a node is unhealthy, it will not run any pods and will not participate in cluster activity.Zero visibility and manageability of HELM charts
Many organizations use them to deploy their Kubernetes applications at scale. Unfortunately, Kubernetes Dashboard does not provide the capability to HELM Dashboards.Lack of application view
Kubernetes Dashboard provides the resource or object view but needs to provide more information about applications, making it cumbersome for developers to modify any deployments. Without application view, Kubernetes Dashboard has restricted its usage to only the Ops team.Audit
Kubernetes Dashboard does not offer audit reports of deployments, such as who, when, and how an application is being deployed.
Note, although Kubernetes Dashboard is also developed to make the deployment easy from UI, today, there is no mechanism to apply advanced deployment strategies such as canary from the UI.
Open source alternatives to Kubernetes Dashboards
There are a number of alternatives to the default Kubernetes dashboard. Let us explore a few of these dashboards.
Devtron
Devtron provides an open-source Kubernetes-native DevOps platform that automates the entire software delivery process from CI, CD, GitOps, security and governance, progressive deployment, observability, monitoring, and troubleshooting. Devtron Kubernetes dashboard provides powerful features in a single pane to make DevOps, SREs, and developers' life simpler:
HELM chart dashboard and management from a single pane of dashboard
Events and real-time logs, and pod execution for debugging
UI-based deployments (or modifications to existing manifest files)
Instant rollback of new deployments to production
DORA metrics
Granular RBAC for users, action and resources.
OpenLens
An open-source software with an MIT license used for multicluster management and monitoring workloads. It also provides basic HELM resource management and resource grouping, but it may require a learning curve. Secondly, it has a few blind spots as it does not provide HELM chart groups for multicluster deployments, Chart config differences, etc. Read more about Devtron vs OpenLens
Octant
Open source dashboard started by VMware but is archived now- no community support, and you are on your own. Initially, the project was targeted for developers to use the UI to ship code faster into clusters. Octane has limited functionalities w.r.t cluster visualization and management. Read more about Devtron vs Octant.




