1. Understand how Jenkins and Argo CD power CI/CD pipelines for Kubernetes environments.
2. Learn the differences between Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment (CD).
3. Discover the limitations of Jenkins and Argo CD in modern, large-scale Kubernetes operations.
4. See how GitOps improves deployment consistency and control.
5. Explore how Devtron unifies Jenkins, Argo CD, and GitOps principles into one enterprise-grade Kubernetes platform.
Introduction
In the modern software landscape, where teams deploy to production multiple times a day, Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment (CD) are essential to maintain both speed and stability.
CI/CD pipelines automate repetitive development tasks — from testing and building to deploying applications — enabling teams to innovate faster while minimizing risk.
In this blog, we’ll explore how tools like Jenkins (for CI) and Argo CD (for CD) form the backbone of reliable CI/CD pipelines. We’ll also discuss where these tools fall short and how Devtron enhances them to deliver unified control across Kubernetes environments.
Continuous Integration
Continuous Integration (CI) is a DevOps practice that streamlines development by automating code integration, building, and testing. It allows developers to frequently commit changes to a shared repository, triggering automatic builds and tests. This process ensures code quality, and smooth integration, and accelerates software delivery.
What is Jenkins?
Jenkins is an open-source CI server that automates key stages of the development lifecycle, building code, running tests, performing security scans, and generating Docker images.
At its core, Jenkins uses Pipelines, typically written in Groovy, to define multi-stage workflows that can integrate with hundreds of external tools through its vast plugin ecosystem.
Jenkins supports all major version control systems, build tools, testing frameworks, and cloud platforms, making it an adaptable choice for diverse environments.
Why Jenkins Still Matters
Despite the rise of newer CI/CD tools like GitHub Actions and CircleCI, Jenkins remains widely used due to its flexibility and maturity.
- Customization & Plugins: Thousands of plugins enable tailored workflows and integrations.
- Open-Source & Community-Driven: Continuous innovation and community support keep Jenkins evolving.
- Declarative Pipelines: A structured, YAML-like syntax simplifies complex automation logic.
- On-Premise Deployment: Ideal for organizations with strict compliance or data control needs.
- Proven Reliability: Over a decade of production use makes Jenkins a trusted enterprise solution.
To deepen your understanding of using Jenkins for CI in Kubernetes environments, we recommend exploring our comprehensive guide: What is Jenkins? A Quick Guide for CI/CD with Jenkins
Continuous Deployment
Continuous Deployment automates the release of validated code into production environments. Tools like Argo CD apply GitOps principles, treating Git as the single source of truth for configuration and infrastructure. This ensures traceable, version-controlled deployments with minimal manual effort.
Why ArgoCD
Argo CD is a declarative GitOps tool built for Kubernetes. It continuously syncs the desired state (from Git) with the actual state (in the cluster), ensuring consistency and enabling rollbacks with ease.
Key strengths include:
- Kubernetes-Native Integration: Supports Helm charts, Kustomize, and raw YAML for deployment flexibility.
- Advanced Deployment Strategies: Built-in support for blue-green and canary rollouts reduces downtime.
- User-Friendly Dashboard: Enables non-CLI users to manage applications visually.
This makes Argo CD a strong candidate for teams adopting GitOps workflows in Kubernetes.
Deployment to Kubernetes
In the above sections of CI with Jenkins, the pipeline was configured to build the docker image and update the deployment.yml file with the latest image for deployment. Now going forward with the deployment we will use ArgoCD a GitOps tool for deployment to the Kubernetes cluster and maintain the history of our deployments to the Git repository. As ArgoCD treats Git repositories as a single source of truth it continuously syncs the changes from the Git repository to the target deployment environment. As ArgoCD also requires a deployment.yml file to execute the deployments to the Kubernetes cluster, we need to provide the deployment.yml file stored in the Git repository.
Let’s configure ArgoCD for CD, for installation of ArgoCD you need a Kubernetes cluster. For experimentation purposes, you can spin a Minikube cluster and proceed with the ArgoCD installation.
Step 1: Setting up the Environment
Spin up a Kubernetes cluster, for starting up you can opt for the Minikube cluster, refer to this documentation for firing up a Minikube cluster.
For ArgoCD installation there are two methods, you can install ArgoCD by Helm chart or by using the Controller and Operator of ArgoCD. For installation through Controller and Operator navigate to Operatorhub, click Install, and execute the given commands for installation of ArgoCD Controller. Once the Controller is installed, proceed with the installation of the Operator. Once all pods of ArgoCD are up and running the dashboard of ArgoCD can be accessed.
Step 2: Accessing the ArgoCD Dashboard
ArgoCD provides its dashboard where you can configure and manage the deployments to your Kubernetes clusters. Once the pods of ArgoCD are running, you need to change the type of example-argocd-server to access the dashboard from ClusterIP to NodePort. Now, try to access the service through the minikube service example-argocd-serve command. As the command is executed you will be redirected to the dashboard of ArgoCD.

Step 3: ArgoCD Credentials
The ArgoCD dashboard requires a username and password to access and execute the deployments. The initial Username for the ArgoCD dashboard is admin.
The password for the ArgoCD dashboard is stored in one of the secrets created at the time of ArgoCD installation.
- To get the password navigate to the terminal and execute
argocd admin initial-password -n argocd
- The password needs to be decoded as it's base64 encoded, To decode the password execute
echo <base64-encoded-password> | base64 -d
- Paste the output password on the ArgoCD dashboard with the username as admin and you can access the ArgoCD dashboard now.
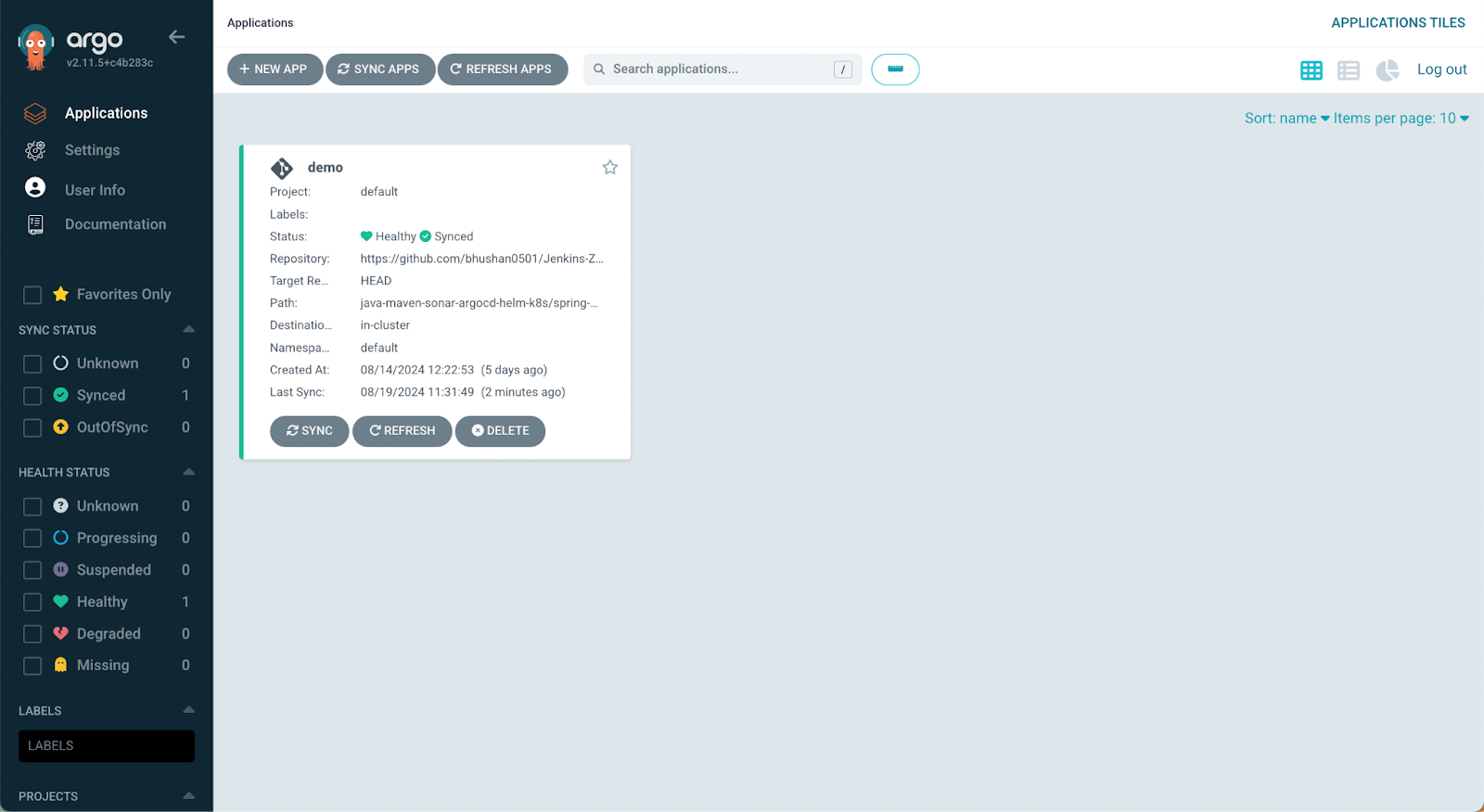
Step 4: Deploying Application Using ArgoCD
Let’s deploy the application to the Kubernetes cluster using the ArgoCD dashboard.
- On the dashboard navigate to + New App.
- Provide an application name argo-demo.
- Choose the project default.
- Choose the SYNC POLICY as Automatic.
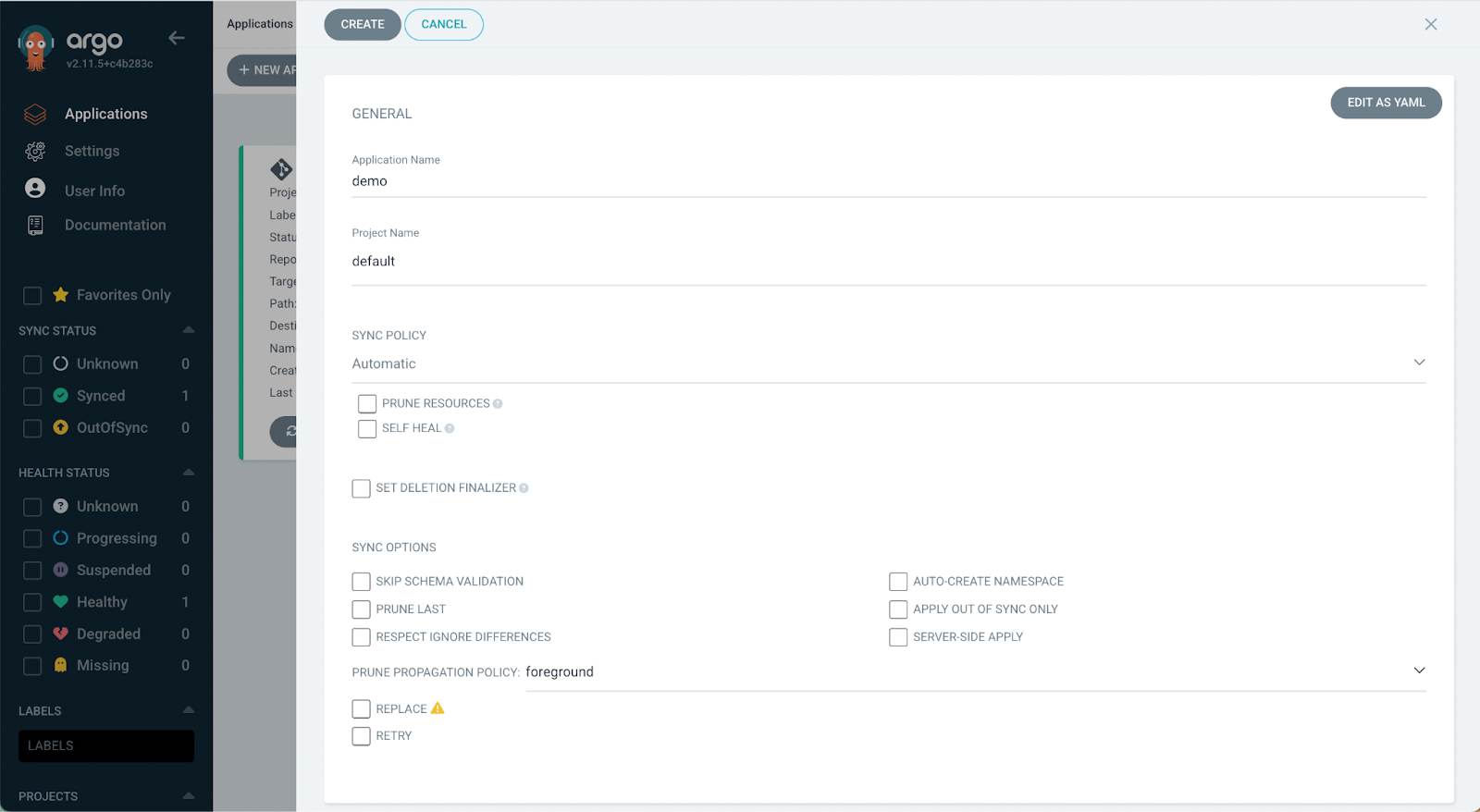
- Under the SOURCE section provide the URL of the application repository in the Repository URL field.
- Under the Revision field choose the branch of Git Repository.
- At the Path, field the Path to the deployment.yml file which we updated through the Jenkins pipeline.
- Under the DESTINATION section, we need to provide the details of where we have to deploy the application. Provide a Cluster URL and the Namespace where the application should be deployed.
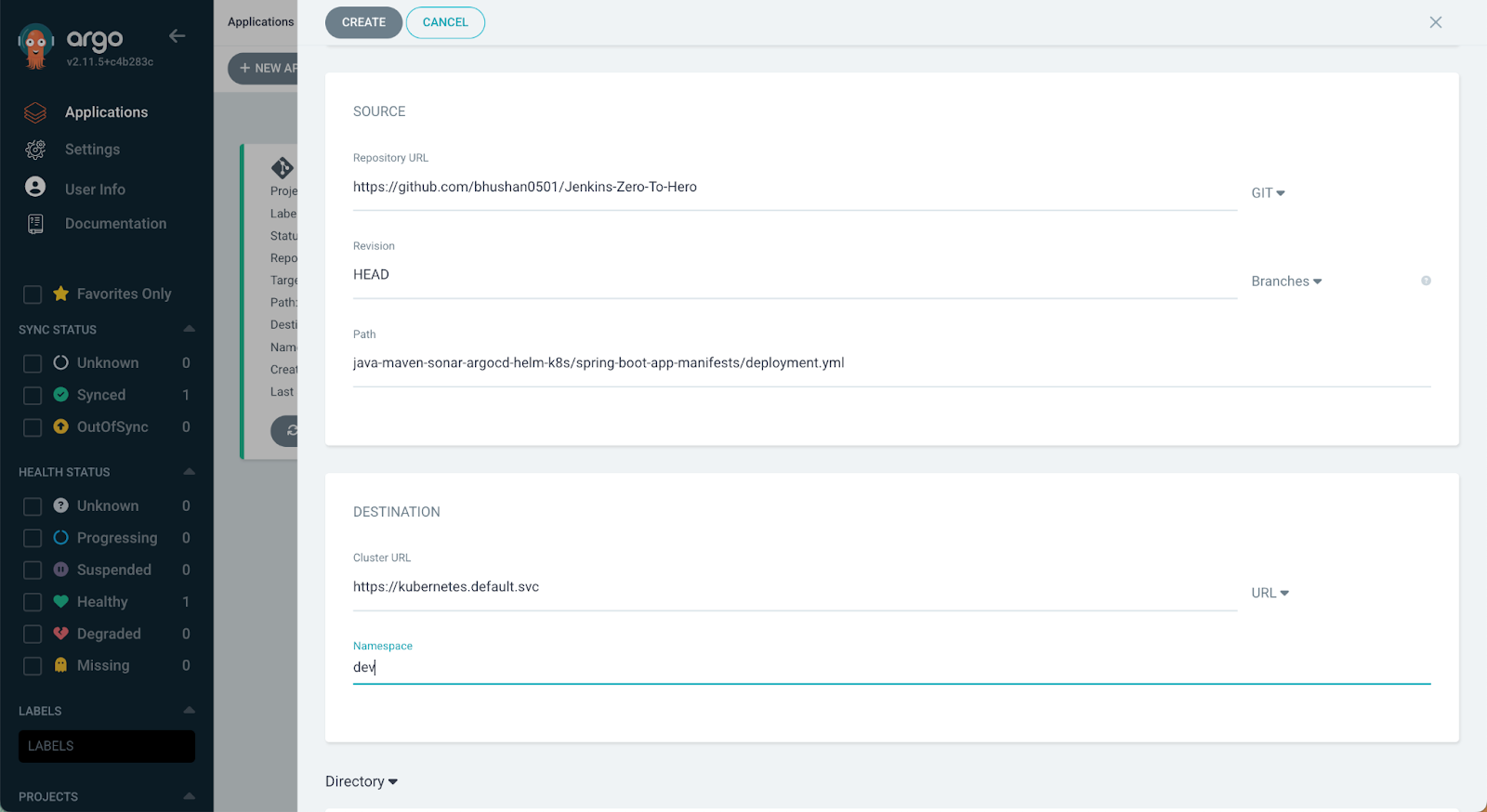
Once all required fields are filled, click CREATE. The application will be created and deployed to the target environment.
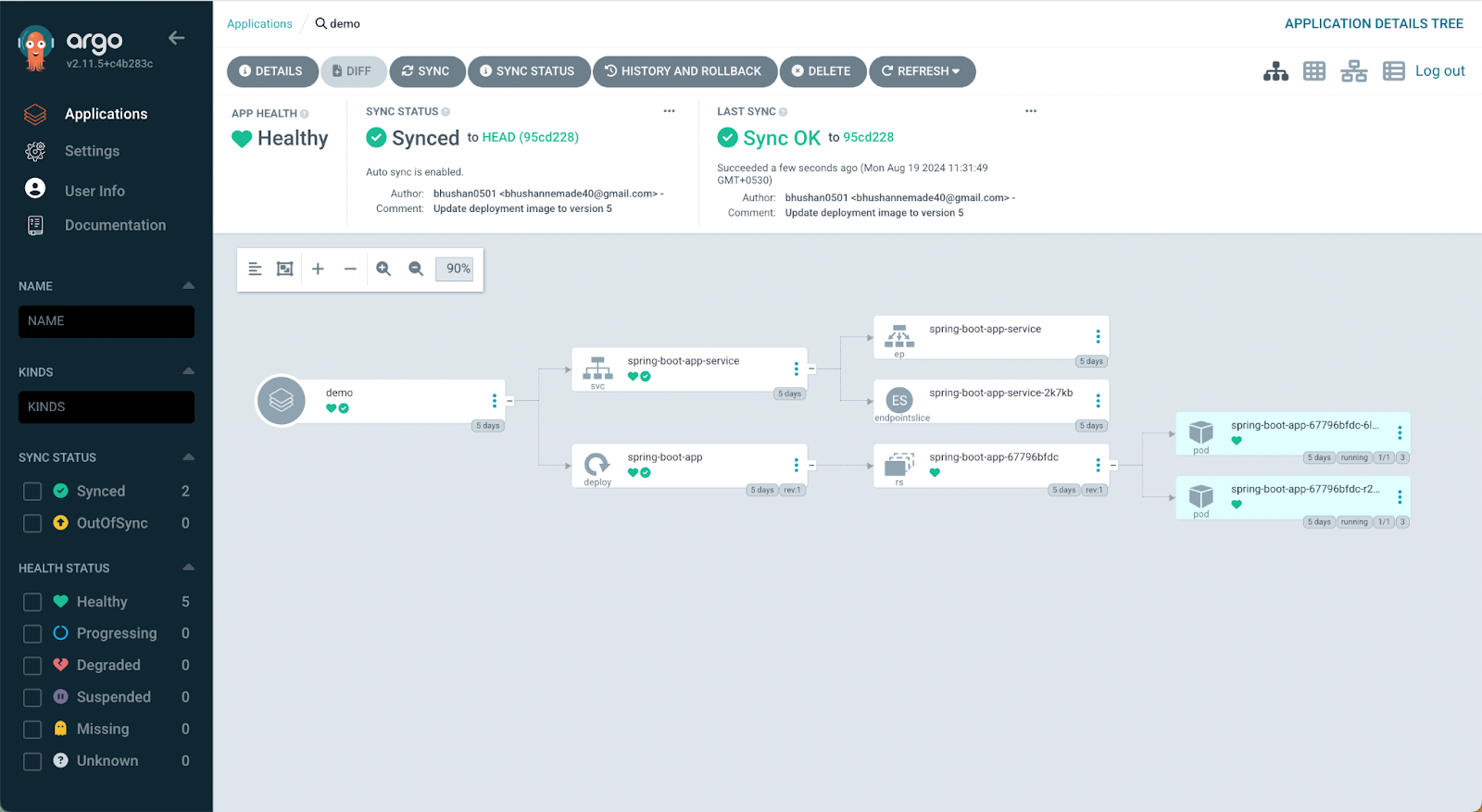
With this, your application has been deployed to the target Kubernetes cluster and environment. Now ArgoCD will be treating the Git repository as the single source of truth and, as soon as it detects any change to the deployment.yml file from the Git repository, the current state of the application will be automatically updated. In case someone changes the state of the application directly at the Kubernetes cluster, the ArgoCD will bring back the application to the state defined in the Git repository.
You can also automate the entire process by creating an ArgoCD application object and pushing it to the git repository using Jenkins. This will create a continuous deployment flow and streamline the GitOps-based deployments using ArgoCD and Jenkins.
Where Argo CD Falls Short
While Argo CD simplifies GitOps-based deployments, it faces scalability and management challenges in complex, multi-cluster environments.
Common Limitations
- Multi-Cluster Complexity: Managing multiple Argo CD instances or a single global instance can create scaling bottlenecks.
- Limited Access Controls: No native approval workflows for production deployments.
- Lack of Global Visibility: Application insights remain environment-specific.
- Manual Rollbacks: No built-in SLO-based rollback automation.
- Weak Configuration Comparison: Difficult to visually compare configurations across environments.
- No Integrated Security Scanning: Lacks native image or vulnerability insights.
- Resource Intensive: Large-scale environments may require significant compute for reconciliation loops.
While Argo CD handles GitOps well, it wasn’t designed to manage the full Kubernetes lifecycle from build to deployment, security, and post-deployment intelligence.
How Devtron Enhances Jenkins and Argo CD
To overcome these challenges, Devtron delivers a unified Kubernetes management platform that integrates seamlessly with both Jenkins and Argo CD, eliminating operational chaos and enabling enterprise-scale reliability.
Devtron extends the CI/CD pipeline into a single, AI-ready platform that handles build, deployment, and Day-2 operations all within one control plane.
Key Capabilities
- Unified Visibility: See application health, resource usage, and deployment history across all clusters in one dashboard.
- GitOps + Governance: Combine GitOps automation with enterprise-grade policy enforcement, role-based access, and audit logging.
- Advanced Rollouts & Auto-Rollbacks: Support for blue-green, canary, and SLO-based rollback strategies.
- Security Integration: Native image vulnerability scanning ensures safe and compliant deployments.
- Multi-Cluster Control: Manage 3 or 300 clusters with equal ease, without context switching.
- AI Operations: Devtron’s Agentic SRE automates cross-domain incident detection and resolution, enabling 24/7 self-healing Kubernetes operations.
Conclusion
CI/CD pipelines have redefined software delivery by automating builds, testing, and deployments with Jenkins driving integration and Argo CD enabling GitOps-based delivery. Yet, managing both separately at scale often leads to tool sprawl, visibility gaps, and operational complexity.
Devtron solves this by unifying CI, CD, security, and Day-2 operations in a single Kubernetes-native platform. It brings complete visibility, control, and AI-powered intelligence to your software delivery pipeline — helping teams innovate faster without the operational chaos.
To learn about CI/CD implementation within Devtron, we recommend the following articles:
Simplifying the Kubernetes CI/CD Pipeline
Kubernetes CI/CD Pipeline with Jenkins and Devtron
Kubernetes CI/CD Pipelines: GitHub Actions with Devtron
FAQ
What is the role of Jenkins in a CI/CD pipeline?
Jenkins automates the Continuous Integration (CI) process — building, testing, and validating code changes before deployment. It helps teams detect bugs early, streamline collaboration, and maintain consistent build quality across projects.
How does Argo CD enhance Kubernetes deployments?
Argo CD applies GitOps principles to Continuous Deployment (CD). It treats Git as the single source of truth, continuously syncing changes from Git to Kubernetes clusters. This ensures version-controlled, reliable, and fully traceable deployments.
What challenges arise when using Jenkins and Argo CD together?
While Jenkins and Argo CD complement each other, scaling them independently can lead to tool fragmentation, manual rollbacks, and lack of centralized visibility — especially in multi-cluster environments. Managing both can quickly become complex without unified governance.
How does Devtron improve the Jenkins and Argo CD workflow?
Devtron unifies Jenkins-based CI and Argo CD–based CD within a single Kubernetes-native platform. It adds centralized visibility, policy-based governance, security scanning, and advanced rollout strategies — enabling teams to manage 3 or 300 clusters effortlessly.
Does Devtron support AI-powered Kubernetes operations?
Yes. Devtron’s upcoming Agentic SRE introduces AI-powered operations that understand both applications and infrastructure. It automates incident detection and resolution, transforming Kubernetes from reactive management to proactive, autonomous operations.









