SVN or subversion is an open-source version control system which has a centralized server unlike git which is a distributed version control system. It tracks changes to files and directories, allows collaboration among users, supports branching and merging, and provides access control. While less popular than Git, SVN is still used in organizations with established infrastructure or specific needs. The main factor which differentiates svn from git is that it allows granular access control due to which it is widely used by enterprises.
What does granular access control mean?
SVN provides fine-grained access control at the repository level, allowing administrators to set permissions for individual users or groups. Access rules can be defined based on specific files and directories within the repository.
Git, by default, lacks built-in granular access control mechanisms. However, hosting platforms like GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket offer features to set permissions at the repository, branch, or file level, allowing for fine-grained access control.
In summary, SVN has built-in granular access control, while Git relies on external tools and hosting platforms to achieve fine-grained access control.
Deploy an SVN application using Devtron
While most modern CI/CD platforms do not provide native support for SVN, Devtron offers an alternative approach. Devtron, an open-source continuous delivery platform primarily focused on Git repositories, provides a Helm chart that allows you to synchronize SVN repository with Git. This Helm chart enables the syncing of code changes from SVN to Git, leveraging the benefits and features of Devtron's CI/CD workflows. By utilizing the SVN-to-Git synchronization capability in Devtron, organizations with existing SVN infrastructure can seamlessly integrate their SVN-based applications into the Devtron platform, benefiting from its advanced deployment and automation functionalities.
Pre-requisites
- SVN repository url should be accessible from Devtron
- A new git repository
- Credentials which can read/clone complete svn repository
- Credentials which can read/write to git repository
Deploy svn-git-sync helm chart
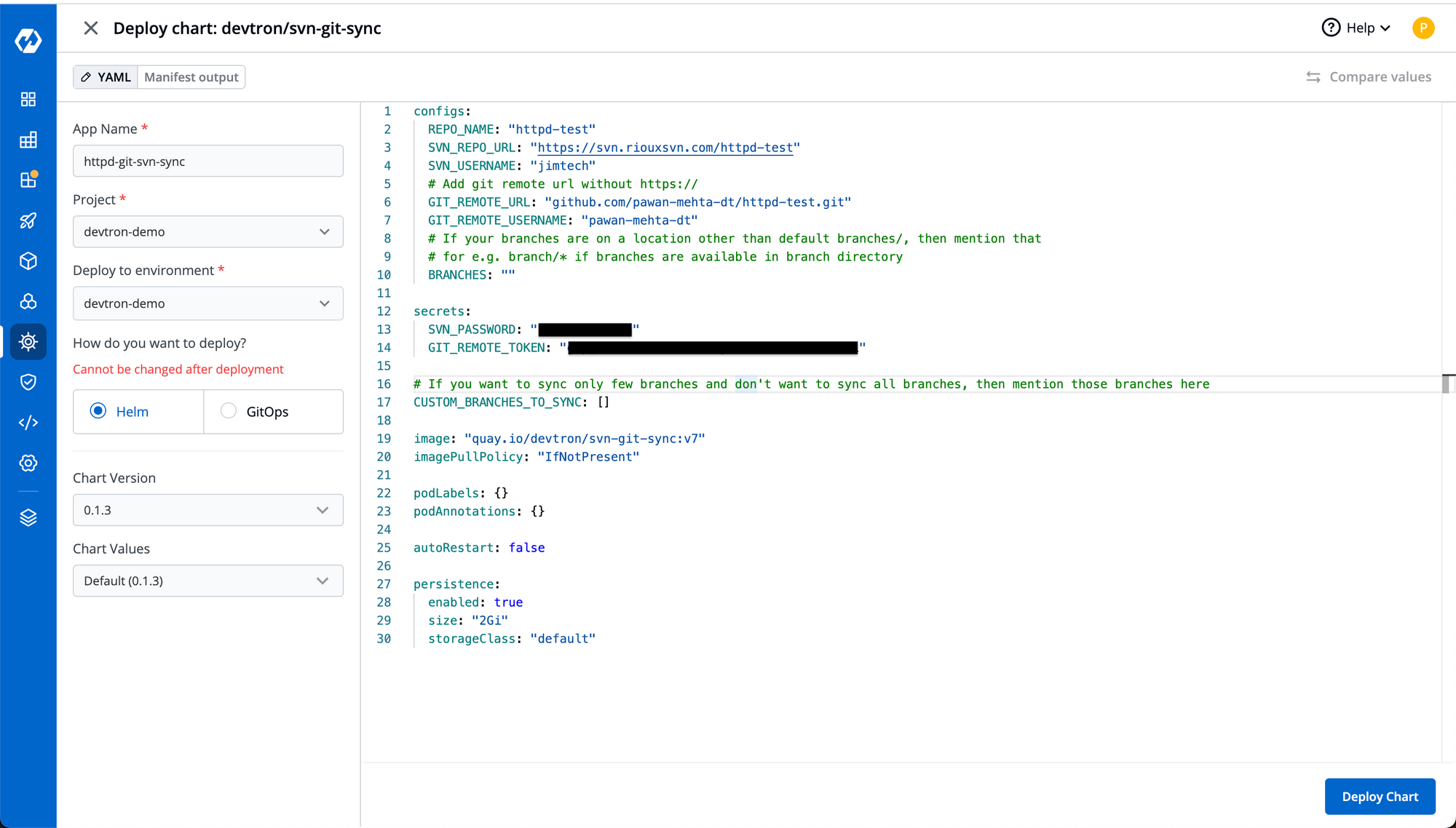
Step-1: Go to chart store on Devtron UI and search for svn-git-sync. Click on chart from devtron repo and then click configure and deploy. It will open the default values.yaml for you to edit.

Step-2: Update the values in the chart. Replace the repository urls as well as credentials with your own and click deploy chart.
Step-3: Once you click deploy chart, it'll create a pod which will clone your svn repository and push it's content including all branches to the new git repository that you have created. It'll also sync commit authors from svn commits to commits on git repository.
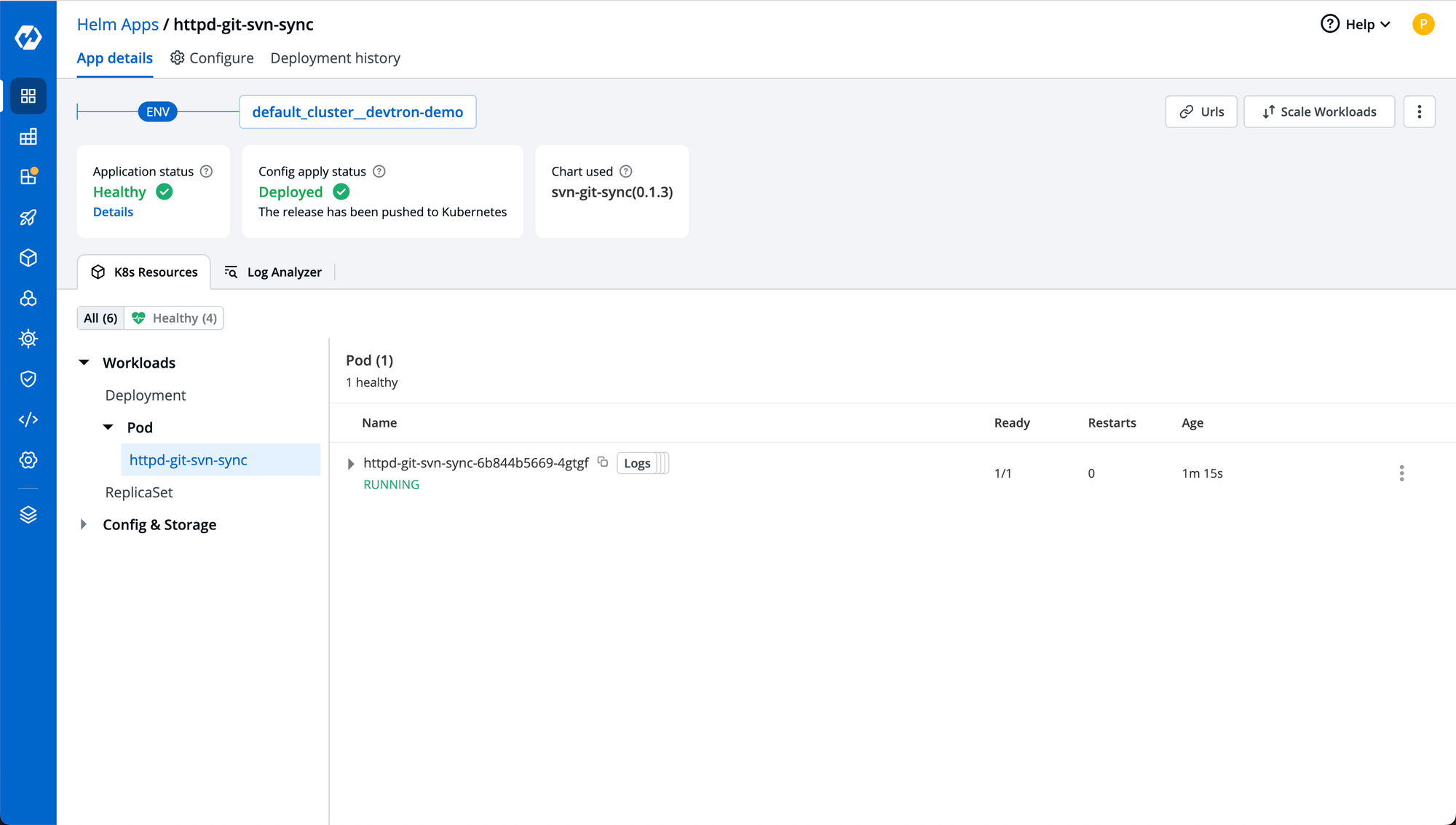
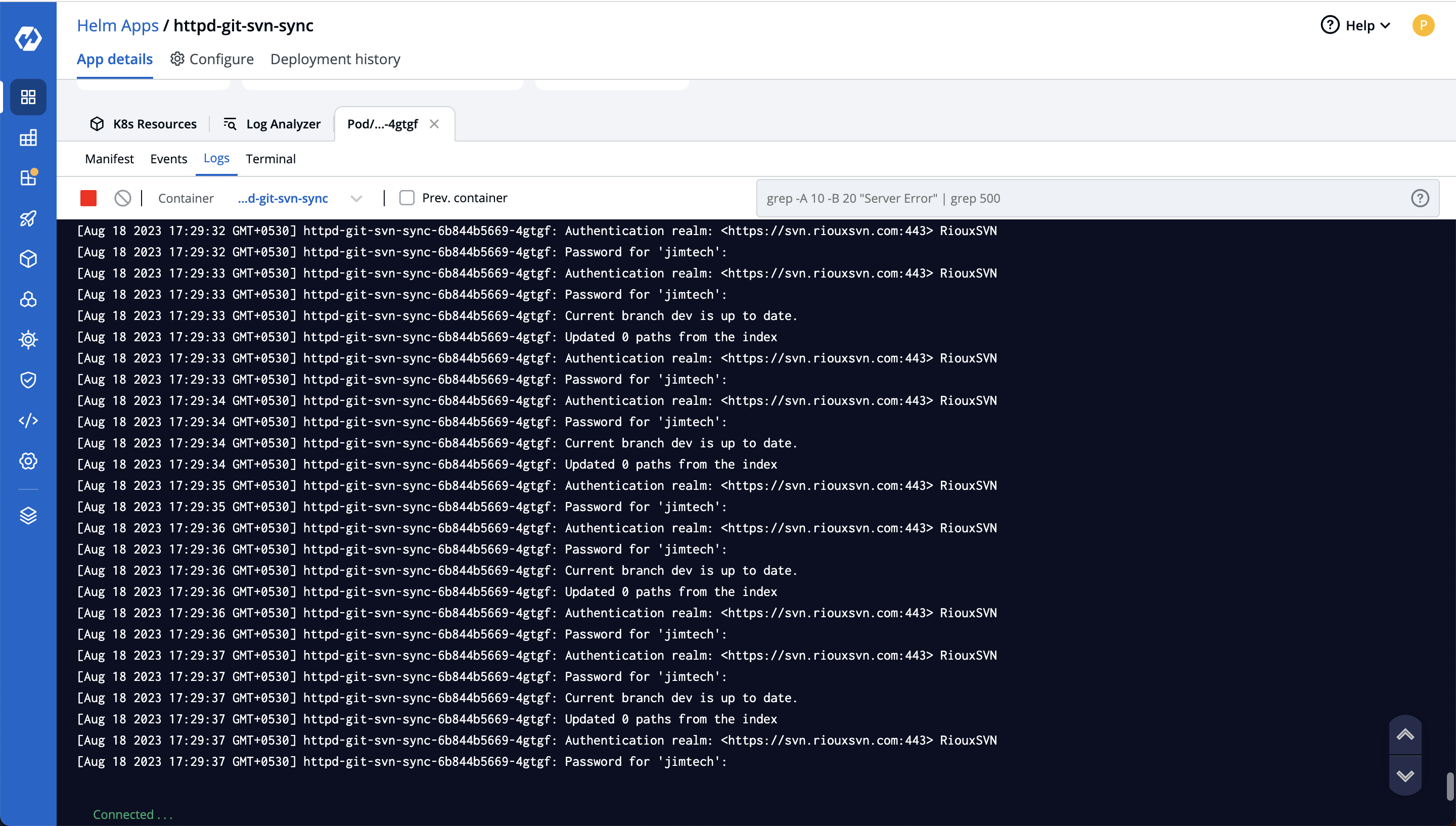
Step-4: You can click on logs to check the live status of sync, it'll also keep checking for all the latest commits on your svn repository and keep syncing it with the git repository so that you don't have to worry about switching your development team from svn to git.
Step-5: You can check your git repository, it should have your latest source code as well as all your branches of svn.
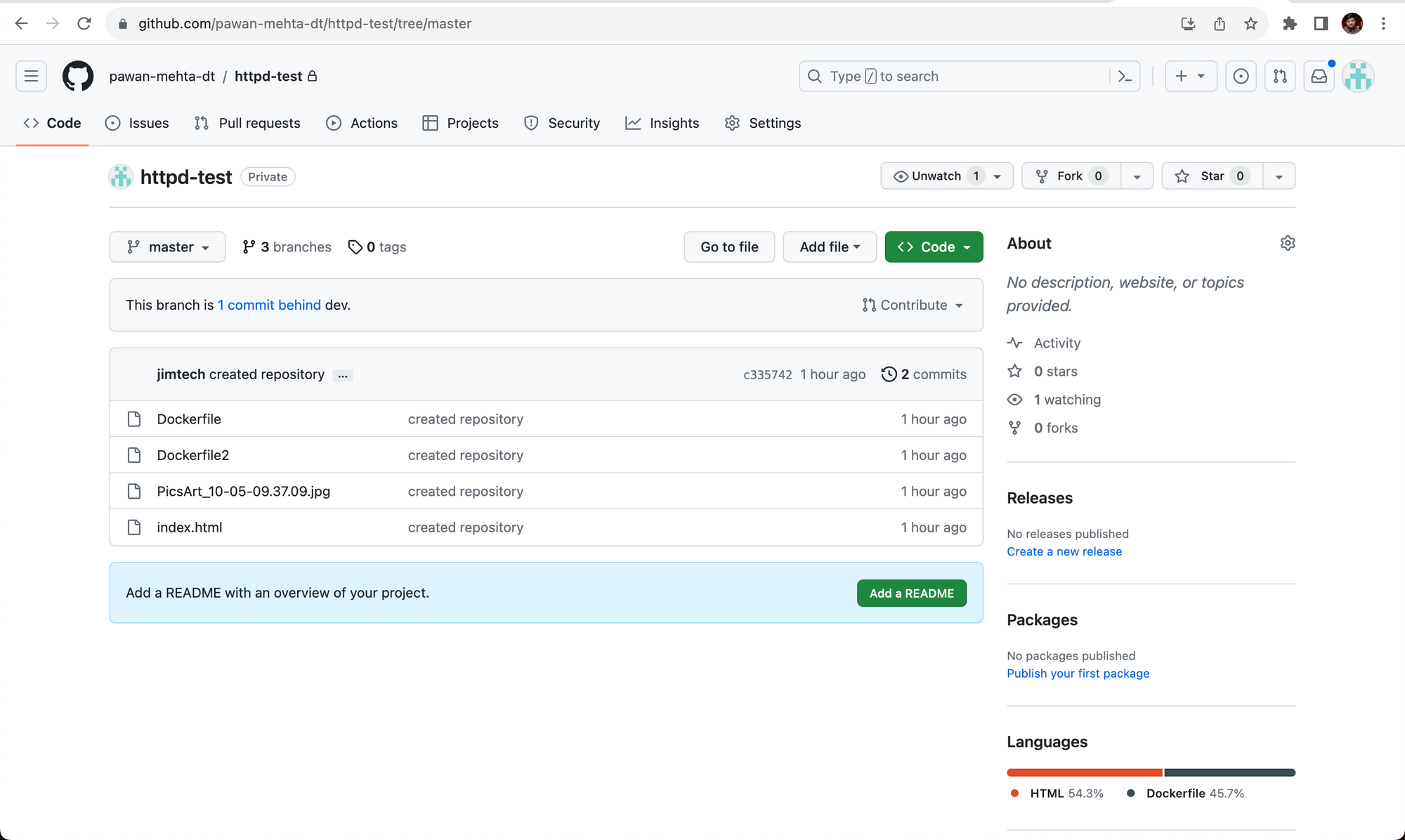
That's it! Now that you have your svn repository synced to git, you can now start deploying your application using the git repository from devtron.
Creating CI/CD Pipeline for the SVN Application
Step-1: To deploy your application using devtron, you can read documentation for creating a new application on devtron docs. Make sure you have added credentials for git account in global configurations which has the read access to the source code repository where the svn source code is synced.
Step-2: Once you create the application, configure the git repository in the application and select the git account which has access to the git repository:
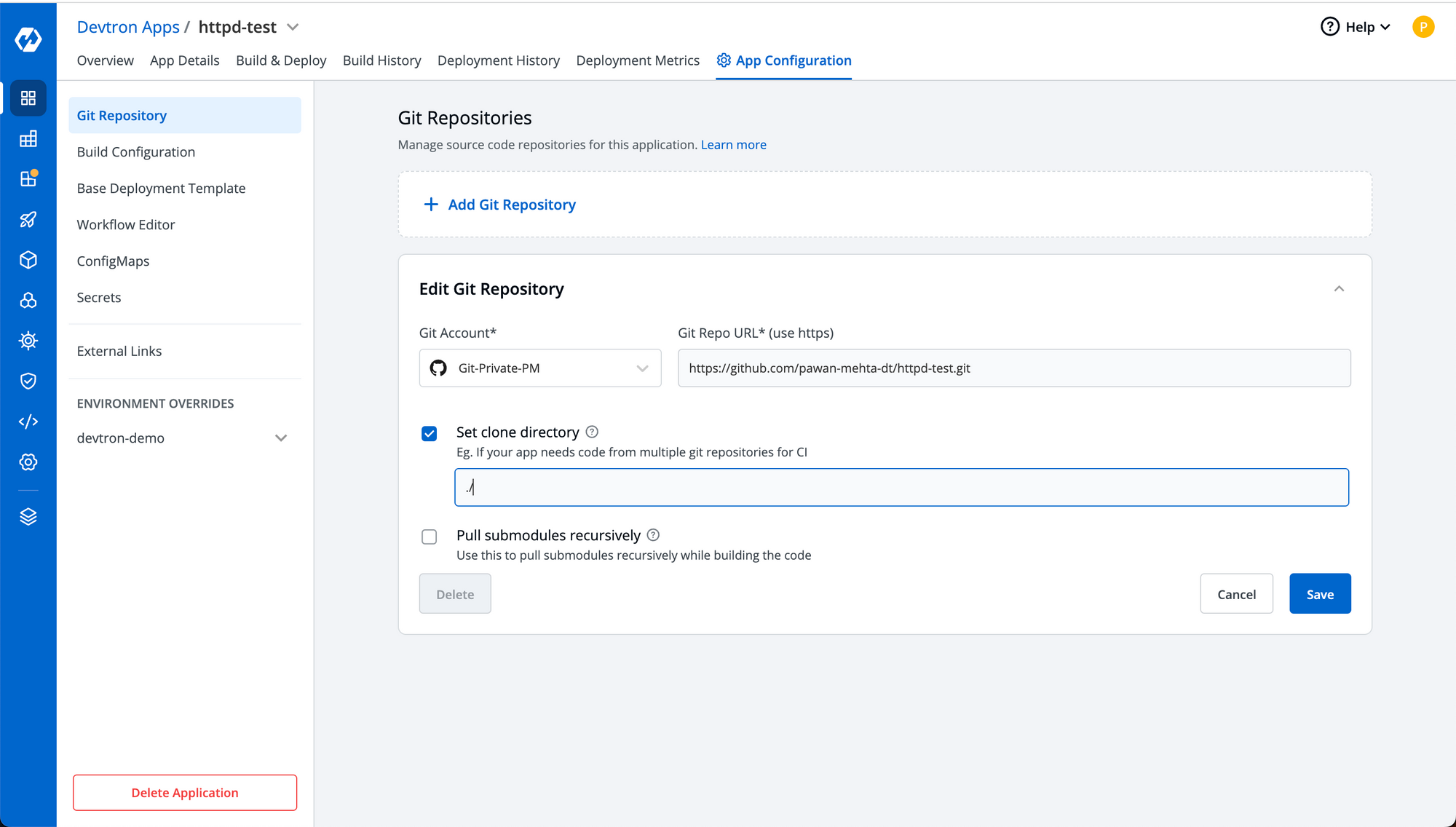
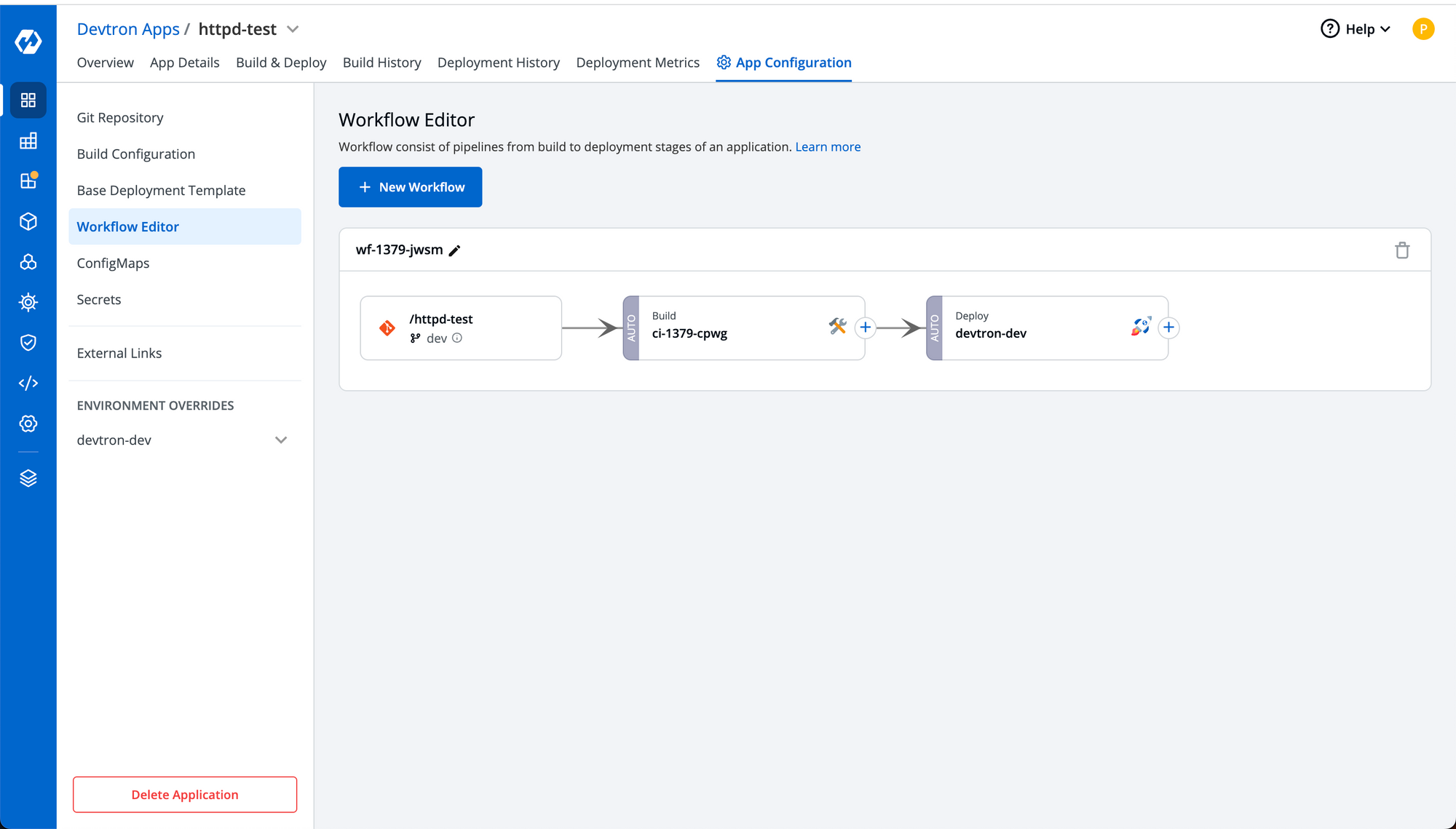
Step-3: Complete the steps of configuring the application including the CI/CD workflow. For demo purpose, our workflow is configured with dev branch and both CI as well as CD are set to automatic which means as soon as we get new commits in our git repository, it'll automatically start a new build and deployment will be initiated once the build gets completed.
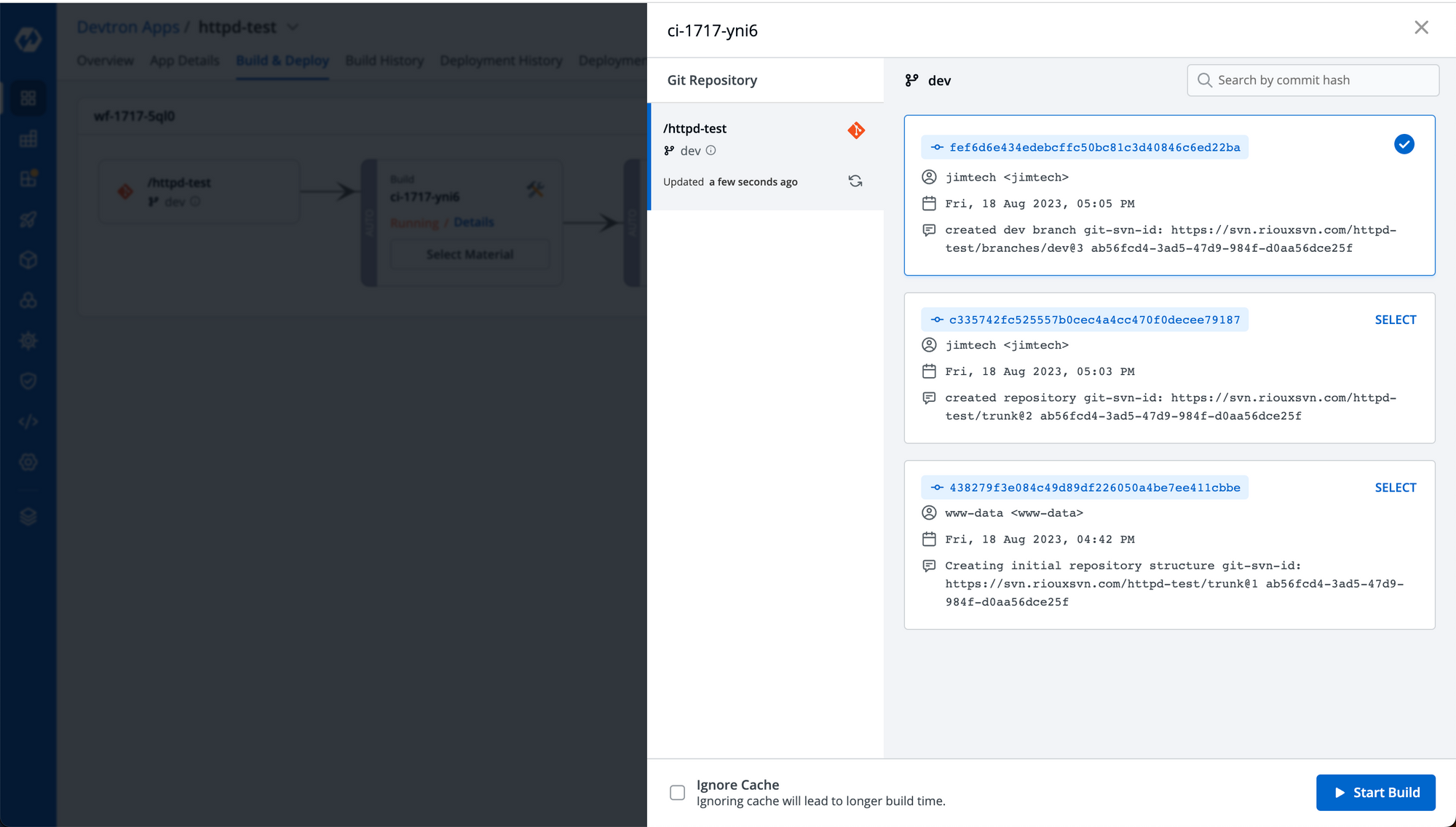
Step-4: Now go to Build and Deploy page, select the commit from which you want to trigger the first build and click Start Build.
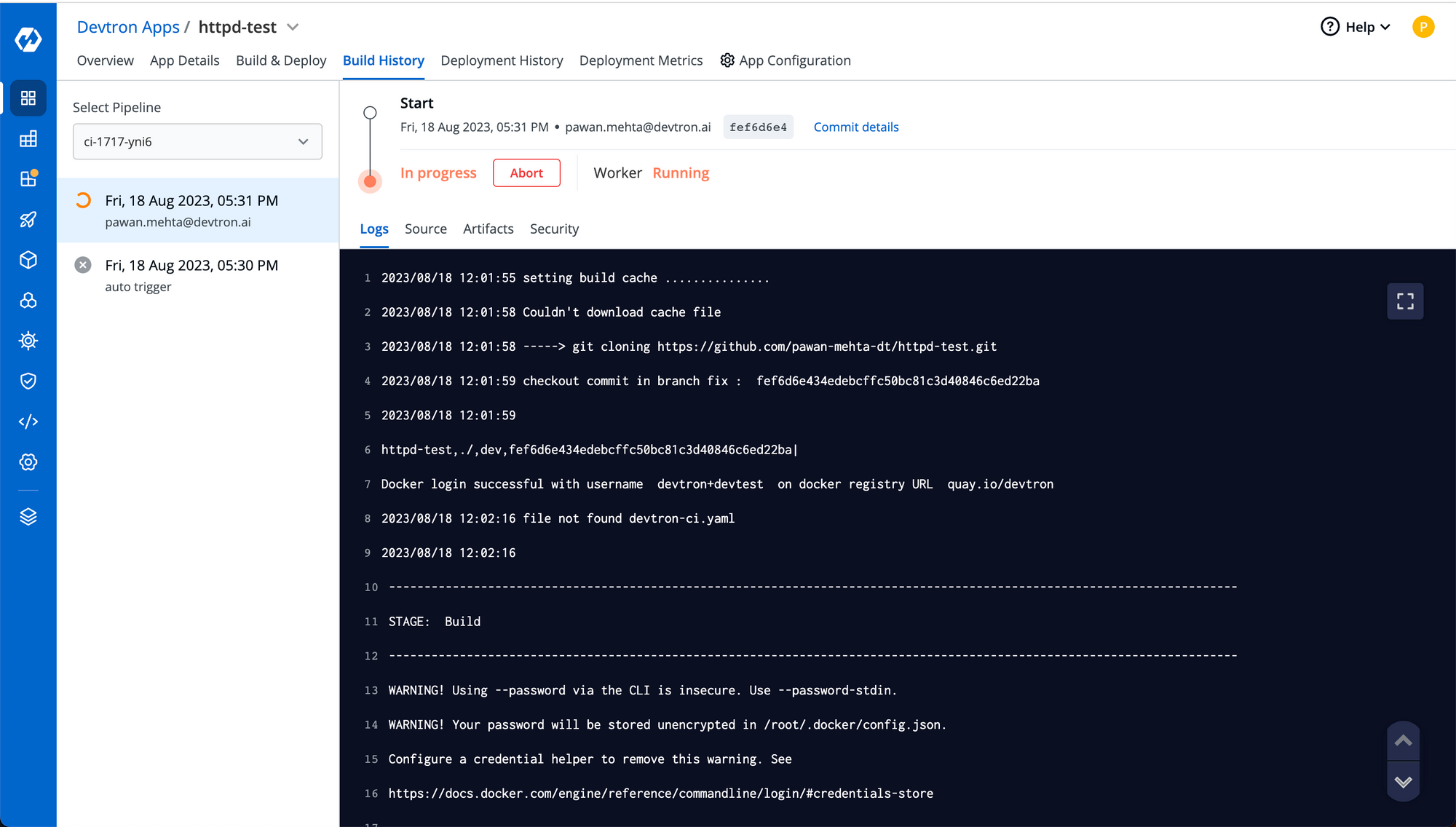
Step-5: Once the build starts, you can click on details to check live logs of your build.
Step-6: Deployment is triggered automatically once the build completes and your application will be deployed within few minutes.
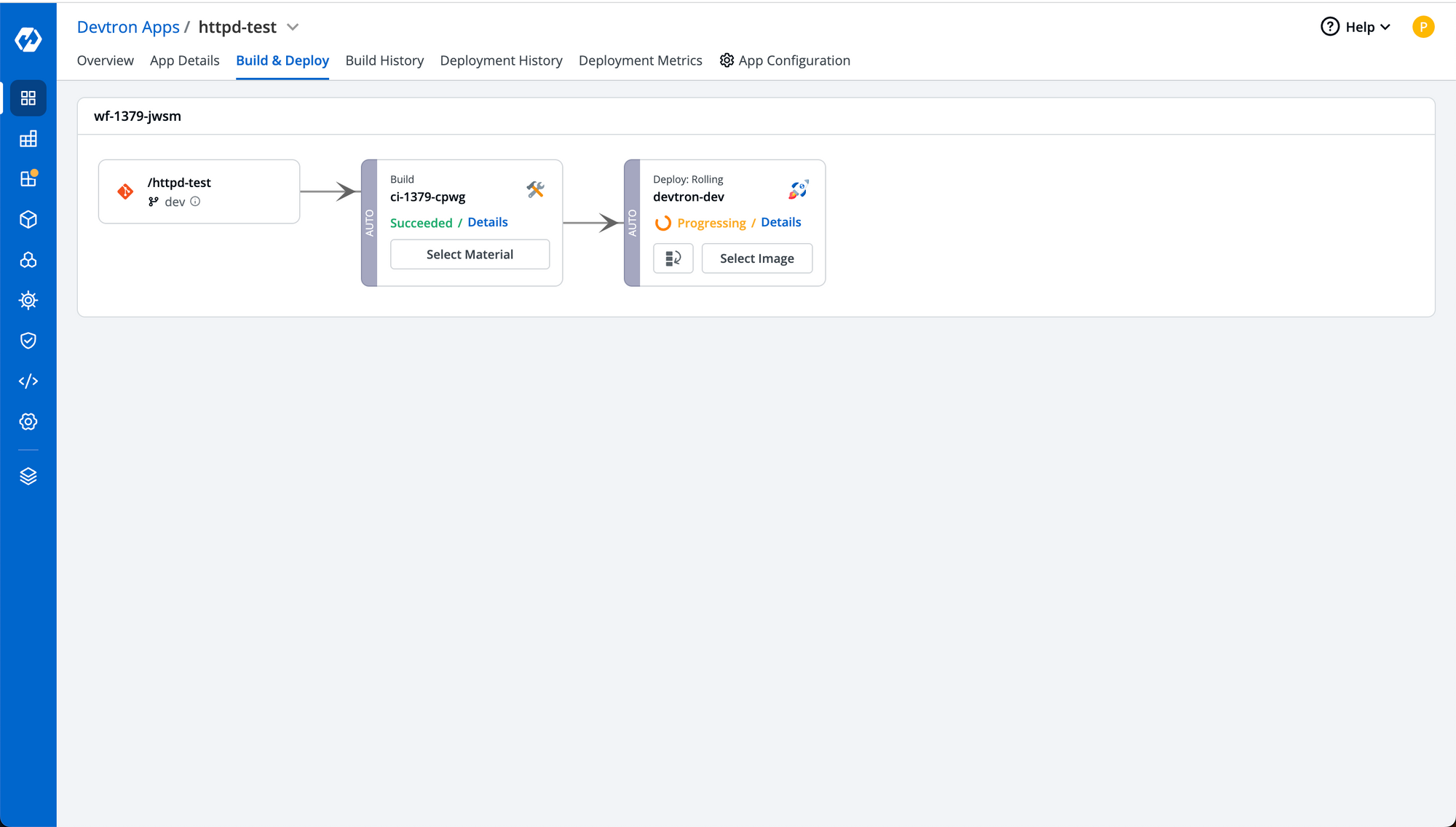
Step-7: You can click details on deployment step same as build step to check real time status of deployment of your application. It'll also show you the resources created by the deployment in app details page.
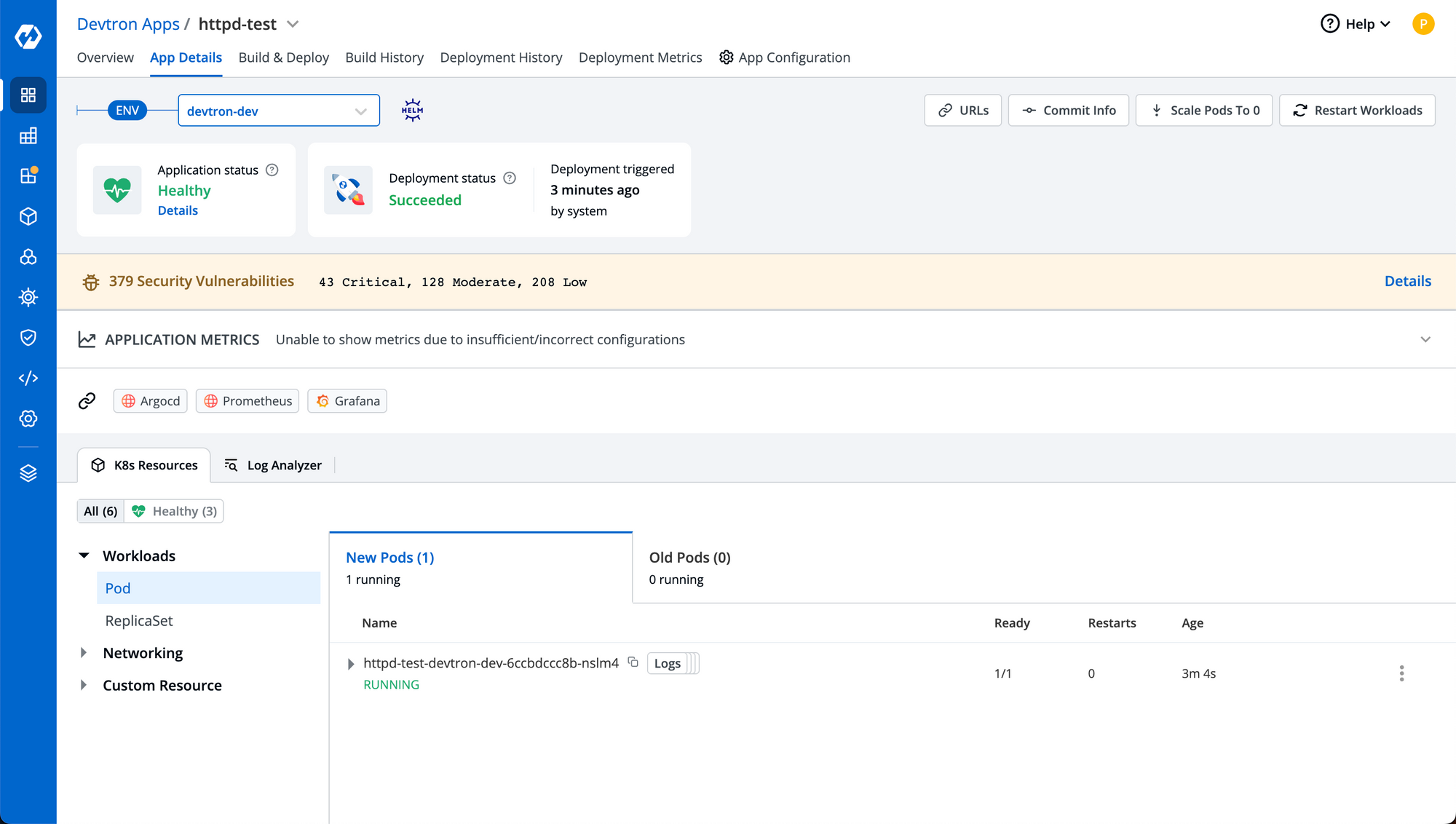
Congratulations! you have successfully deployed an application with source code in svn repository utilizing the modern CI/CD provided by Devtron.
Conclusion
In this article we learned about how you can sync the SVN repository with Git repository using helm chart and how easily one can create a CI/CD pipeline for Kubernetes and deploy the SVN application with a ease.
Feel free to join our community discord server if you have any questions and do give it a star if you liked Devtron.







