1. KEDA simplifies event-driven scaling by extending Kubernetes HPA to work with external metrics such as Kafka, Prometheus, AWS ALB, and more.
2. It supports 50+ built-in scalers, integrates seamlessly with HPA, and runs as a lightweight Kubernetes controller.
3. Devtron enhances KEDA adoption through low-code configuration, GitOps-based deployments, and built-in security/audit controls - eliminating the complexity of Helm charts and YAML.
4. Real-world examples (Kafka lag, Prometheus metrics, ALB traffic) show how Devtron + KEDA deliver dynamic scaling for diverse workloads.
5. Together, Devtron and KEDA enable teams to achieve efficient resource utilization, improved application performance, and lower operational overhead in Kubernetes environments.
As cloud-native applications grow in complexity and demand, efficient resource scaling has become critical. Kubernetes Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) handles some of the scaling use cases, but when workloads depend on external metrics like message queues, databases, or custom metrics, KEDA (Kubernetes Event-Driven Autoscaling) shines as a purpose-built solution
What is KEDA?
KEDA is a Kubernetes-based Event-Driven Autoscaler that lets you scale your pods based on the number of events needing processing, such as the length of a Kafka topic, RabbitMQ queue, Azure Service Bus, Prometheus metrics, HTTP queue length, etc.
Key Highlights of KEDA:
- Works with custom and external metrics
- Lightweight and runs as a Kubernetes custom controller
- Supports over 50 built-in scalers
- Compatible with HPA and other Kubernetes-native components
Interested in diving deeper? Read the full article here
Devtron and KEDA: The Importance of Integration
Installing Helm charts and managing their values can often be complex. Devtron simplifies this process significantly. Below are some key advantages of using Devtron:
- Low-code configuration
- Environment-level abstraction
- GitOps-based deployment management
- Security and audit controls
This helps DevOps engineers and developers focus on scalability logic rather than the YAML intricacies.
Configuring Autoscaling with KEDA in Devtron
- Add your Keda helm chart to Devtron
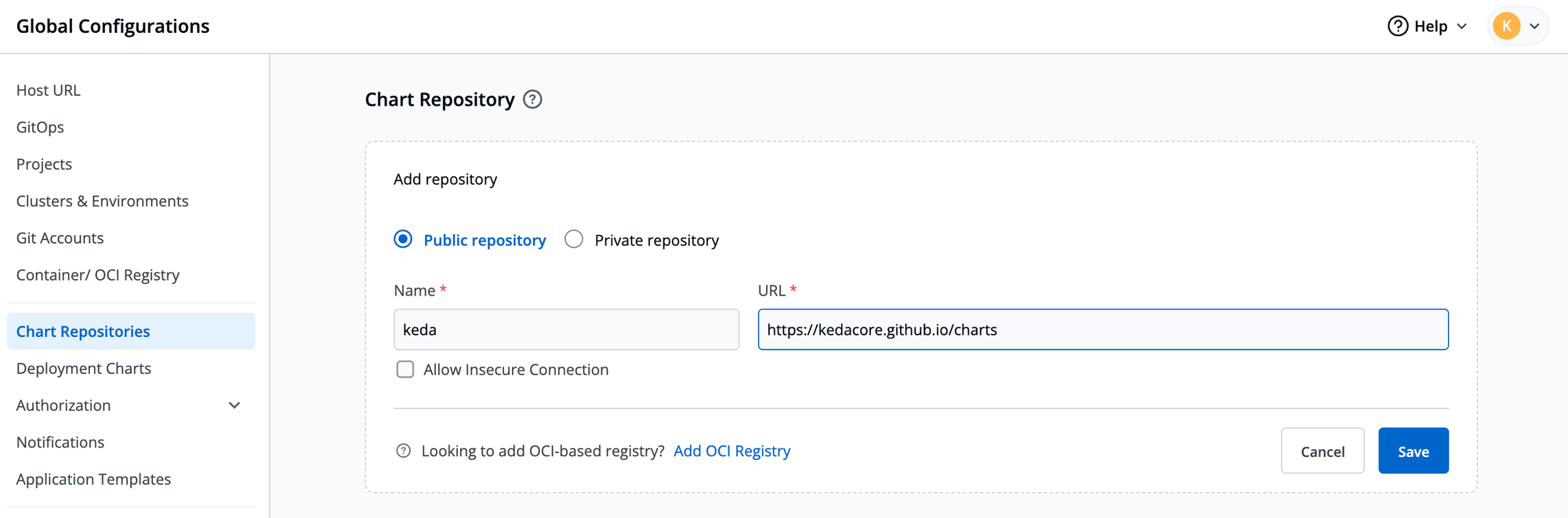
- Go to the chart store and search for Keda, and deploy the controller
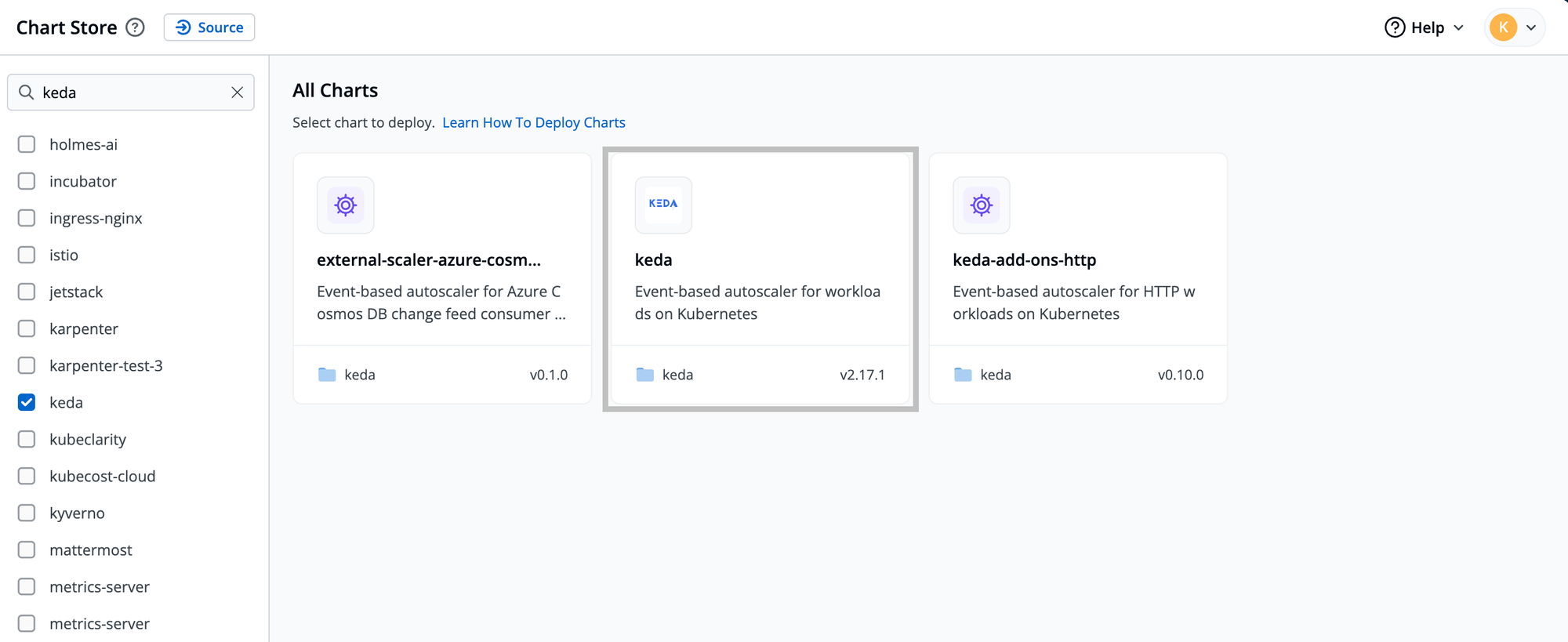
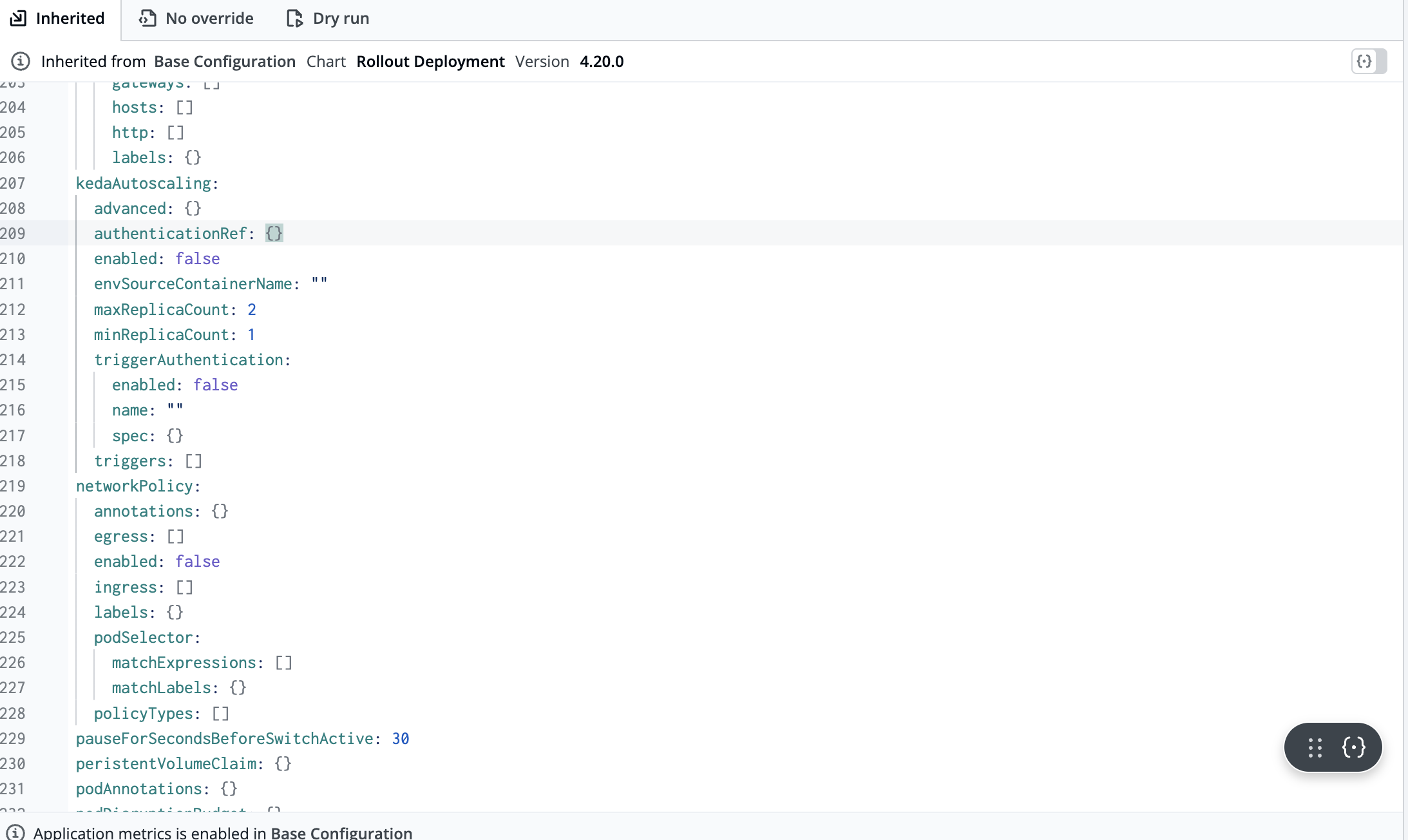
- Go to your application and enable Keda autoscaling as per your custom metrics
Look for the kedaAutoscaling section in the Deployment Template of the application.
Explore Real World Examples of Keda autoscaling using Devtron
Explore practical use cases of KEDA autoscaling with popular event sources such as Kafka, Prometheus, and AWS ALB. These examples showcase how KEDA dynamically scales workloads in response to real-time application demand, ensuring efficient resource utilization and optimal performance.
AutoScaling with Prometheus Metrics
The most fundamental metrics that can be scraped and utilized for KEDA autoscaling come from Prometheus.
What is Prometheus?
Prometheus is an open-source tool used for metrics-based monitoring and alerting. It offers a simple yet powerful data model and a query language (PromQL). With the right query, Prometheus provides detailed and actionable metrics, allowing teams to analyze application performance.
Read more on how to implement KEDA for autoscaling using Prometheus.
AutoScaling with Kafka Metrics
AutoScaling with Kafka metrics enables dynamic scaling based on real-time message load in Kafka topics.
What is Kafka?
Kafka is a distributed message streaming platform that uses a publish and subscribe mechanism to stream records or messages. For horizontal pod autoscaling, we will use KEDA's readily available Kafka scaler to achieve auto-scaling needs, such as starting a job as soon as possible when the request is received, cost-effectively, and eliminating or shutting down all unnecessary jobs.
Read here on how you can use Kafka Lag for autoscaling.
AutoScaling with ALB Metrics
AutoScaling with ALB metrics allows workloads to scale dynamically based on incoming traffic and target request load from the AWS Application Load Balancer.
What is ALB??
An Application Load Balancer (ALB) distributes incoming traffic among multiple applications, typically routing HTTP and HTTPS requests to specific targets such as Amazon EC2 instances, containers, or IP addresses.ALB publishes data points to AWS CloudWatch, tracking them as time-ordered metrics. Using these ALB metrics, we can configure KEDA Autoscaling to automatically scale application workloads based on traffic patterns and load distribution.
Read more on how to implement KEDA for autoscaling using ALB Metrics.
Conclusion
Devtron's integration with KEDA enables seamless and efficient autoscaling within Kubernetes by allowing applications to scale based on real-time event-driven metrics. This ensures optimal resource utilization, improved application performance, and reduced operational overhead, making autoscaling intelligent and effortless for Dev and DevOps teams.
FAQ
What is KEDA in Kubernetes?
KEDA (Kubernetes Event-Driven Autoscaler) is a lightweight component that lets you scale pods based on events or external metrics such as Kafka lag, Prometheus queries, or AWS ALB traffic.
How does Devtron simplify KEDA installation and management?
Devtron provides a low-code interface, environment-level abstraction, and GitOps-based deployment flows that make installing the KEDA Helm chart and configuring scalers much easier than managing raw YAML.
Can I use KEDA and Horizontal Pod Autoscaler together?
Yes. KEDA integrates with HPA, allowing you to extend native Kubernetes autoscaling with event-driven metrics while still leveraging HPA for CPU or memory-based scaling.
Which external metrics does KEDA support?
KEDA offers 50+ built-in scalers, including Kafka, RabbitMQ, Azure Service Bus, Prometheus, AWS ALB, PostgreSQL, and many more.


