1. HashiCorp Vault securely manages sensitive data in Kubernetes clusters.
2. Dynamic secrets & encryption reduce exposure risks and strengthen security.
3. Devtron simplifies Helm chart deployments of Vault and integrates seamlessly with External Secrets Operator.
4. Automated secret injection into Kubernetes pods ensures security without manual intervention.
What is HashiCorp Vault ?
HashiCorp Vault is a secure, centralized secret management tool designed to protect sensitive data such as credentials, API keys, and tokens. Vault provides:
- Secret Engines: Store and generate dynamic secrets for databases, cloud platforms, and services.
- Authentication Methods: Support multiple mechanisms to ensure only authorized access.
- Policies & Access Control: Fine-grained permission control for sensitive data.
- Encryption & Data Protection: Secrets remain secure even if storage is compromised.
- Dynamic Secrets: Generate short-lived credentials to minimize attack surface.
Key Concepts and Components
To truly understand how HashiCorp Vault works , let's explore its core concepts and components:
- Secret Engines: Vault employs different secret engines for various types of secrets, like databases, cloud platforms, and more. Each secret engine is tailored to handle specific secret types, ensuring a high level of security.
- Authentication Methods: Just as you'd need a unique key to access different doors, Vault offers multiple authentication methods to ensure that only authorized users can access specific secrets.
- Policies and Access Control: Vault's policy system acts as a rulebook, determining who can access what secrets. This fine-grained control ensures that secrets are only accessible by those who need them.
- Encryption and Data Protection: All secrets stored within Vault are encrypted, ensuring that even if the underlying storage is compromised, the secrets remain secure.
- Dynamic Secrets: Vault can generate dynamic, short-lived credentials for external systems. This enhances security by reducing the window of vulnerability in case of a breach.
Installing Hashicorp Vault Helm chart using Devtron
You can use Devtron's chart store for installing the HashiCorp Vault Helm chart. If the vault chart isn't available there, it's possible to incorporate the chart repository using global configurations.
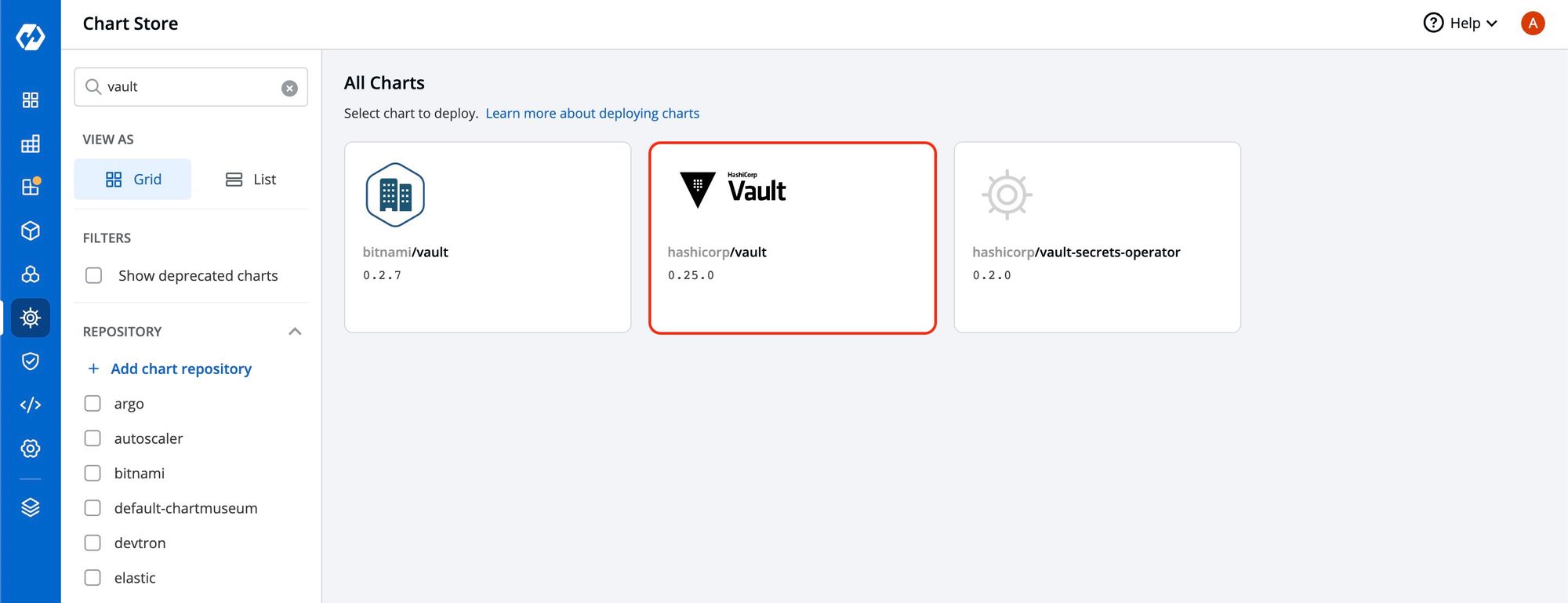
Visit Global Configuration -> Chart Repositories -> + Add Repository to add Hashicorp official helm chart.
Here is the HashiCorp Vault repository URL: https://helm.releases.hashicorp.com
Take a look around how to add custom charts and deploy helm charts using Devtron for detailed understanding and deploying helm charts with Devtron.
To access the Vault’s dashboard, you need to configure ingress as shown below:
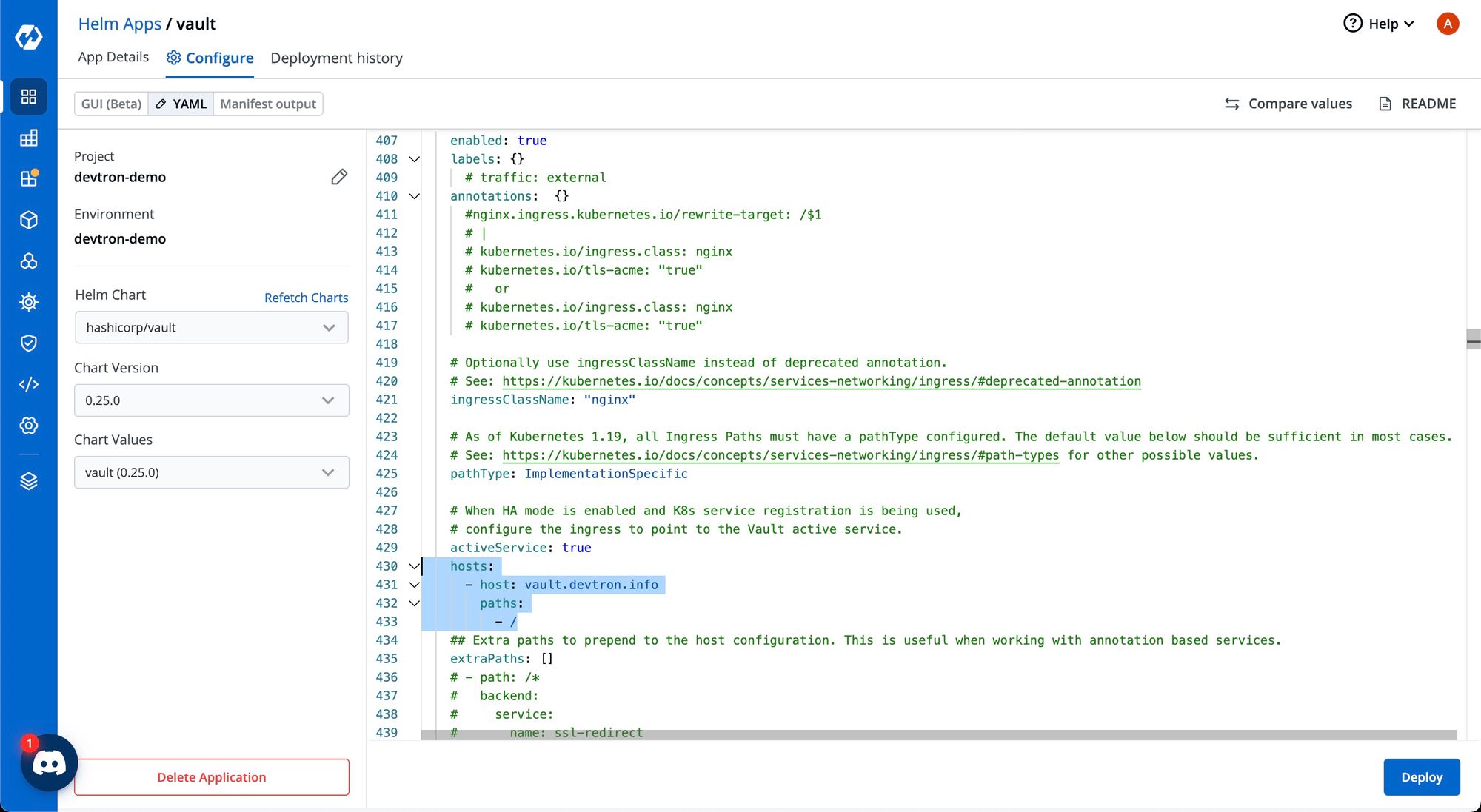
Once the Helm chart is deployed, it might take a few minutes for the application to become healthy.
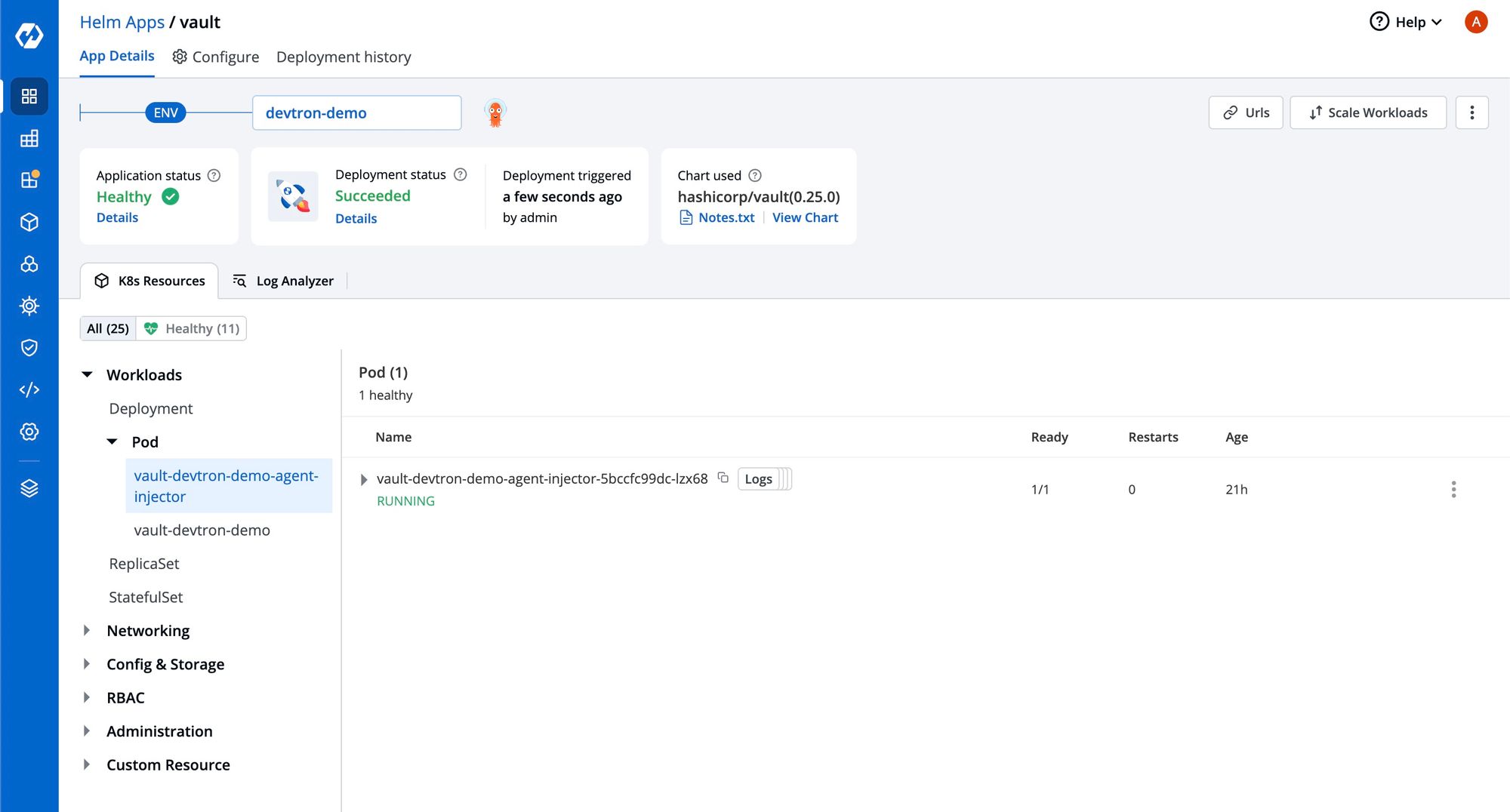
Once the Vault Helm application is in a healthy state, you can access the Vault dashboard using the hostname specified in the ingress configuration.
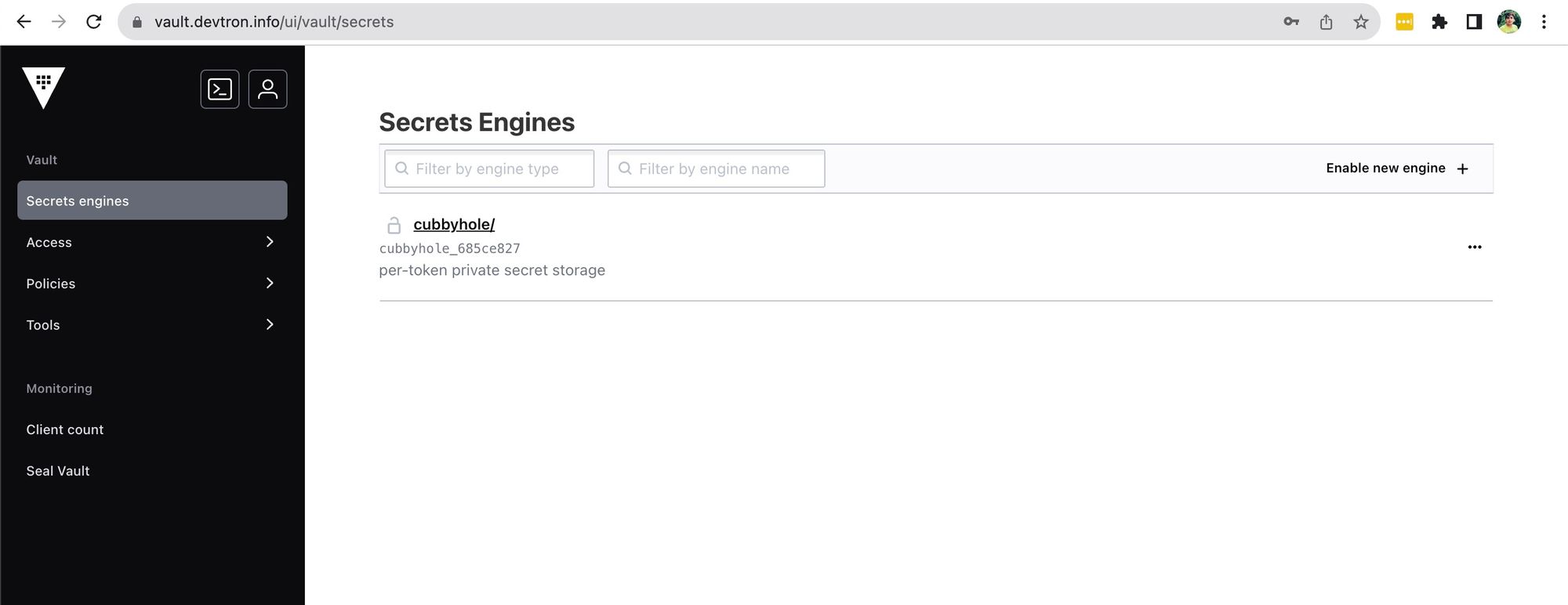
To include new secrets in the vault, click on the Enable new engine option within the secrets engines section. In this area, you will find various secrets engines categorized as Generic, Cloud, and Infra.
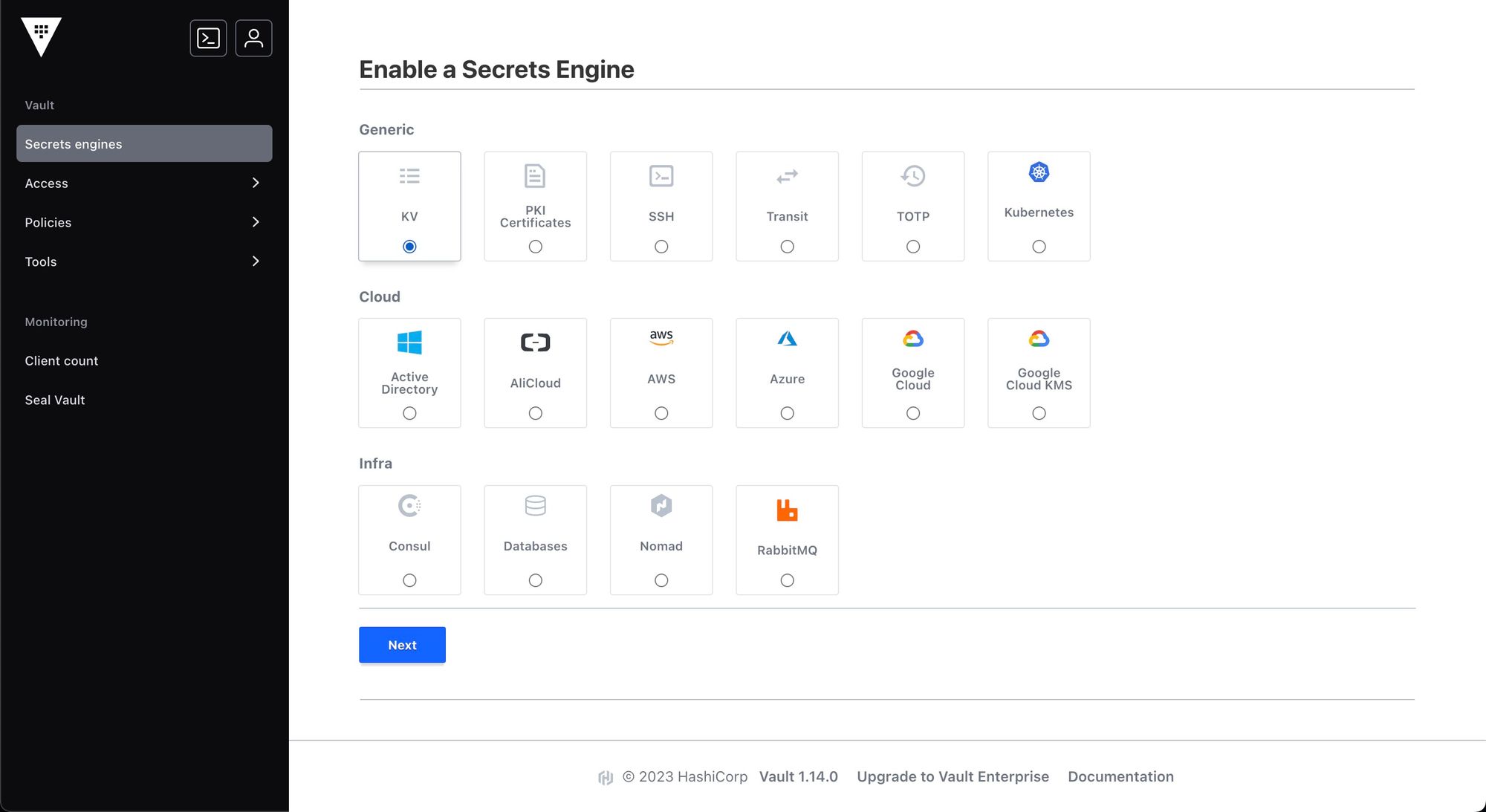
You can use the KV secrets engine to save secrets in a key-value manner within the storage set up in Vault.
Give a path and maximum number of versions and enable the engine.
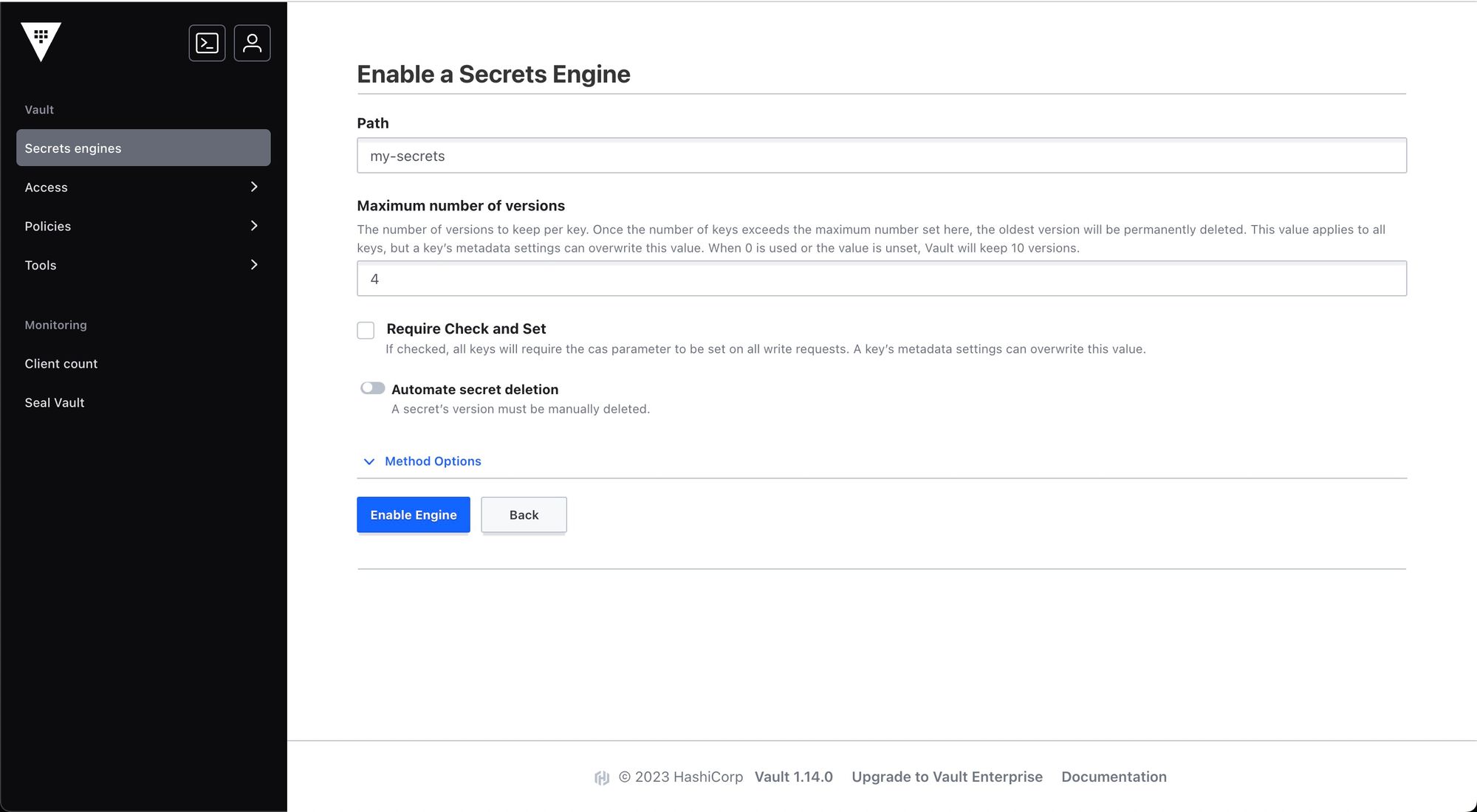
To add new secrets in a key-value pair, click on create secret.
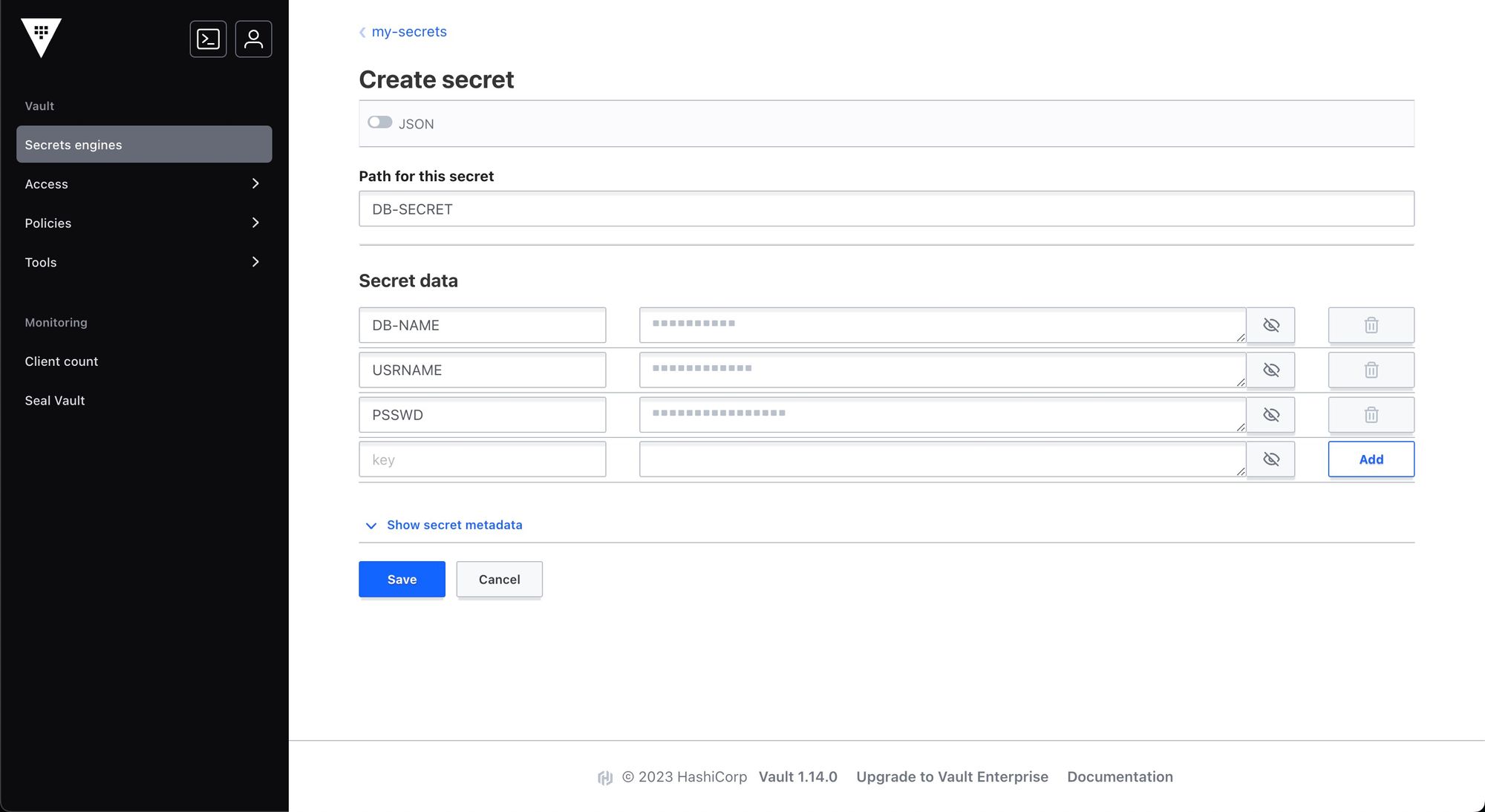
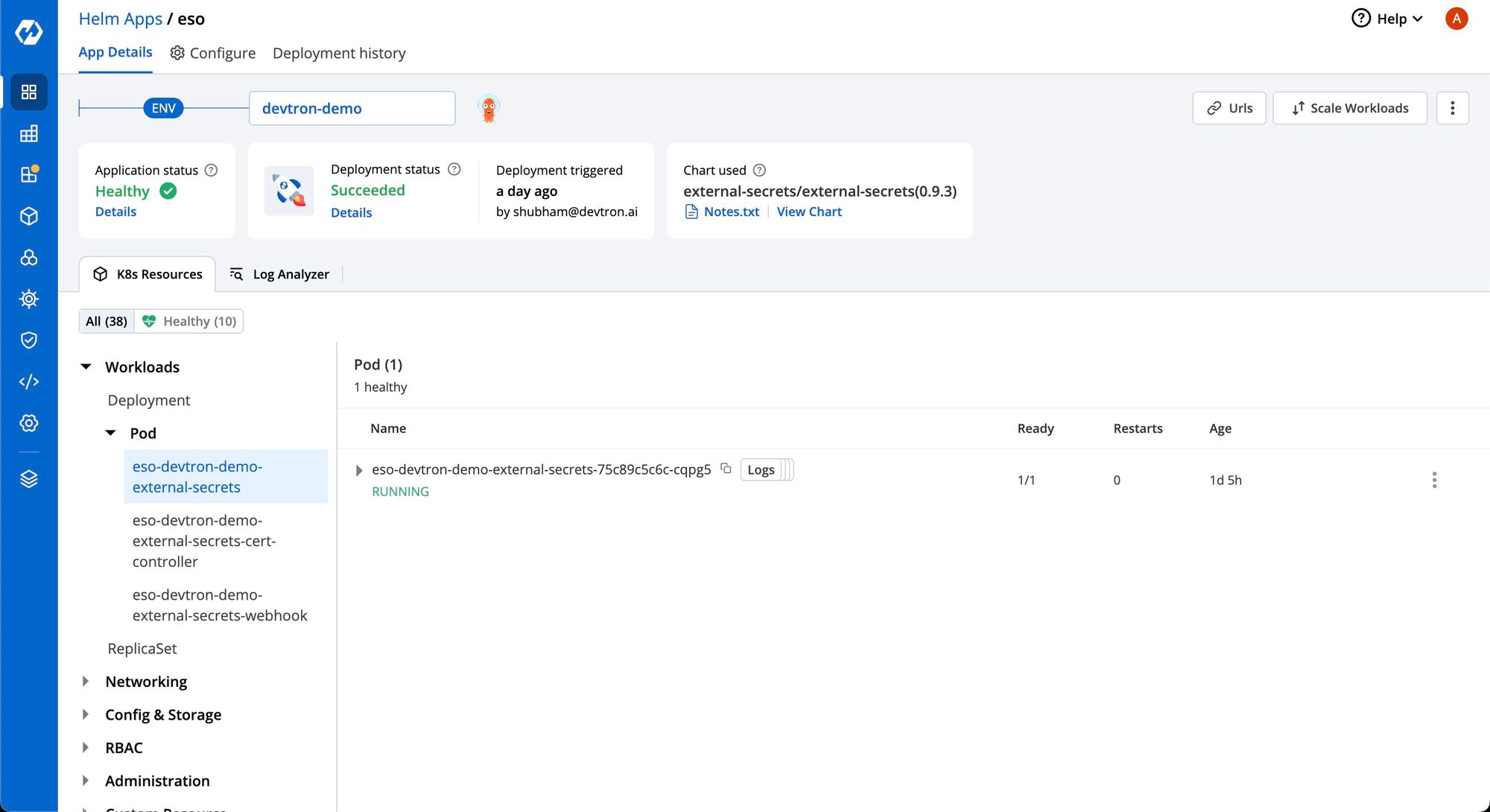
Now the secrets have been added to the vault. Let’s move to how we can use these secrets in Devtron applications using External Secrets Operator.
External Secrets Operator is a Kubernetes operator that integrates external secret management systems like AWS Secrets Manager, HashiCorp Vault, Google Secrets Manager, Azure Key Vault and many more. The operator reads information from external APIs and automatically injects the values into a Kubernetes Secret.
Install External Secret Operator
Before creating any external secrets on Devtron, External Secret Operator must be installed on the target cluster. External Secret Operator allows you to use external secret management systems (e.g., AWS Secrets Manager, Hashicorp Vault, Azure Secrets Manager, Google Secrets Manager etc.) to securely inject secrets in Kubernetes.
You can install External Secrets Operator using charts store:
- Go to the charts store.
- Search chart with name external-secrets and deploy with the default values.
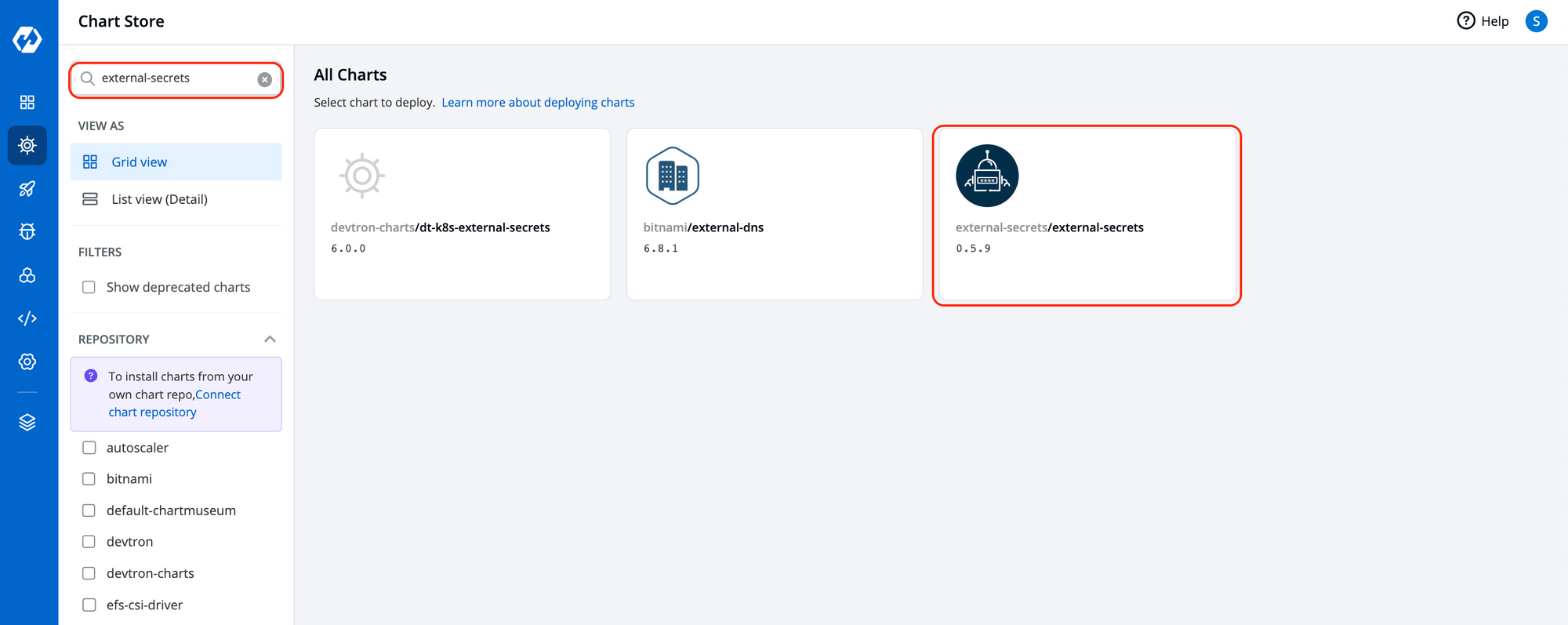
To incorporate secrets from HashiCorp Vault, you need to create a generic Kubernetes secret that will be used for vault authentication. This involves creating a Kubernetes secret in the specific namespace where your application will be deployed. The secret should store the base64-encoded password or token obtained from the vault. To simplify the process, you can utilize the devtron/devtron-generic-chart . An example yaml is given below:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
type: Opaque
data:
token: <vault-password>
metadata:
name: vault-token
namespace: <namespace>
Note: There is no requirement to generate the Kubernetes secret each time you're creating an External Secret for that specific namespace.
After successfully generating the generic secret, proceed with the following instructions in the Secrets section of your application:
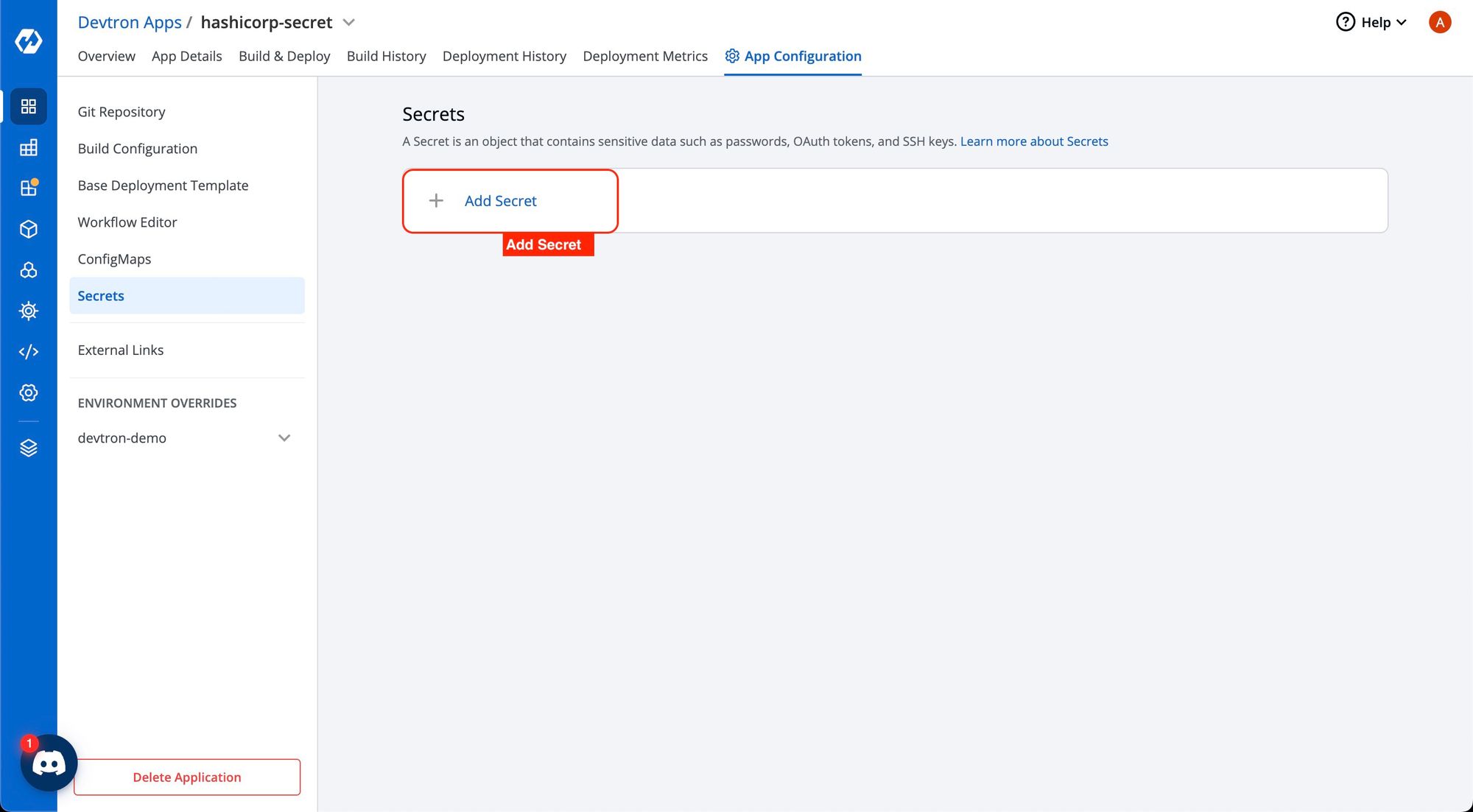
1. Create a new secret
To add a new secret to your application, go to the App Configuration section. Then, on the left side, choose Secrets and click Add Secret.
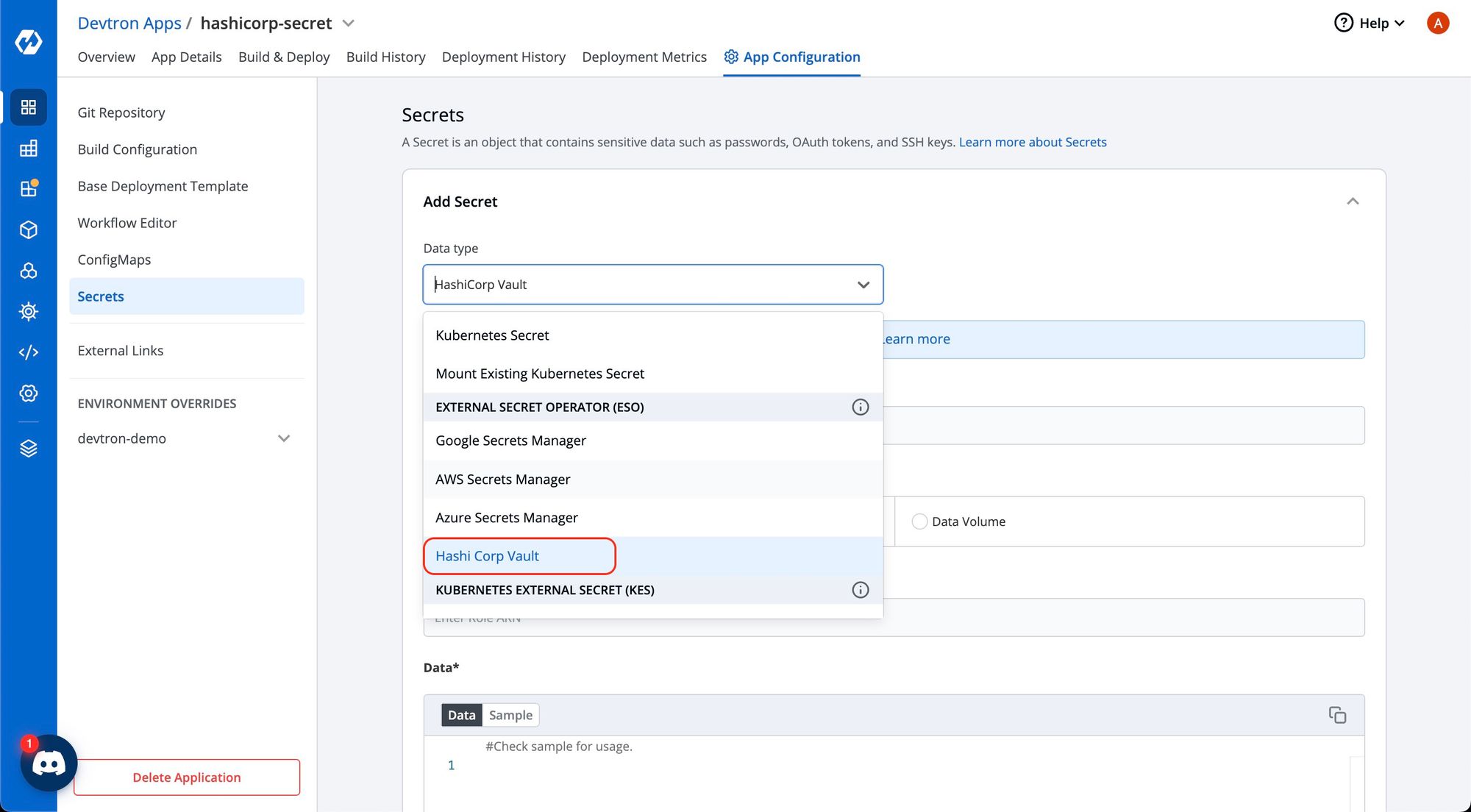
2. Select HashiCorp Vault as the External Secret Operator
After clicking the Add Secret button, select HashiCorp Vault from the dropdown menu for the Data type option. Provide a name for the secret you are creating, and then proceed to configure the external secret as described in the next step.
3. Configure the secret
To configure the external secret that will be fetched from HashiCorp Vault for your application, you will need to provide specific details using the following key-value pairs:
| Key | Description |
|---|---|
vault.server |
Server is the connection address for the Vaultserver, e.g: "https://vault.example.com:8200" |
vault.path |
Specify the path where the secret is stored in Vault |
tokenSecretRef.name |
Enter the name of the secret that will be used for authentication |
tokenSecretRef.key |
Specify the key name within the secret that contains the token |
secretKey |
Provide a name for the secret in Kubernetes |
key |
Enter the name of the secret in Vault |
property |
Specify the key within the Vault secret |
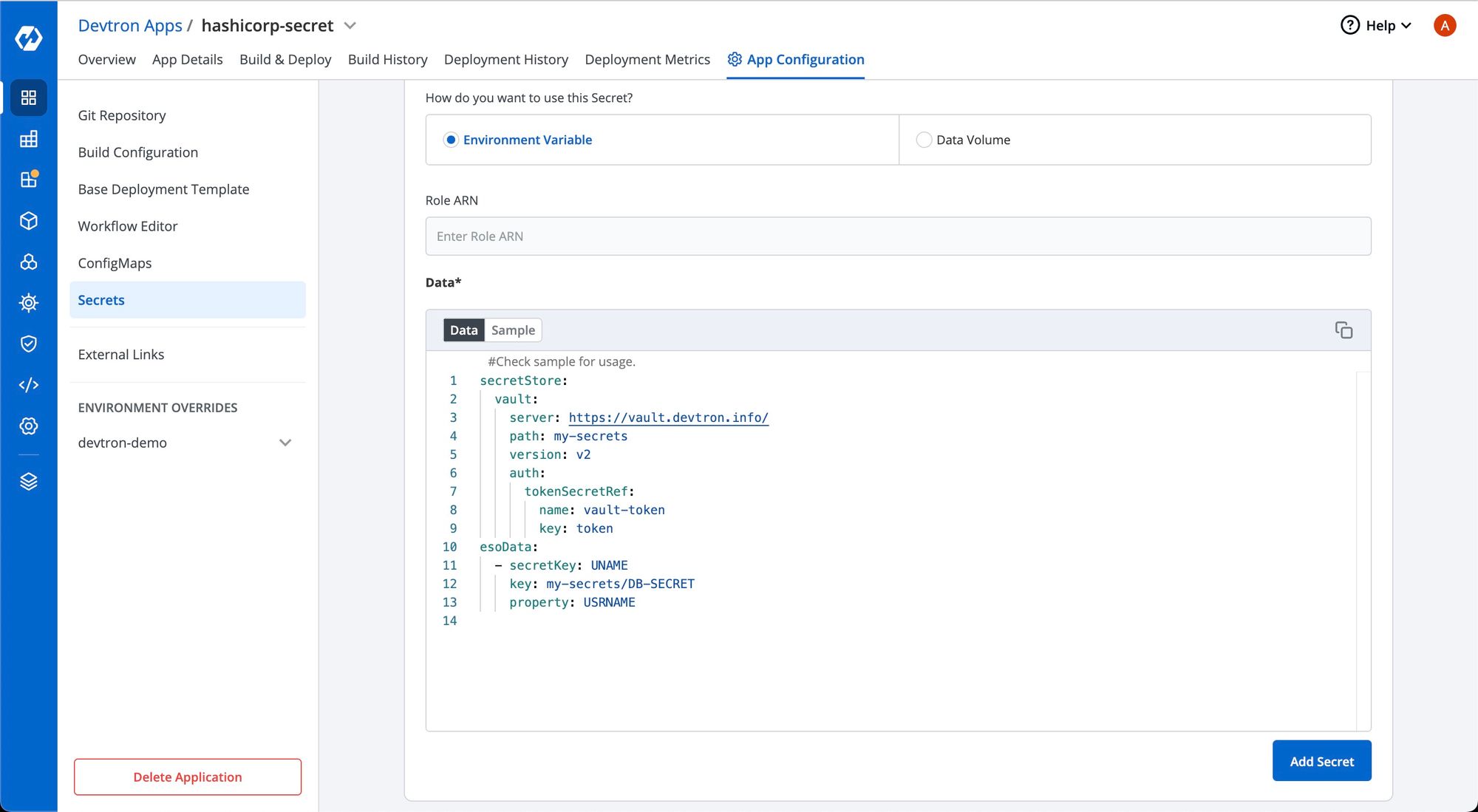
4. Save the secret
After configuring the external secret from HashiCorp Vault, proceed to save the secret by clicking the Save button.
5. Deploy the application
By following the steps mentioned above and configuring these values correctly, you can seamlessly fetch and utilize external secrets from HashiCorp Vault within your application environment by deploying the application. For this, go to build and deploy page and deploy the application in the environment.
Once the application become Healthy, you can see two custom resources on app details page; ExternalSecret and SecretStore. If you see the SecretStore successfully created, it indicates that the authentication process with Vault has been successful. If it's not created, there might be an issue with Vault authentication.
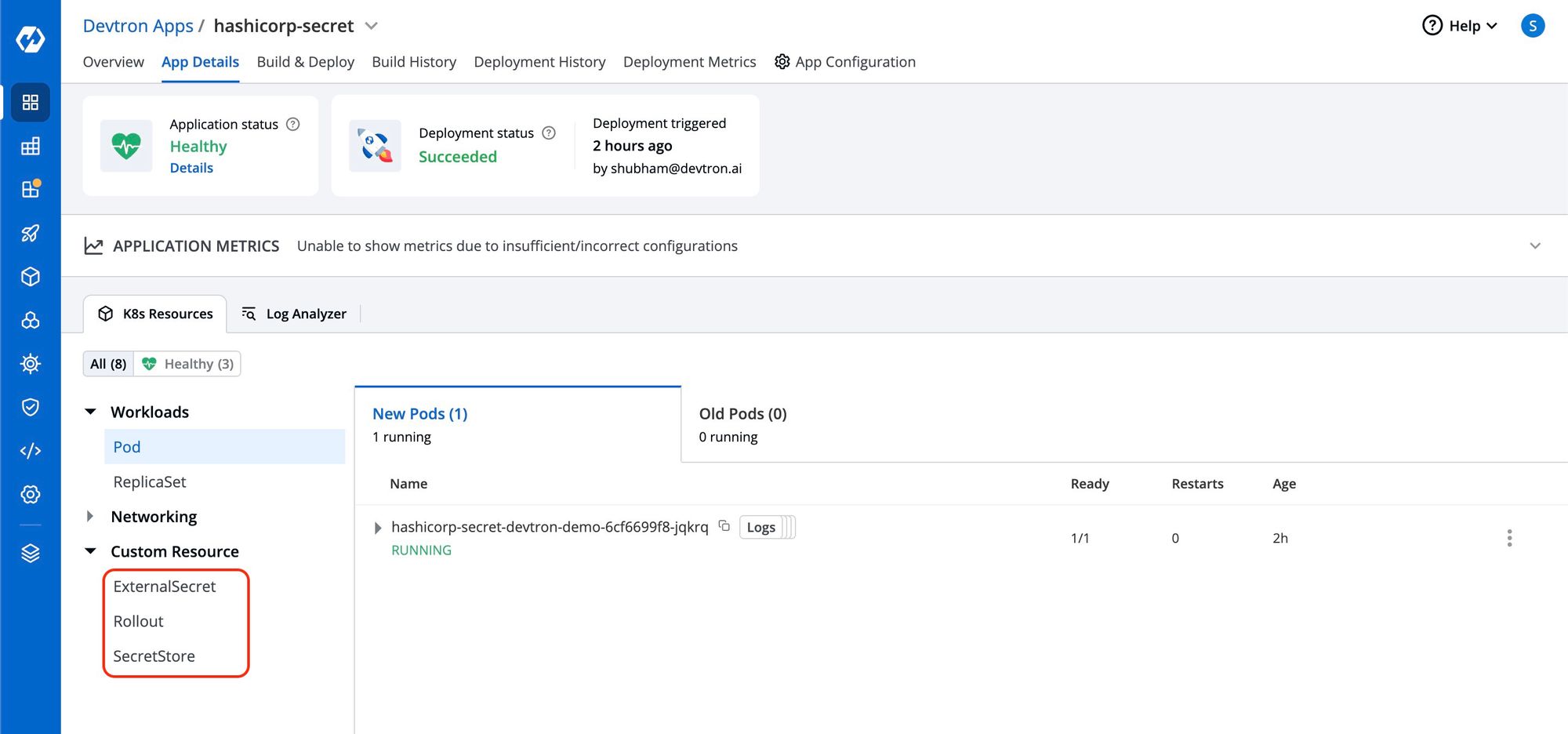
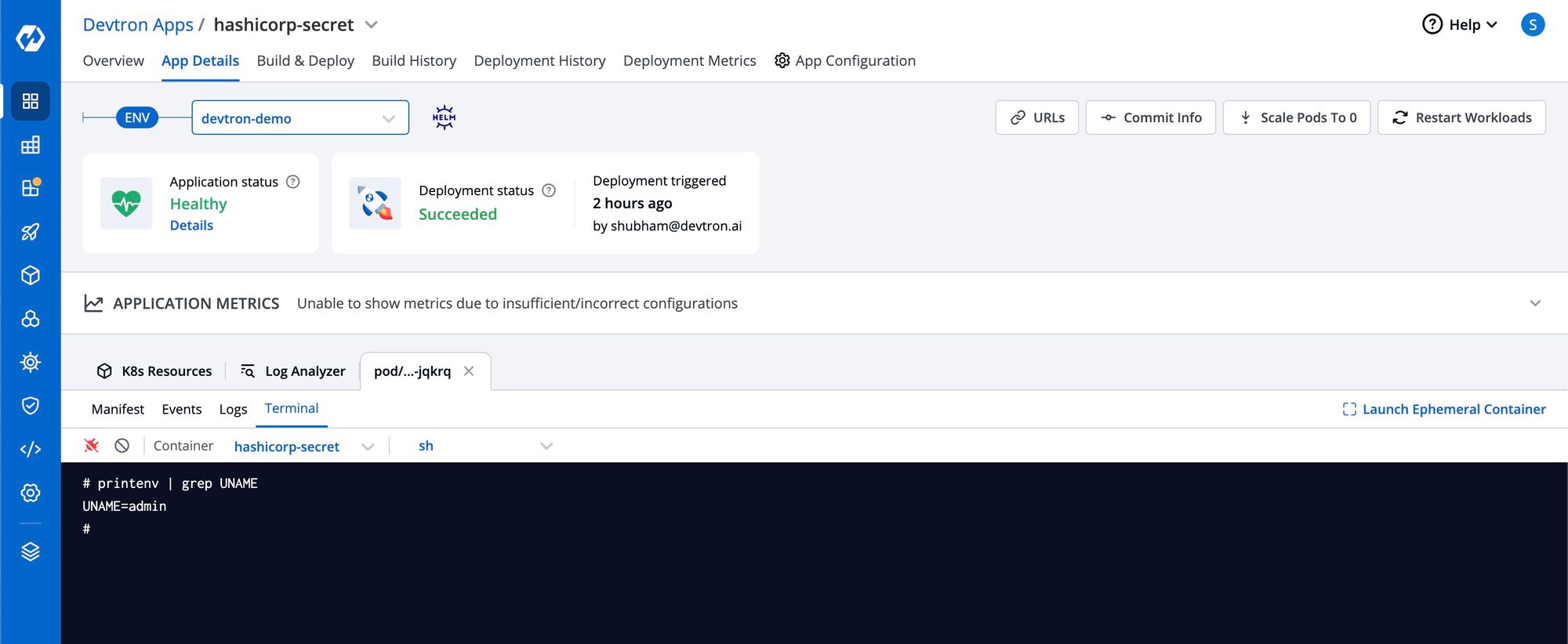
If you find that ExternalSecret has been created, it signifies that secrets from the Vault secret manager have been successfully retrieved and propagated to the environment variables of the application's Pod. To verify this, you can establish a connection with the Pod's terminal and display the environment variables. Then, use a grep command to search for the specific variable name you defined under esoData as the secretKey.
Why Use Devtron for Vault Management?
- Simplified Helm Deployments: No manual Helm/YAML handling.
- Unified Dashboard: Manage secrets, nodes, and apps in one place.
- Integrated External Secrets: Automatic syncing of Vault secrets with Kubernetes apps.
Conclusion
Think of HashiCorp Vault and Devtron as your dynamic digital defenders. Vault secures secrets, Devtron empowers applications. Together, they ensure strong security, smooth operations, and innovative progress. Embrace this powerful partnership for protected secrets and elevated applications.
FAQ
What is HashiCorp Vault used for in Kubernetes?
HashiCorp Vault is used to securely store and manage secrets such as API keys, database credentials, and tokens in Kubernetes clusters. It provides encryption, dynamic secrets, and fine-grained access control to enhance cluster security.
How do I deploy HashiCorp Vault on Kubernetes?
You can deploy Vault using:
- Helm charts from the HashiCorp official repository
- Kubernetes manifests (YAML files)
- Devtron’s Chart Store, which simplifies the Helm deployment and Ingress configuration.
What are dynamic secrets in HashiCorp Vault?
Dynamic secrets are short-lived, automatically generated credentials for databases or cloud services. They enhance security by reducing the risk of compromised long-lived credentials.
How can I use HashiCorp Vault secrets in my Kubernetes applications?
Use the External Secrets Operator (ESO) to fetch secrets from Vault and inject them directly into:
- Kubernetes Secrets
- Pod environment variables
This eliminates the need to hardcode credentials in your applications.
How does Devtron simplify Vault deployment and management?
- Offers one-click Helm deployment of HashiCorp Vault
- Provides integrated secret management with External Secrets Operator
- Displays Vault and Kubernetes secrets in a unified dashboard
- Upcoming: Agentic SRE Assistants for Kubernetes for automated issue detection and remediation