Blue-Green Deployment is a strategy to release new versions with zero downtime by switching traffic between two isolated environments: Blue (current) and Green (new). It reduces risk by allowing production-like testing before going live.
However, managing it manually can be complex: handling dual environments, traffic routing, and rollbacks. So why not automate it? In this post, we’ll show how to streamline Blue-Green Deployments in Kubernetes using Devtron for safer, faster, and downtime-free releases.
Pre-requisites for Performing Blue/Green Deployment
Before starting with the tutorial, let’s look at all the things you’ll require to follow along:
- An Application on GitHub
- Devtron is installed and configured on your machine. If you haven’t installed Devtron, feel free to check out the well-managed installation documentation and join the Discord community for help!
- Setting up the Global Configuration before deploying an app.
- Ingress Controller is deployed on your cluster.
Helpful Reads:
Blue/Green Deployments on Kubernetes using Devtron
Let us start with implementing Blue-Green Deployments in Kubernetes with Devtron! But before we begin, ensure you’ve met the necessary prerequisites to set up a smooth deployment.
Step 1: Create a Devtron Application
Creating an application in Devtron is quick and simple. Just head to the dashboard, select Create New → Custom App, fill in the required details as shown below, and hit Create App to get started.
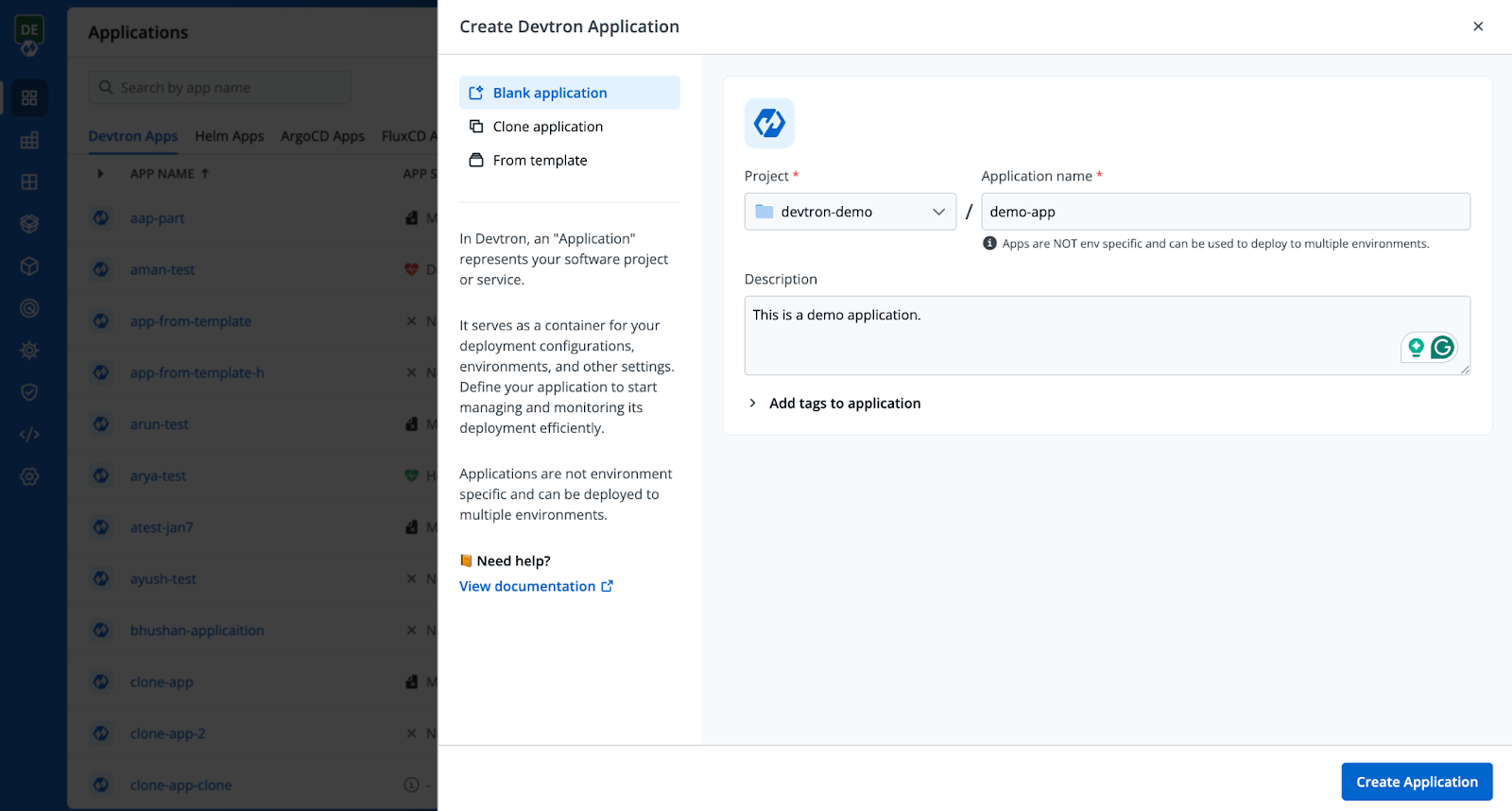
Check out the documentation to learn more about the application creation process.
Step 2: Add Repository
Upon redirection to the Configuration tab, the next step is to set up a few essential settings. The first task is to specify the Git Repository where your application resides.
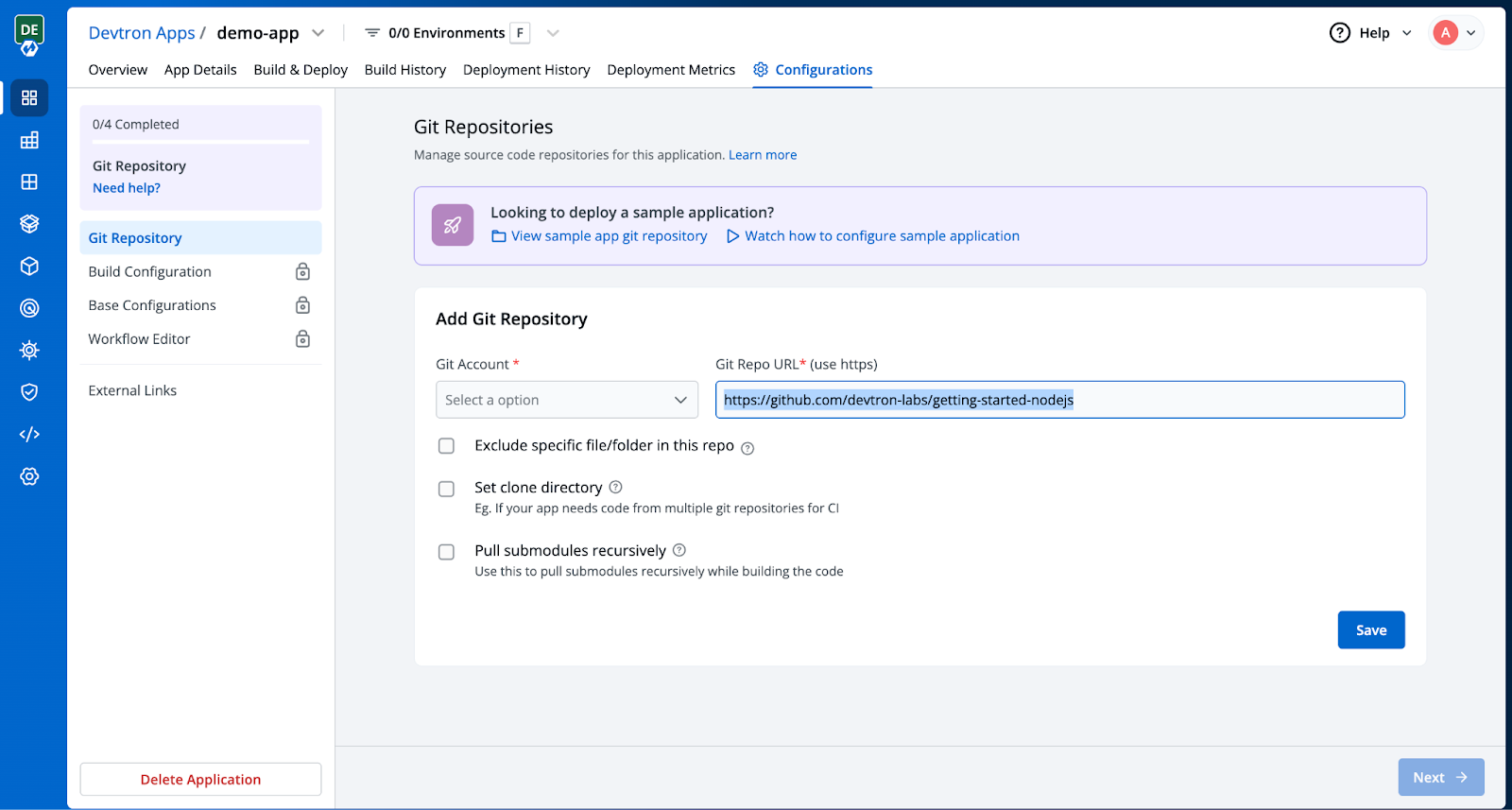
Step 3: Setting up Build Configuration
Next, we need to set up a Build Configuration to generate the container image for your application.
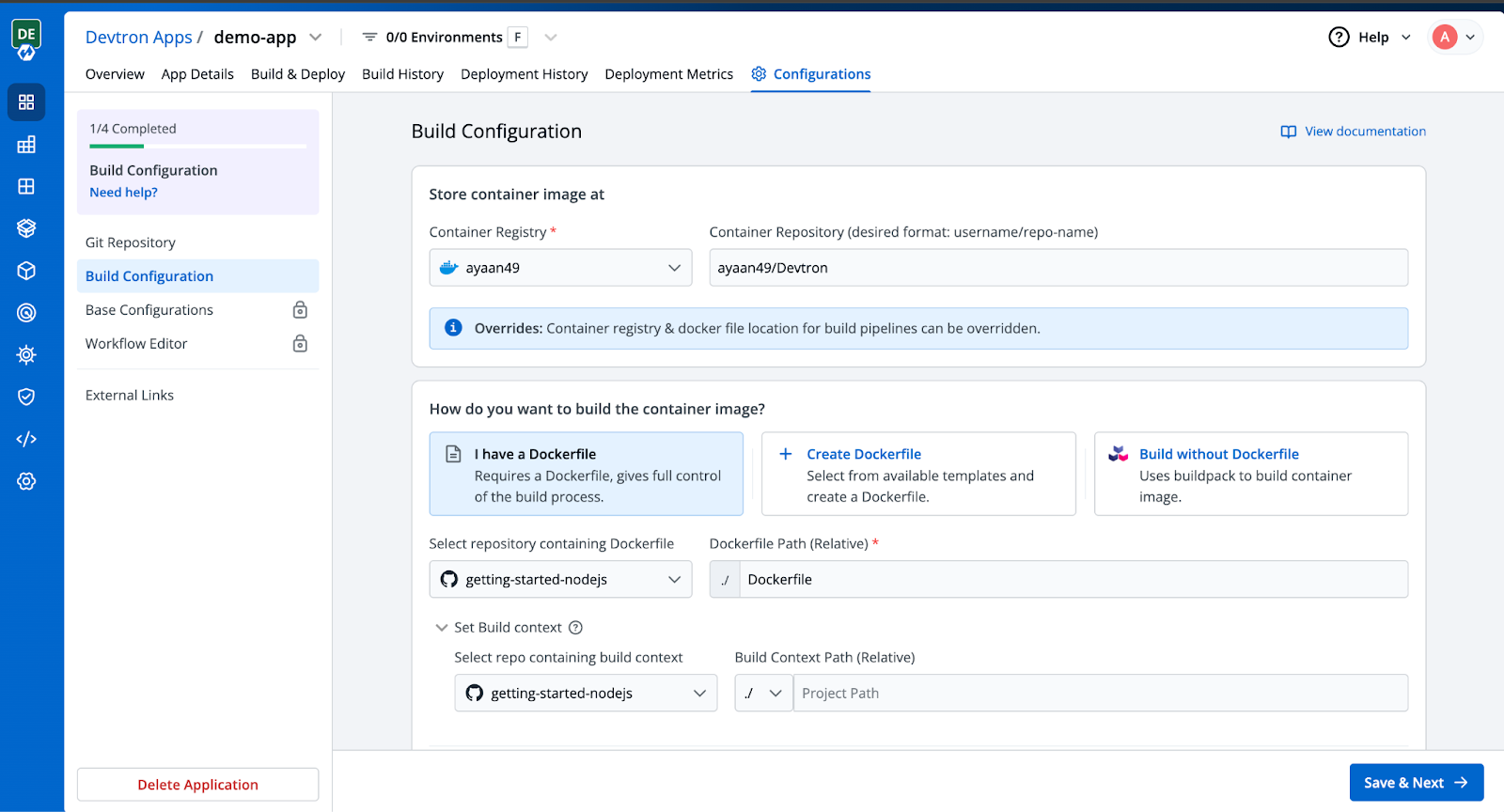
Step 4: Deployment Configurations
Now, you will be redirected to the Base Configuration page, where you need to change the Chart type from Deployment → Rollout Deployment. The Rollout Deployment chart provides us with advanced deployment configurations such as Blue/Green and Canary deployments.
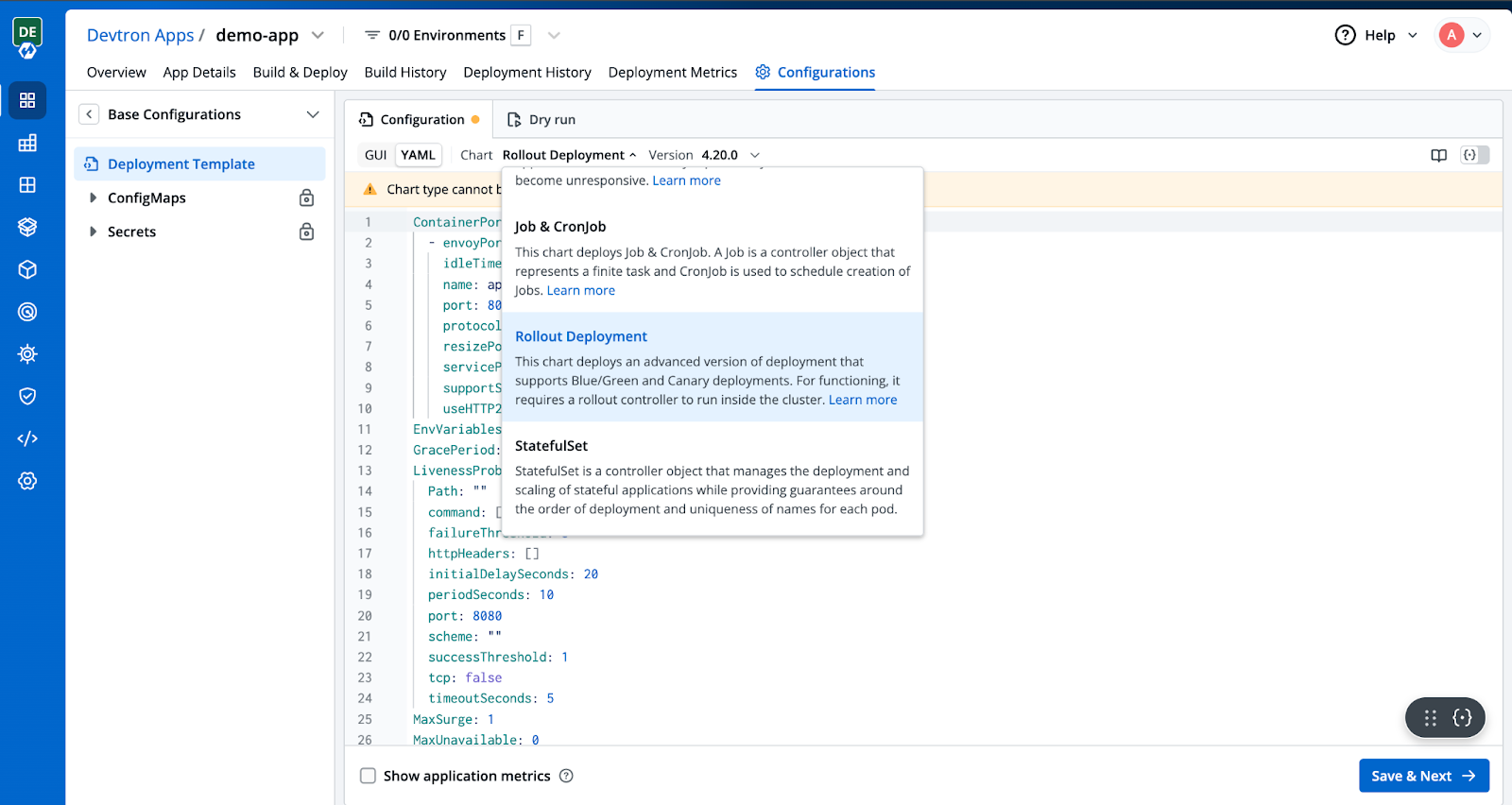
Step 5: Enable Ingress in the Rollout Deployment Chart
Once you've selected the Rollout Deployment chart, search for Ingress in the template, enable it, and apply the necessary changes as shown below.
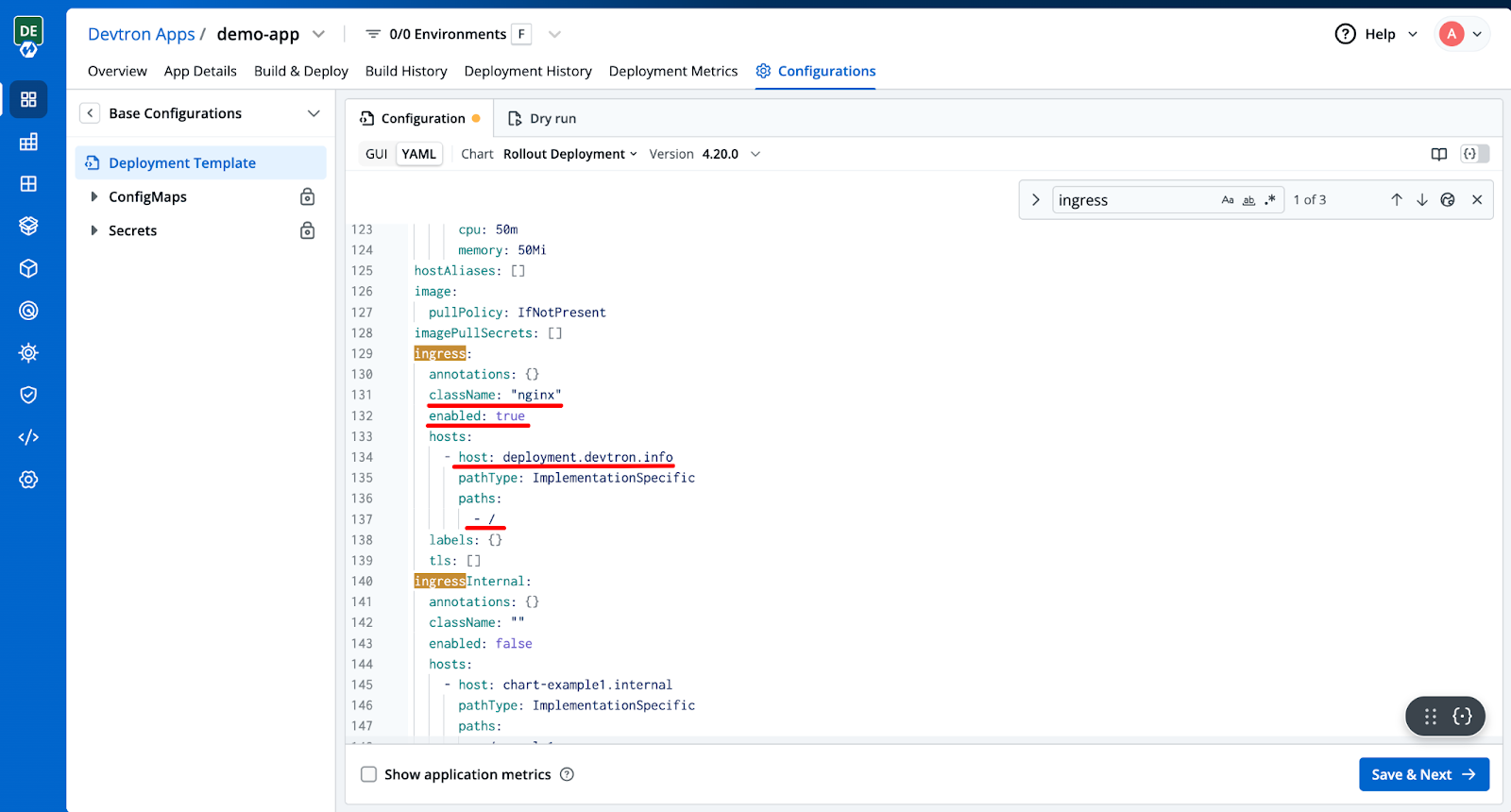
- Set the className to nginx.
- Enable the configuration by changing enabled from false to true.
- Specify the hostname where your application will be hosted.
- Define the application’s path.
Then click Save & Next.
Step 6: Create Build and Deployment Pipelines
Next, set up your build and deployment pipelines, then choose the Blue Green Deployment strategy from the dropdown in your deployment pipeline configuration, as shown below.
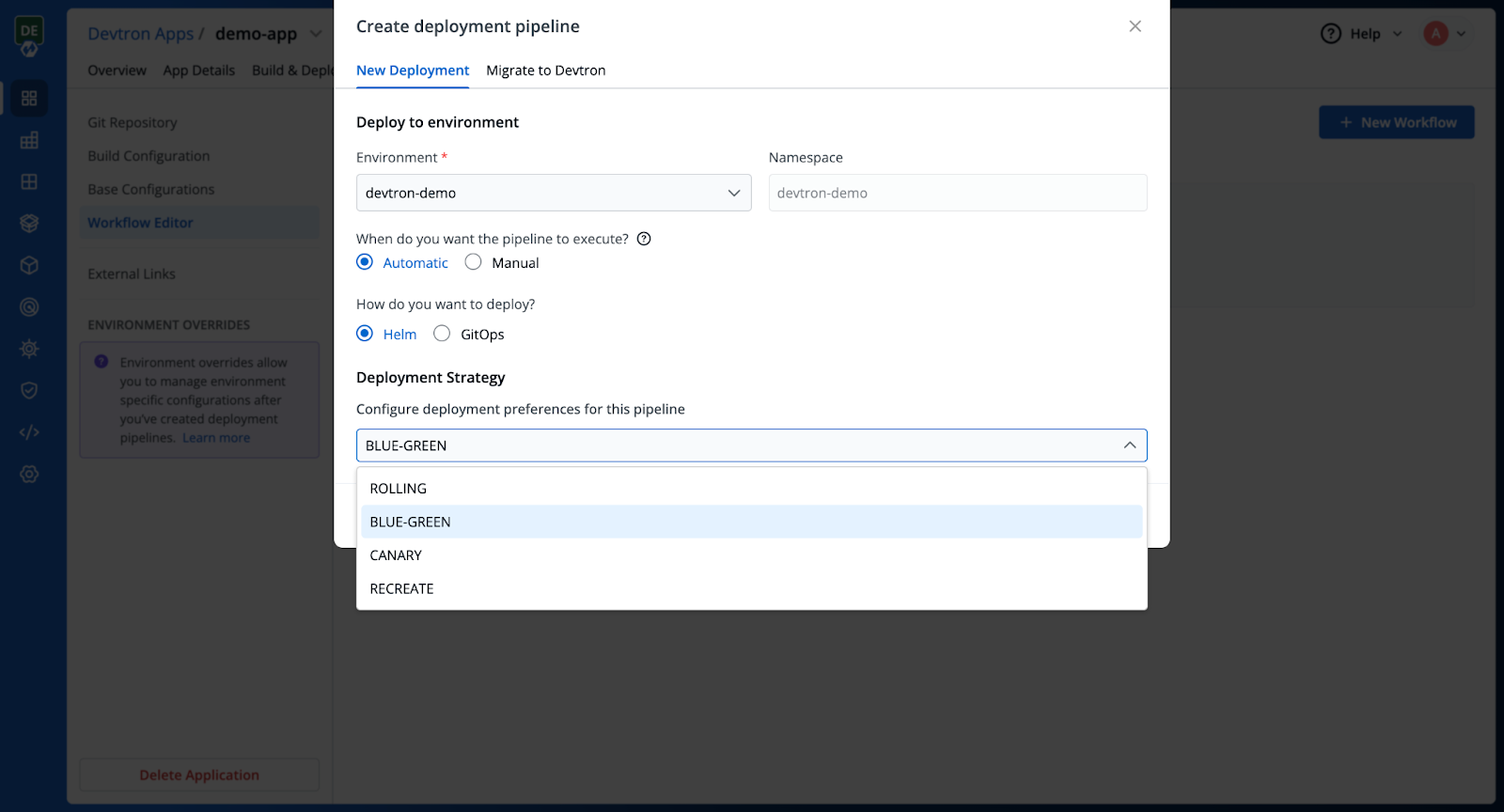
Please check the documentation to learn more about the pipeline configurations.
After creating the deployment pipeline, the workflow editor would look like this:
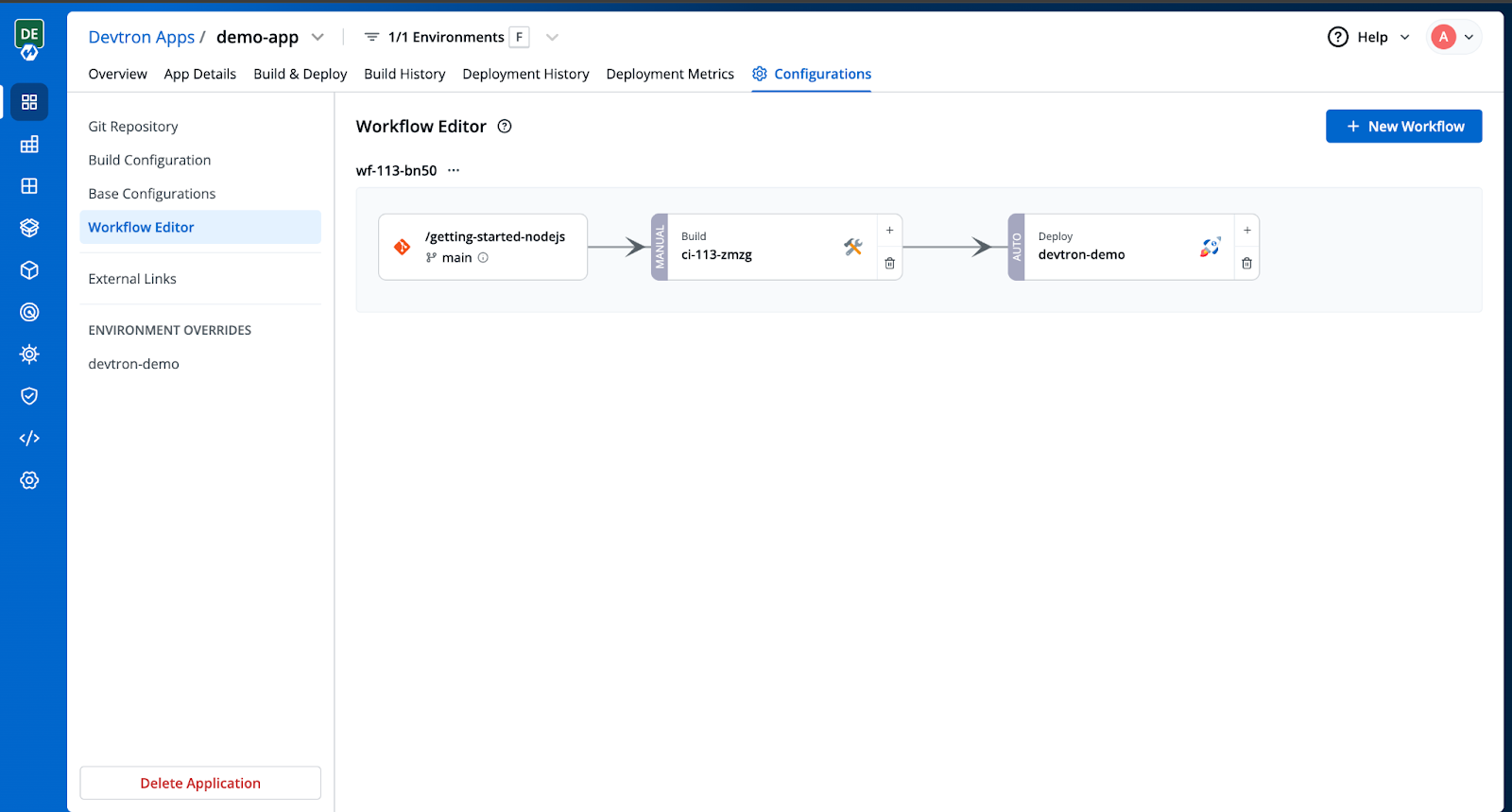
Step 7: Trigger the Build and Deployment Pipelines
Once all the configurations are complete, all that’s left is to trigger the build stage, and subsequently the deployment.
From the Build & Deploy tab, select the Git material to trigger the build stage. The pipeline will build the container image.
Once the build stage is complete, you can trigger the deployment for the built artifact.
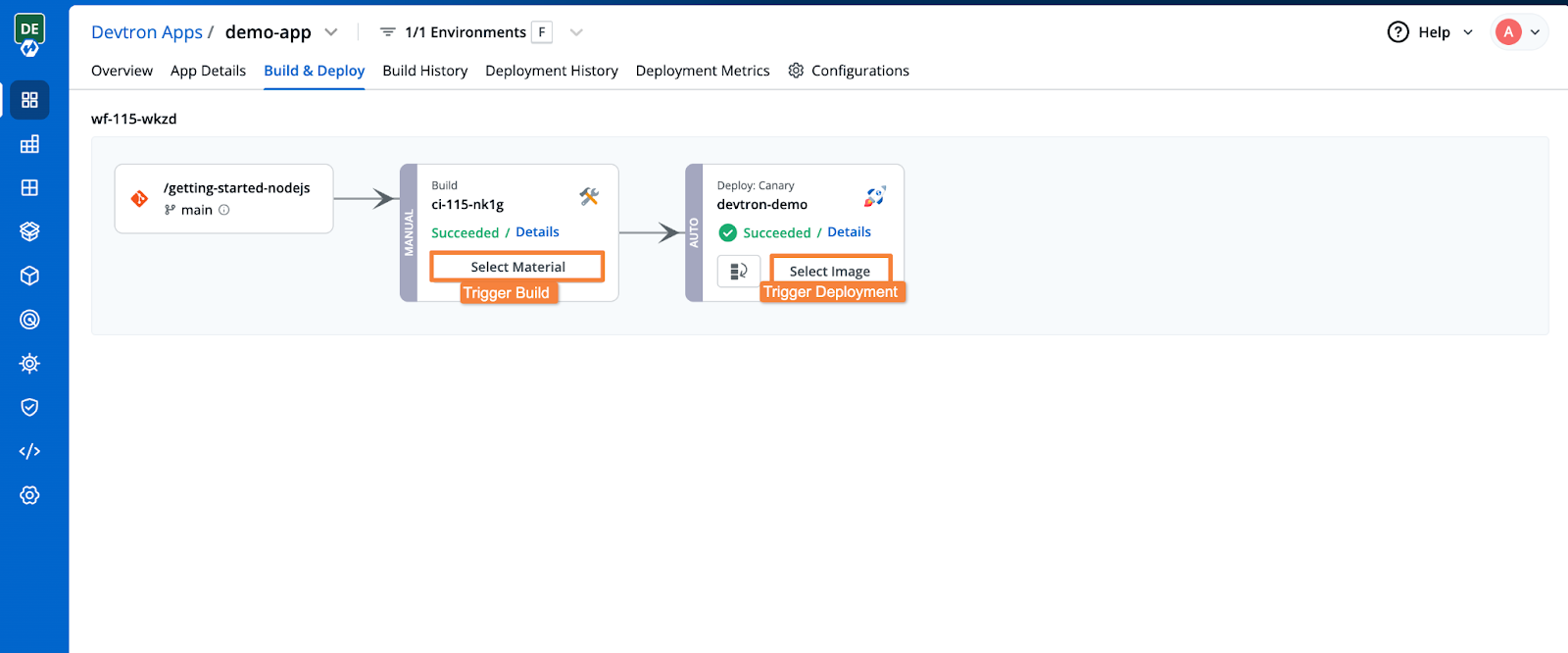
After triggering the deployment, Devtron automatically pushes your application to the cluster, applying the configuration settings you've set up earlier.
Once the application is deployed, you will be able to see the application health, deployment status, security vulnerabilities, the Kubernetes resources of the application, and more.
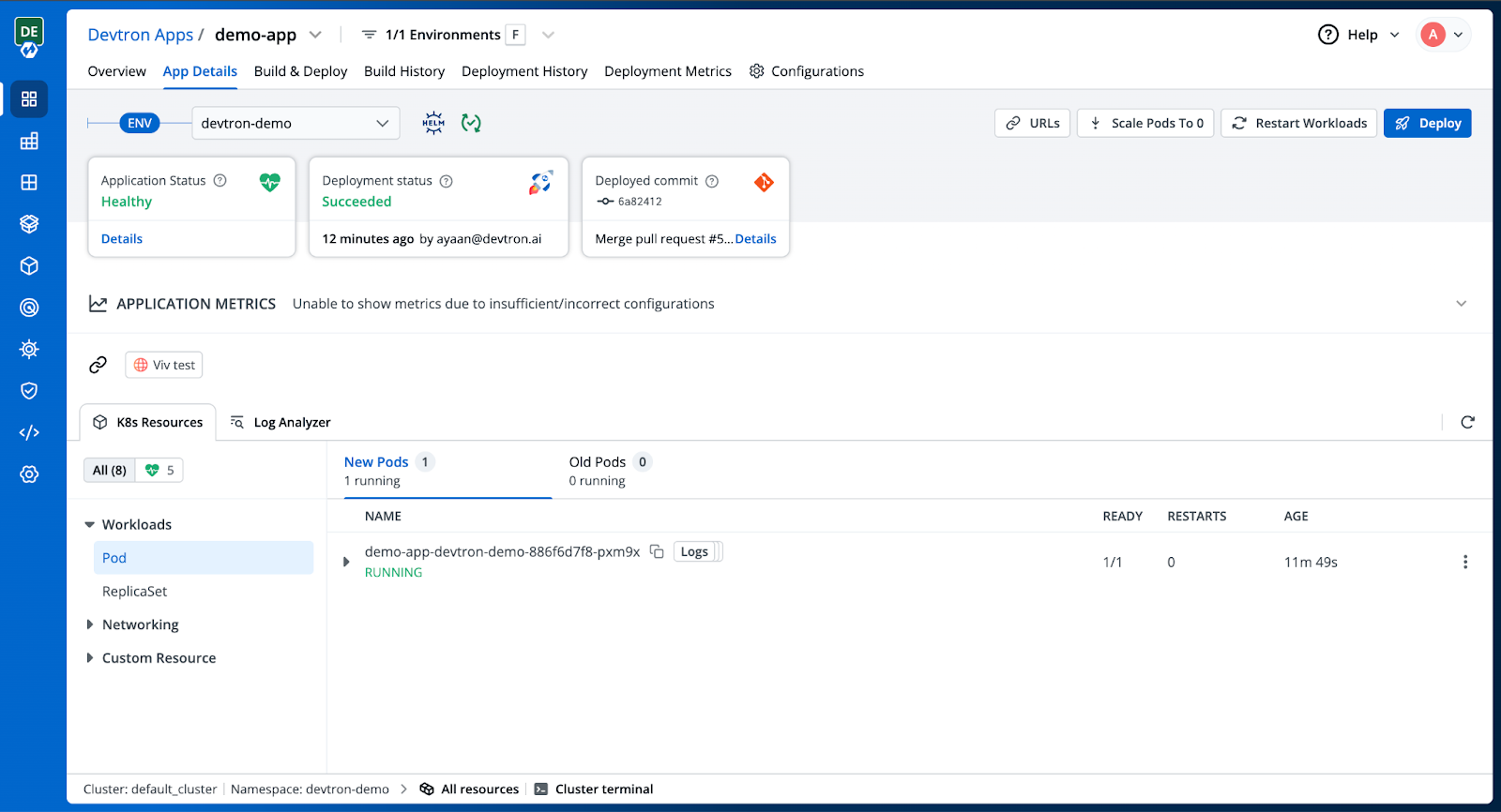
Step 8: Override your Environment
After you deploy the application, go into the Environment Overrides menu when you are on the Configurations tab. There, make the changes with the settings so the Blue-Green strategy parameters are enabled. You will be able to see how Devtron builds a parallel environment (Green) and how it lets you preview the new version before you route traffic in the App Details.
Click on devtron-demo to expand the deployment template configuration. Next, click on + Create Override to enable editing. You can now modify the configuration as needed. In our case, we updated the number of replicas and adjusted the CPU and memory settings. Once done, click Save changes to apply the updates.
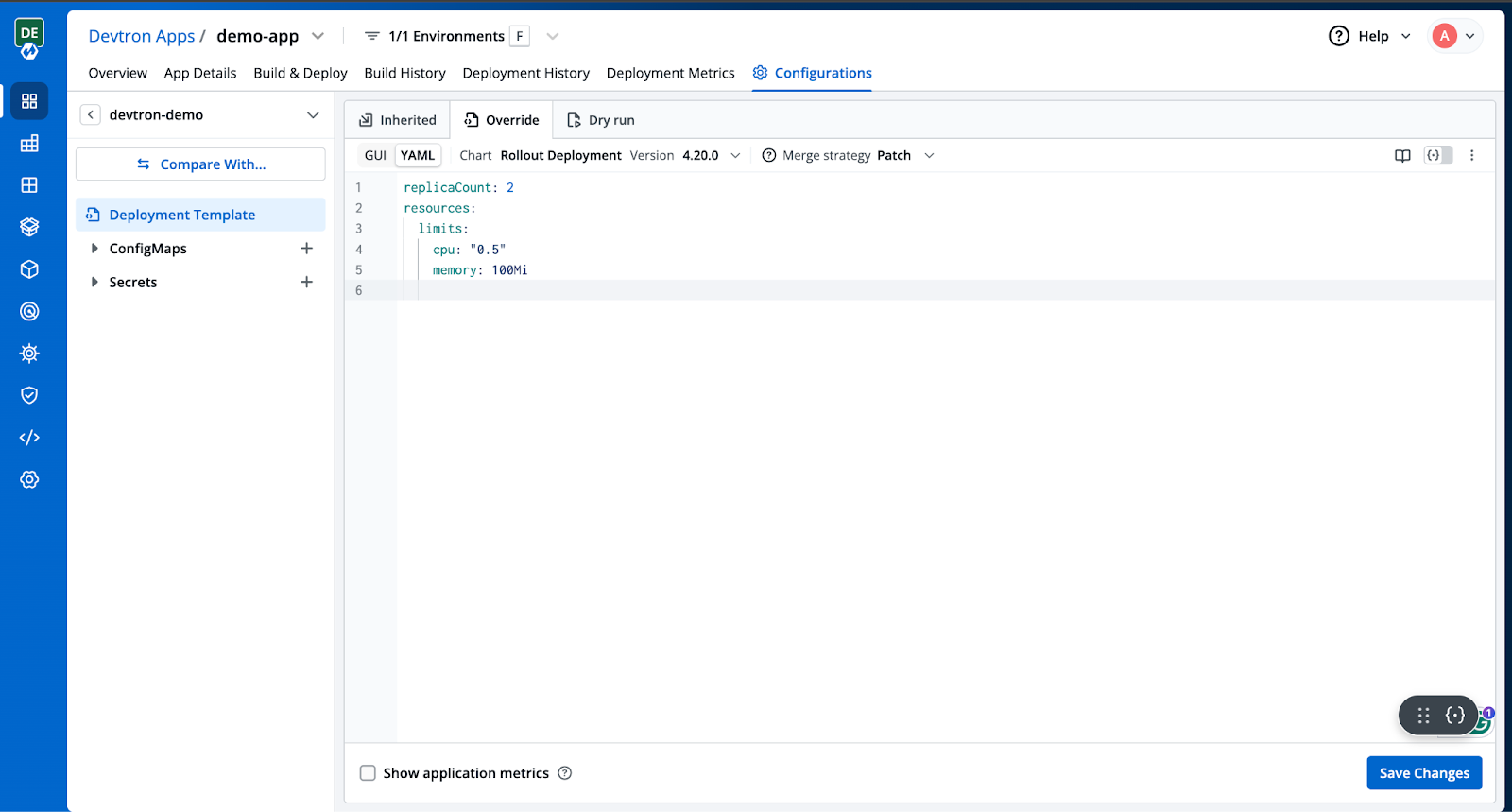
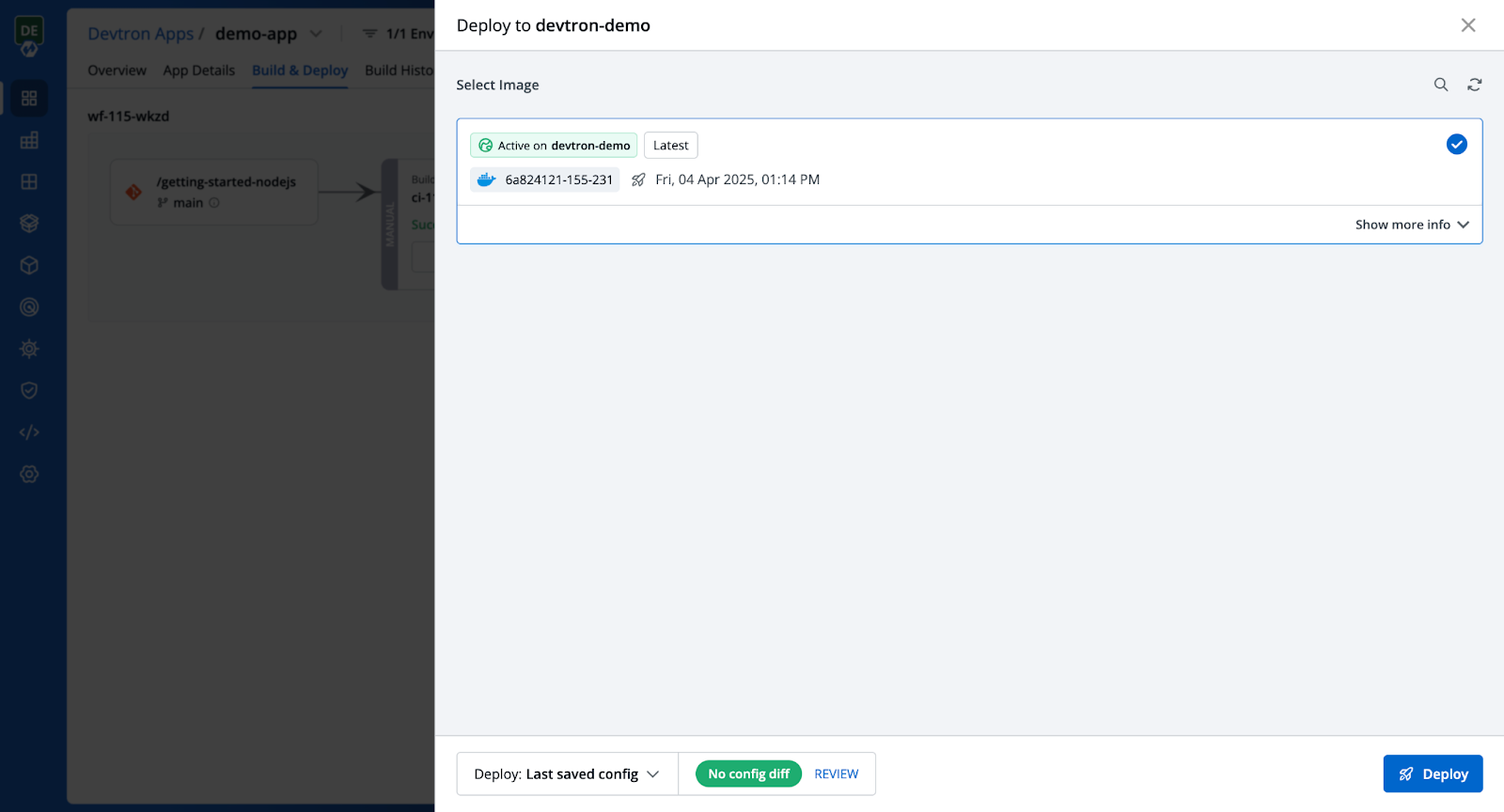
Step 9: Deploy the application
Once again, navigate to the Build & Deploy tab, select the image in the Deployment pipeline, and deploy it using the updated deployment configurations.
Once deployed, navigate to the app details to observe traffic distribution between the 'New Pods' and 'Old Pods' as part of the blue-green deployment.
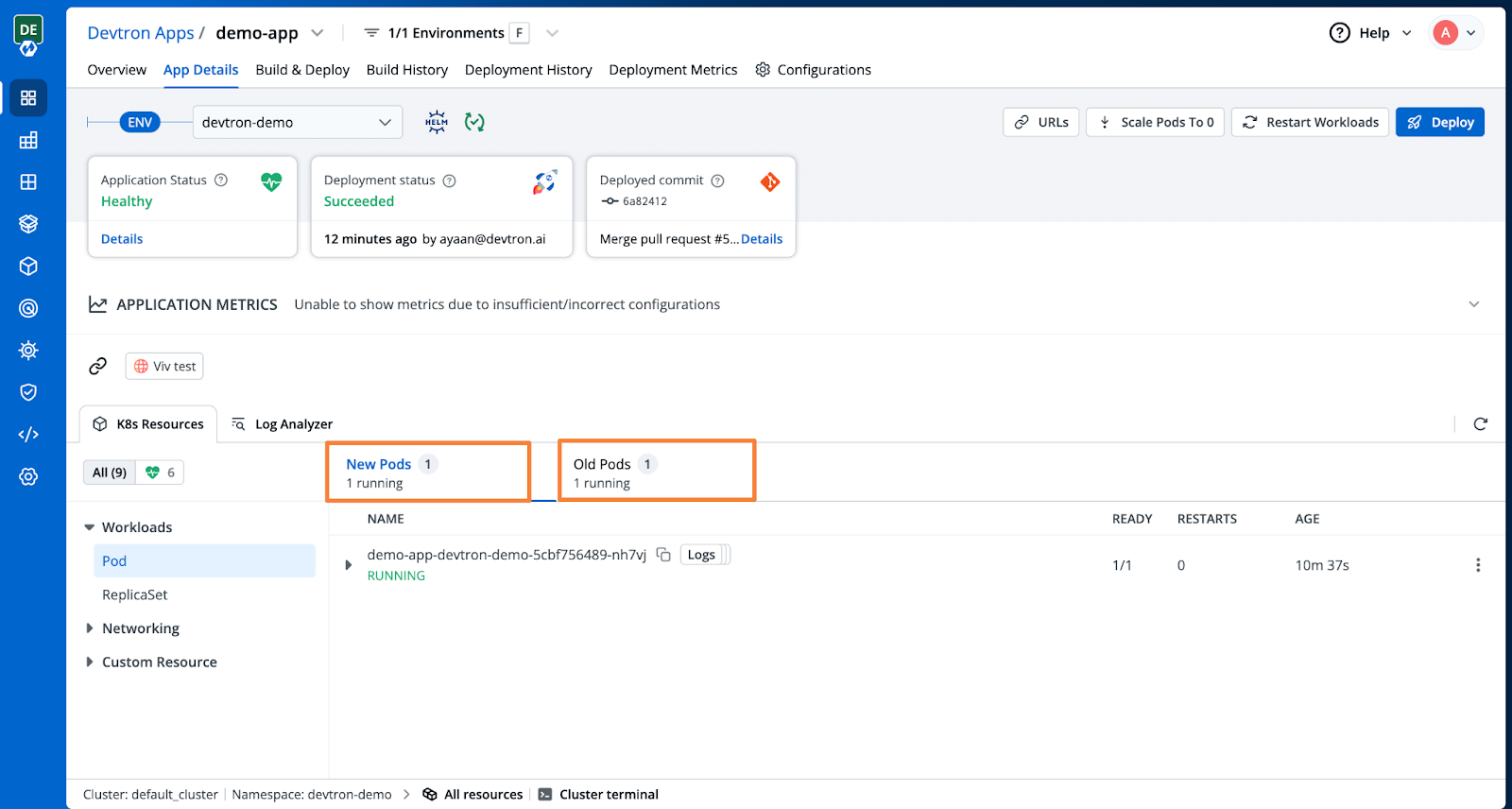
Congratulations! You've just seen how easy it is to configure and implement Blue-Green Deployments using Devtron.
Conclusion
Here's a quick recap of what we covered:
- Creating and configuring a Devtron application
- Setting up Git repositories and build pipelines
- Choosing the Rollout Deployment chart to enable the Blue-Green strategy
- Configuring Ingress for traffic routing
- Building, deploying, and customizing environment overrides
- Observing the traffic split between New Pods and Old Pods during the blue-green rollout
FAQ
What is blue-green deployment?
Blue-green deployment is a release strategy where two environments—blue (current) and green (new)—are used. Traffic is switched from blue to green after testing, enabling zero-downtime updates and easy rollbacks if needed.
What is the difference between blue-green and canary deployment?
Blue-green deployment switches all traffic to the new version at once, while canary deployment gradually shifts traffic to monitor performance and catch issues early. Canary is ideal for incremental rollouts; blue-green is faster for full releases.
How does Devtron help with blue-green deployments in Kubernetes?
Devtron simplifies blue-green deployments by providing a visual interface for configuring and managing environments, switching traffic smoothly, and rolling back easily if issues occur without writing any custom scripts.
How does Devtron handle deployment rollbacks?
Devtron allows you to roll back to a previous version easily with just a few clicks, reducing downtime and minimizing the impact of failed releases
Does Devtron support multi-environment deployments?
Yes, Devtron makes it easy to manage deployments across multiple environments, such as dev, staging, and production, with clear visibility and control.








