C++ is a high-performance, general-purpose programming language widely used in system programming, game development, financial applications, and embedded systems. Its blend of low-level memory control and high-level abstractions makes it a top choice for performance-critical applications. Many foundational technologies, including operating systems, databases like MySQL, and game engines like Unreal Engine, rely on C++ for its speed and reliability.
However, as modern infrastructure moves toward cloud-native architectures, deploying C++ applications efficiently becomes a challenge. Kubernetes provides an ideal platform for managing C++ applications by ensuring scalability, resilience, and streamlined deployments. By containerizing C++ applications, developers can eliminate dependency conflicts and improve portability across different environments.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through both methods step by step and cover best practices for optimizing your deployment. Let’s dive in and make your Kubernetes deployment seamless!
- Devtron for Automated Deployment
- Using Kubernetes Manually
Did you know; Over 70% of Production Outages in Kubernetes Are Due to Failed Deployments. A significant portion of downtime can be traced back to misconfigured deployments, failed upgrades, or improper rolling updates.
Deploying C++ Applications on Kubernetes
Deploying a C++ application to Kubernetes involves several steps. Let’s first review the overall process and then discuss the various steps in depth.
- Write and build the C++ Applications
- Containerize the C++ Application
- Push the container to a Container Registry such as DockerHub
- Create the required YAML Manifest for Kubernetes Resources
- Apply the YAML manifest to the Kubernetes clusters
Let’s dive deeper into all the required steps and deploy a simple C++ application to Kubernetes.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding with the deployment process, please make sure that you have the following prerequisites
- A C++ based application
- Docker
- Kubectl
- A Kubernetes Cluster such as kind
Once you have the prerequisites installed, you can proceed to write the Dockerfile and create the container image.
Method 1: Deploy C++ applications with Devtron
Devtron is an end-to-end Kubernetes management solution that can help simplify the DevOps lifecycle right from the build stage, to deployments and beyond. Deploying a C++ application, it can reduce a lot of the manual steps that we have seen above. Devtron will handle creating the Dockerfile, the Kubernetes manifests, building, deploying, and scanning all while following the best practices.
Let’s take a look at how you can deploy the same C++ application using Devtron.
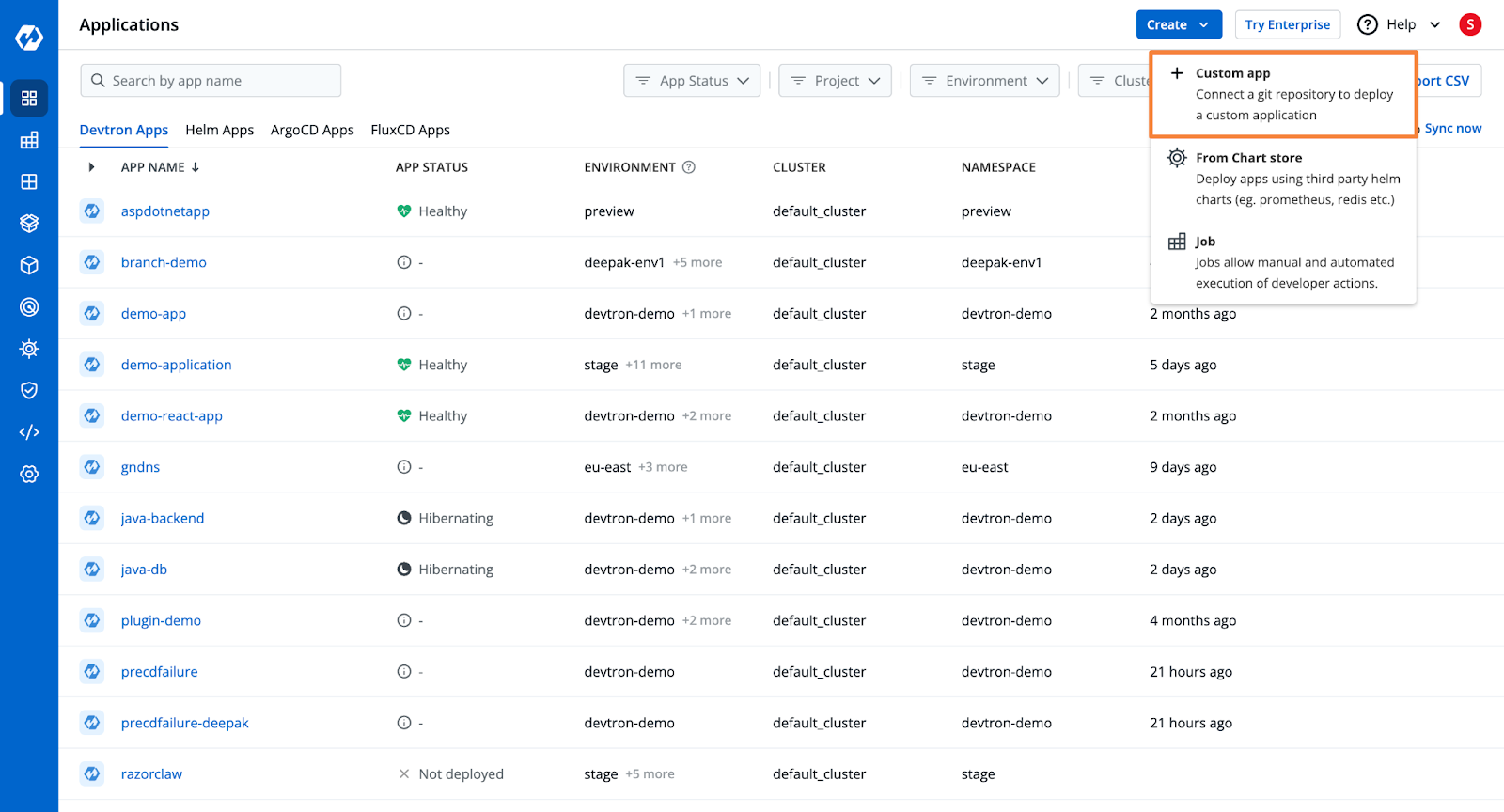
Step 1: Create a Devtron application and add the Git Repository
- From Devtron’s home page, create a new Devtron application.
- Add the Git Repository containing the C++ application code.
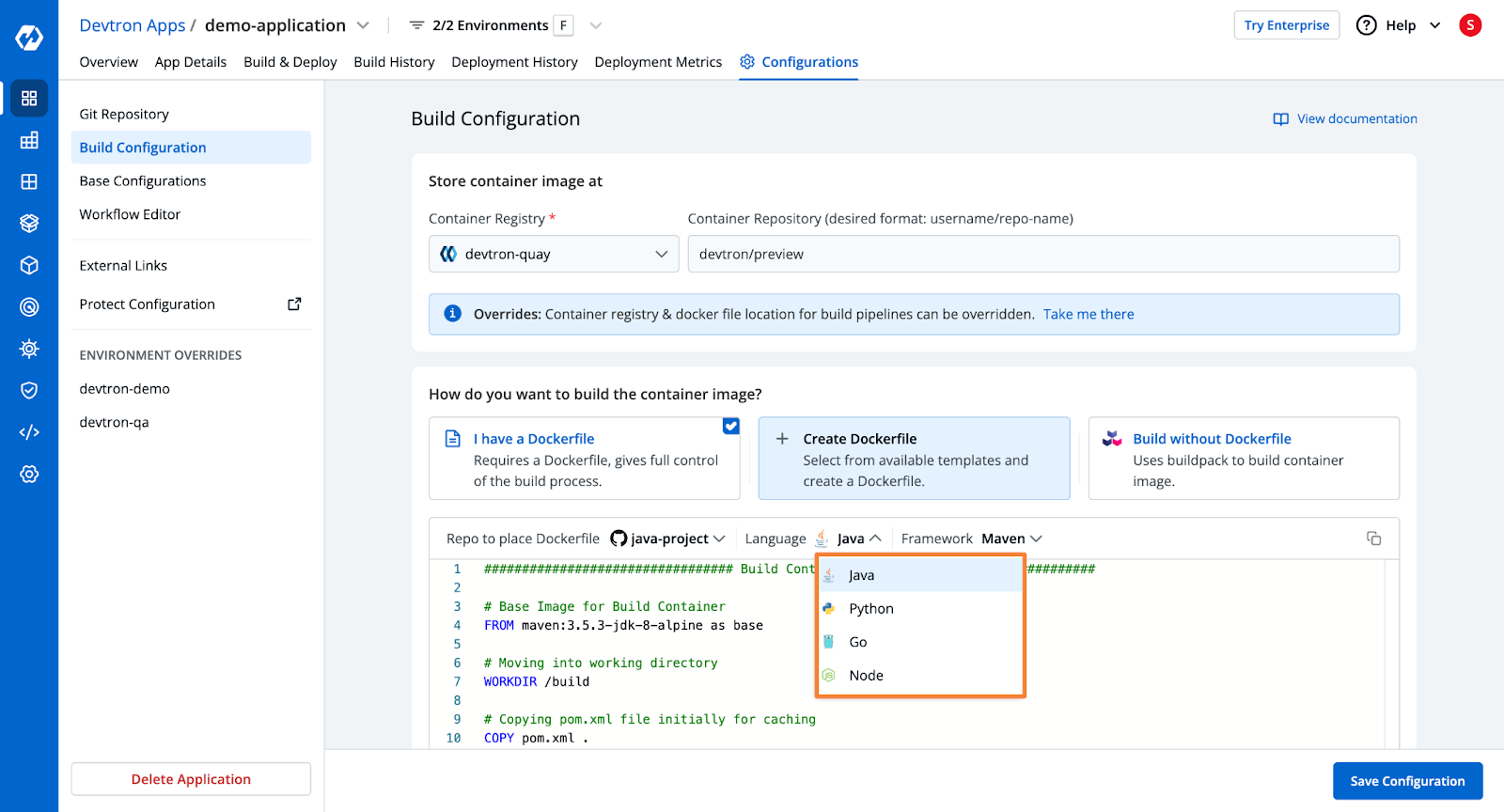
Step 2: Configure the Build
- Devtron will pull code from the repository and build the Docker container.
- You need to configure an OCI Container Registry.
- Choose from three build options:
- Use an existing Dockerfile
- Create a Dockerfile (using Devtron's template for Go applications)
- Use Buildpacks
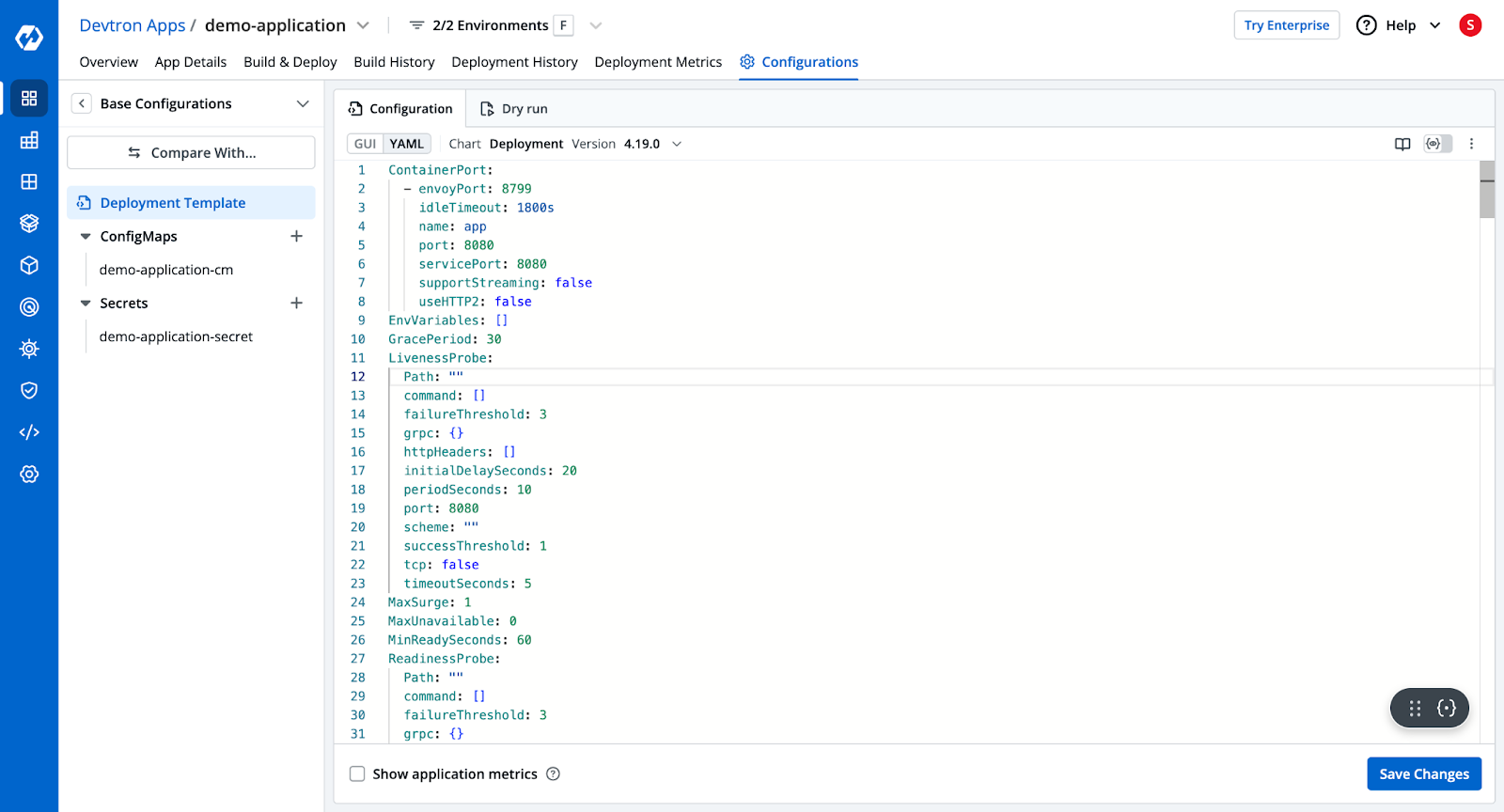
Step 3: Deployment Configurations
- Devtron provides a pre-configured YAML template for Kubernetes deployment.
- Configure ingress, autoscalers, and other deployment settings.
Step 4: Create the Build and Deploy Pipelines
- The CI pipeline will build the application and push the image to a registry.
- The CD pipeline will trigger deployments in the Kubernetes cluster.
Configure Pre and Post Stages (e.g., security scanning, unit testing).
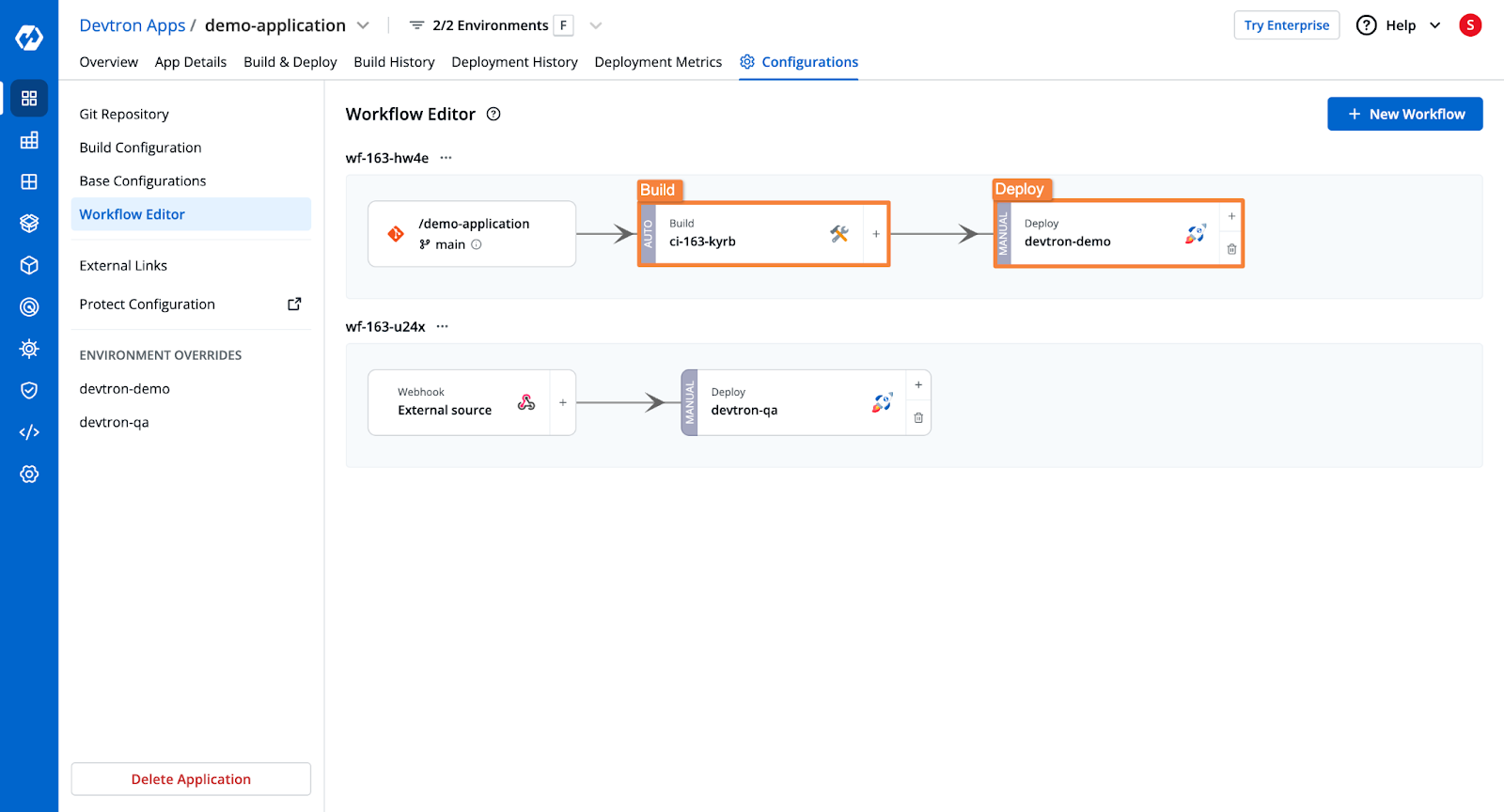
Step 5: Trigger the Build and Deployment Pipelines
- Select the Git branch and trigger the build stage.
- Once the build is complete, trigger the deployment stage.
- Devtron will deploy the application and show:
- Deployment status
- Application health
- Kubernetes resource details
- Security vulnerabilities
- Rollback options in case of errors
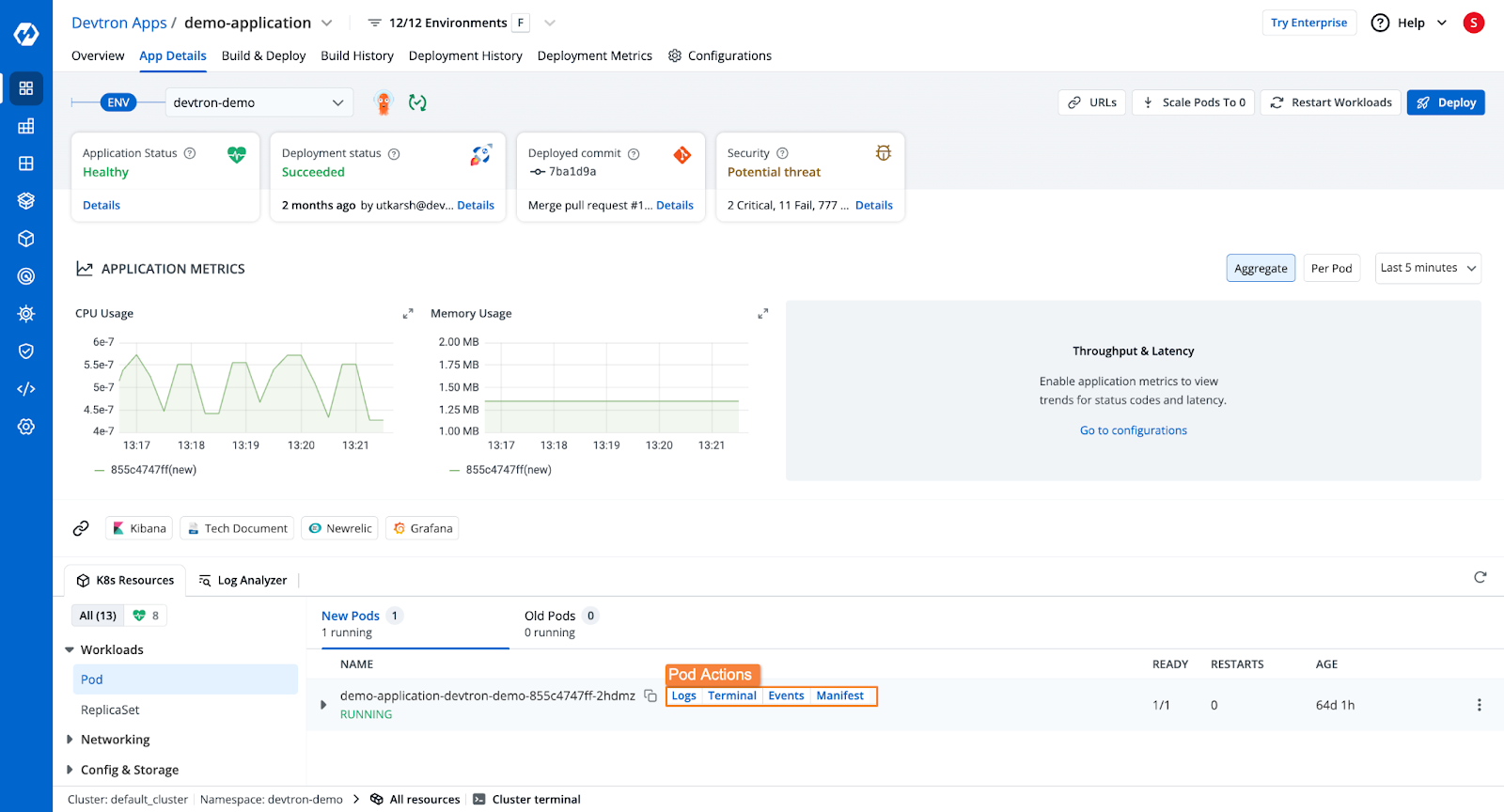
Once the application is deployed, you will be able to see the application's health, deployment status, security vulnerabilities, the Kubernetes resources of the application, and more.
Method 2: Deploying C++ Application Manually to Kubernetes
Step 1: Create the Dockerfile
A Dockerfile is a set of instructions to build a container image. Below is the Dockerfile to containerize your C++ application:
################################# Build Container ###############################
FROM ubuntu:latest AS builder
# Set the working directory
WORKDIR /app
# Install necessary dependencies for building
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y \
g++ \
libcpprest-dev \
libboost-all-dev \
libssl-dev \
cmake \
&& rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
# Copy source code into the container
COPY ok_api.cpp .
# Compile the C++ code
RUN g++ -o ok_api ok_api.cpp -lcpprest -lboost_system -lboost_thread -lboost_chrono -lboost_random -lssl -lcrypto
################################# Prod Container #################################
FROM alpine:latest
# Set the working directory
WORKDIR /app
# Install only the necessary runtime dependencies
RUN apk add --no-cache \
libstdc++ \
boost-system \
boost-thread \
openssl \
gcompat # Improves compatibility with binaries built on Ubuntu
# Copy the compiled binary from the builder stage
COPY --from=builder /app/ok_api /app/ok_api
# Expose the port on which the API will listen
EXPOSE 8080
# Command to run the API
CMD ["./ok_api"]
Step 2: Build and Push the Docker Image
Run the following command to build the Docker image:
docker build -t devtron/cpp:v1 .
Push the image to DockerHub:
docker push devtron/cppStep 3: Creating the Kubernetes Deployment and Service Manifests
Create a deployment.yaml file:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: cpp-deployment
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: Cpp
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: cpp
spec:
containers:
- name: cpp-container
image: siddhantkhisty/cpp-app
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
Create a service.yaml file:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: cpp-service
spec:
selector:
app: cpp
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 8080
type: NodePort
Step 4: Deploy to Kubernetes
Run the following command to apply the manifests:
kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml service.yaml
Your C++ application is now deployed to Kubernetes!
Common Challenges and Solutions
1. Container Image Size Management
- Use Multi-Stage Builds to separate build and runtime environments.
- Use Lightweight Base Images like Alpine or Distroless to reduce size.
2. Resource Management
- Set Memory and CPU Limits to avoid overconsumption.
- Implement Autoscaling (HPA) to handle varying workloads.
3. Deployment Strategies
- Rolling Updates to ensure zero-downtime deployments.
- Graceful Shutdown Handling to avoid breaking live traffic.
Conclusion
In this blog, we have explored the different steps that have to be taken for configuring and deploying a C++ application to a Kubernetes cluster. To summarize, we saw:
- How to build a Dockerfile for a C++ application
- Create the Kubernetes Manifest for the C++ application
- Deploy a C++ application to Kubernetes
- Simplify C++ Application Deployments with Devtron
Devtron can help accelerate deployment velocity, while also ensuring that deployments are more reliable. For working with Kubernetes, Devtron can act as the single solution you need.
FAQ
What are the prerequisites for how to deploy C++ applications to Kubernetes effectively?
Ensure your C++ application is containerized with a minimal Docker image, includes necessary dependencies, and is configured with Kubernetes Deployment, Service, and ConfigMaps/Secrets for environment management.
How can I troubleshoot issues during how to deploy C++ applications to Kubernetes effectively?
Use kubectl logs, kubectl describe, and kubectl exec to diagnose issues, check resource limits, and verify networking, dependencies, and configuration settings.
What tools are recommended for how to deploy C++ applications to Kubernetes effectively?
Use Docker for containerization, Helm or Kustomize for Kubernetes manifests, Prometheus and Grafana for monitoring, and tools like Skaffold or ArgoCD for CI/CD automation.
What are the best practices for how to deploy C++ applications to Kubernetes effectively?
Use a minimal base image, statically link dependencies, optimize resource requests, implement health checks, manage configs with ConfigMaps/Secrets, and enable observability with logging and monitoring.