Ruby on Rails is known for its simplicity and developer-friendly approach, making it a top choice for building everything from APIs to full-scale web applications. But while Rails makes development easier, deploying it on Kubernetes can introduce challenges—bloated containers, misconfigured manifests, and resource inefficiencies can quickly become roadblocks.
That’s where Devtron comes in. By automating deployments and streamlining workflows, Devtron removes the guesswork, helping you get your Rails applications up and running on Kubernetes with minimal effort. Prefer a manual approach? That’s an option too.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through both methods, along with best practices to ensure a smooth and scalable deployment.
Two Ways to Deploy Rails Applications on Kubernetes:
- Using Devtron for Automated Deployment
- Using Kubernetes Manually
Did you know? Over 70% of cloud-native failures stem from misconfigured deployments. From bloated images to inefficient resource allocation, small mistakes can cause big inefficiencies. But don’t worry—this guide will help you avoid them!
Deploying Rails Applications on Kubernetes
Deploying a Rails application to Kubernetes involves several steps. Let’s first review the overall process and then discuss the various steps in depth.
Steps for Deployment
- Write and build the Rails Application
- Containerize the Rails Application
- Push the container to a Container Registry such as DockerHub
- Create the required YAML Manifest for Kubernetes Resources
- Apply the YAML manifest to the Kubernetes clusters
Prerequisites
Before proceeding with the deployment process, please make sure that you have the following prerequisites
- A Rails application
- Docker
- Kubectl
- A Kubernetes Cluster such as kind
Method 1: Deploying Rails Applications Using Devtron
Devtron is a Kubernetes management platform that simplifies the entire DevOps lifecycle. It automates the creation of Dockerfiles, and Kubernetes manifests, builds the application, and manages deployment through an intuitive UI.
Step 1: Create a Devtron Application and Add Git Repository
- From Devtron’s home page, create a new Devtron application.
- Add the Git Repository containing the Rails application code.
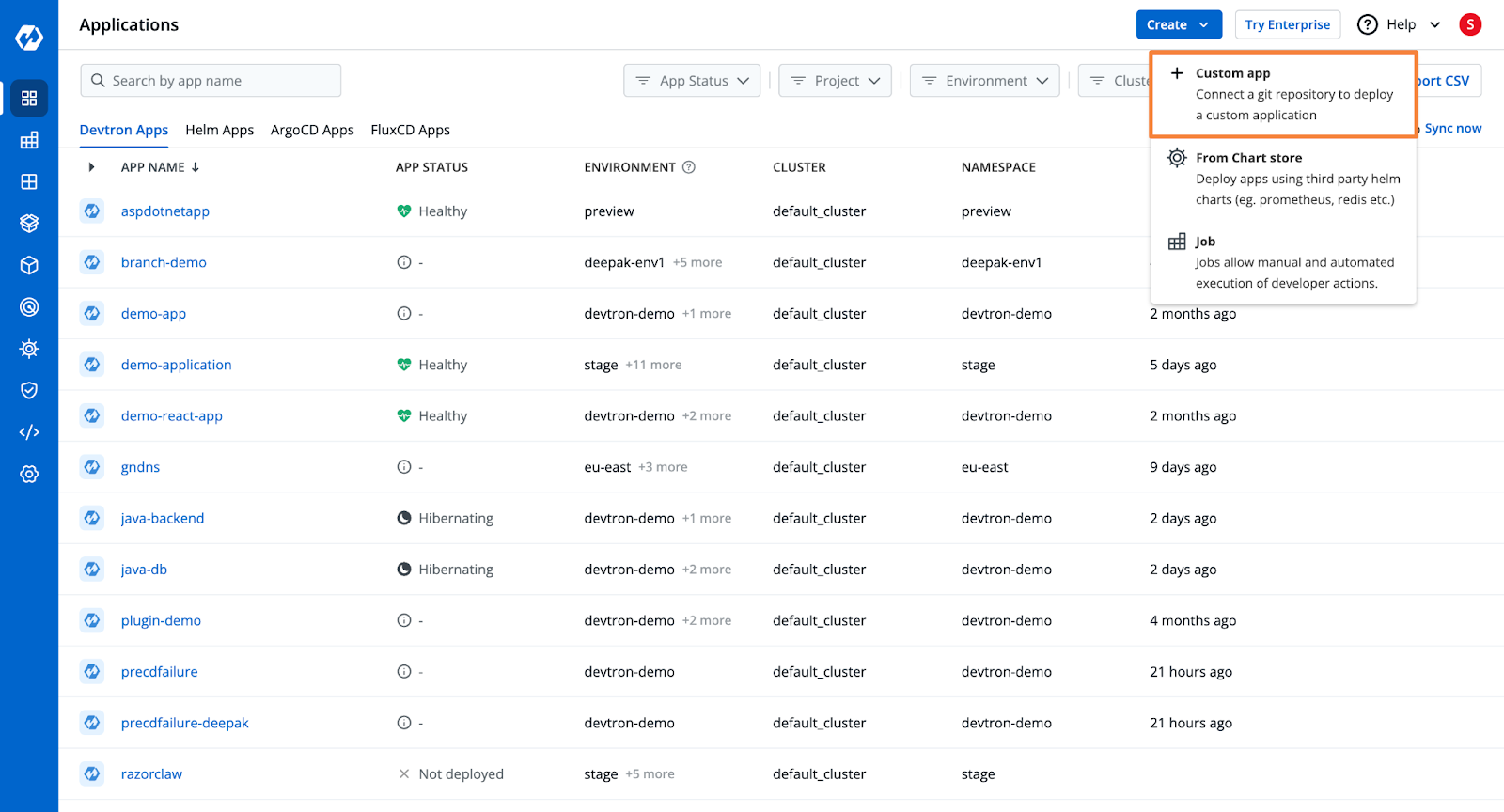
Check out the documentation to learn more about the application creation process.
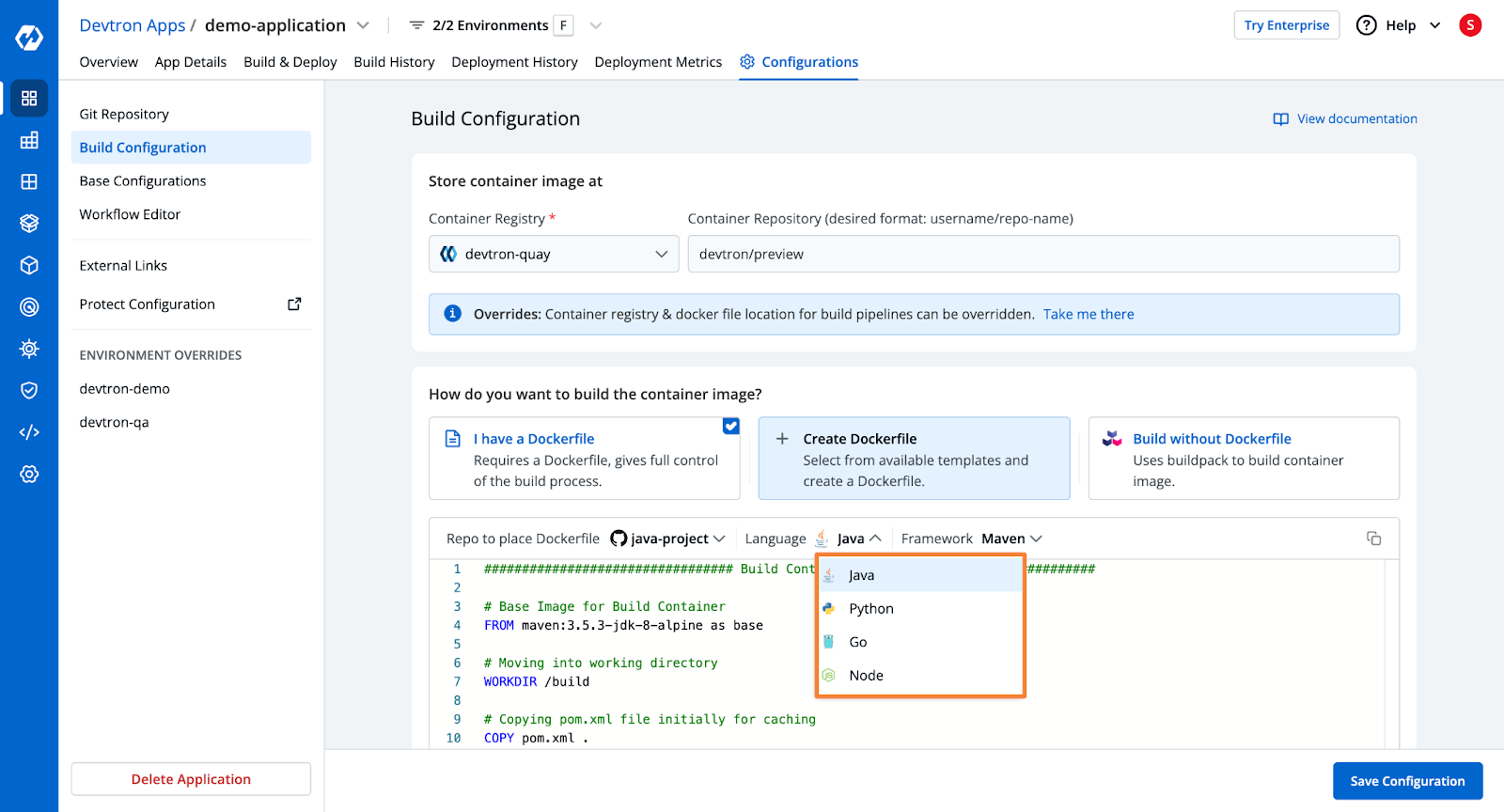
Step 2: Configure the Build
- Devtron will pull code from the repository and build the Docker container.
- You need to configure an OCI Container Registry.
- Choose from three build options:
- Use an existing Dockerfile
- Create a Dockerfile (using Devtron's template for Rails applications)
- Use Buildpacks
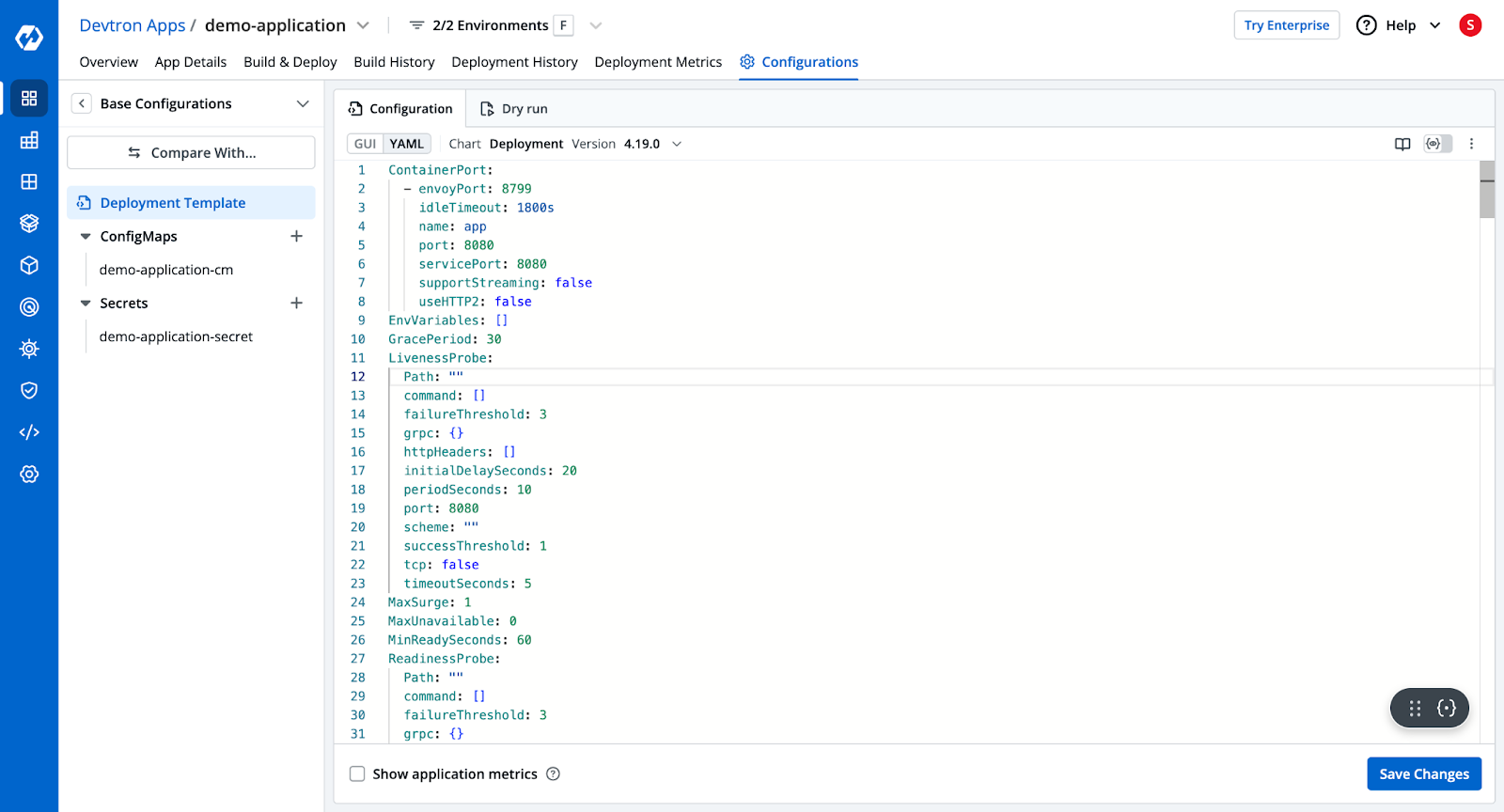
Step 3: Deployment Configurations
- Devtron provides a pre-configured YAML template for Kubernetes deployment.
- Configure ingress, autoscalers, and other deployment settings.
Step 4: Create the CI/CD Pipelines
- The CI pipeline will build the application and push the image to a registry.
- The CD pipeline will trigger deployments in the Kubernetes cluster.
- Configure Pre and Post Stages (e.g., security scanning, unit testing).
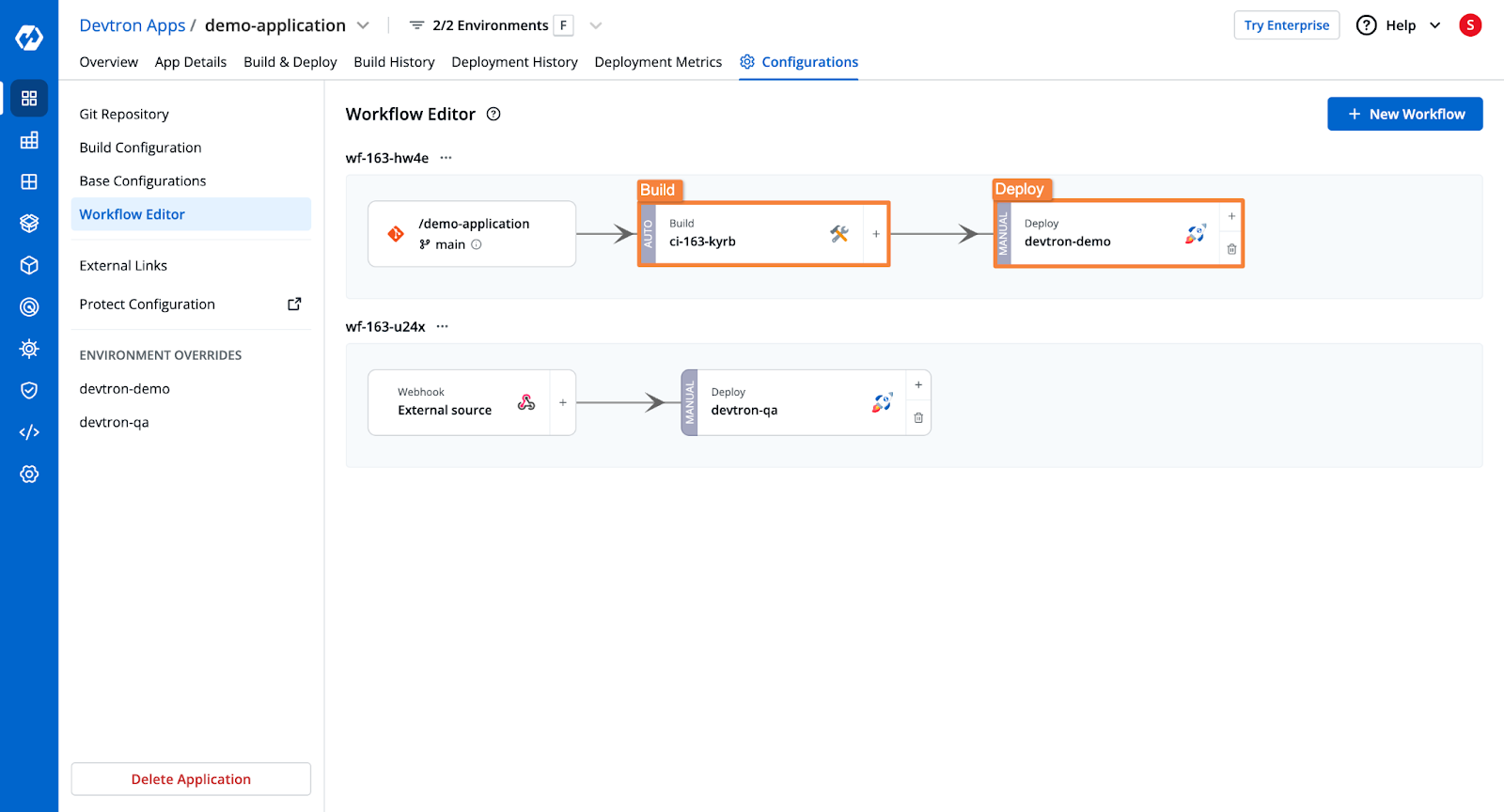
Please check the documentation to learn more about the pipeline configurations.
Step 5: Trigger the Build and Deploy Pipelines
- Select the Git branch and trigger the build stage.
- Once the build is complete, trigger the deployment stage.
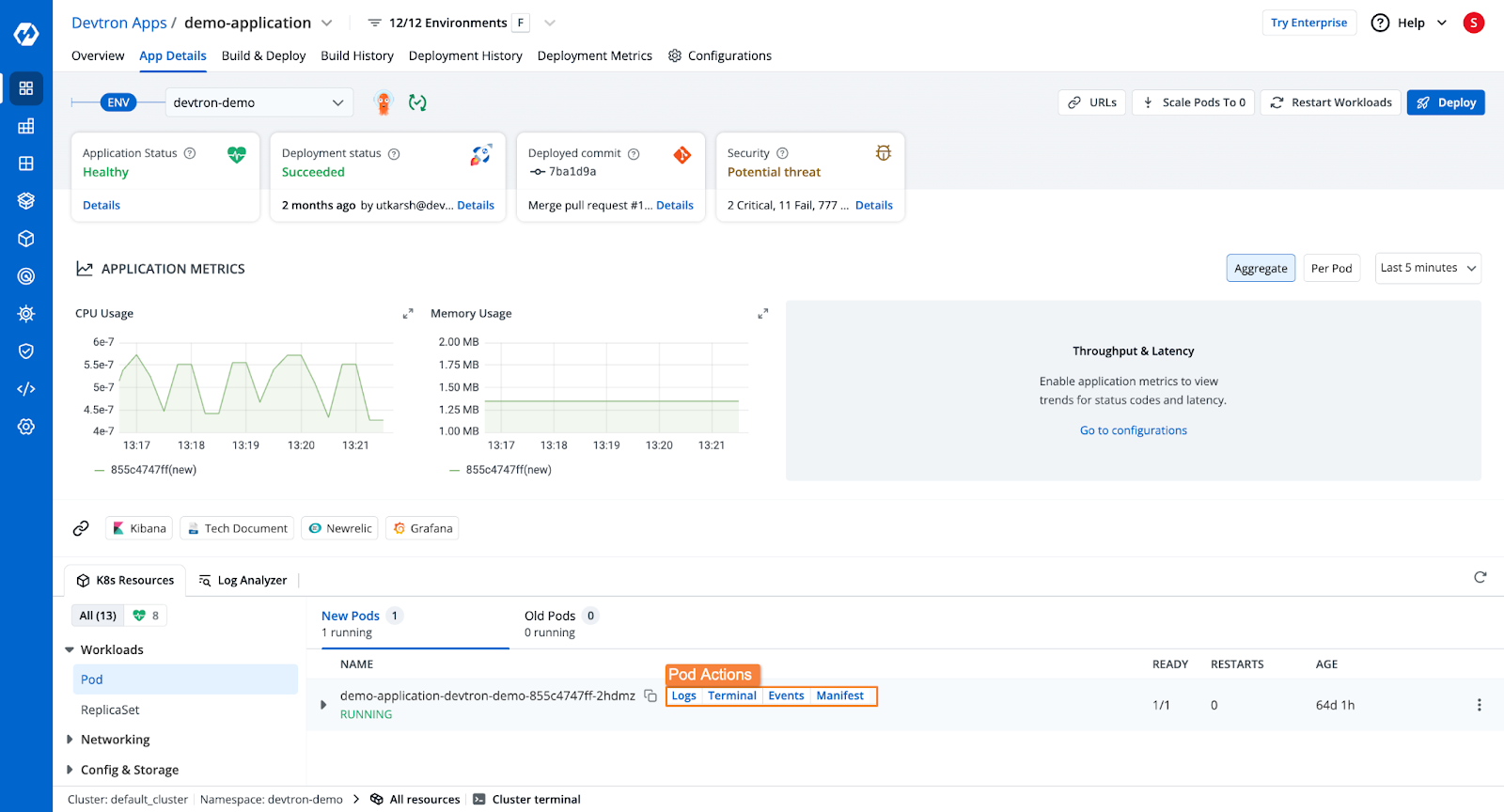
- Devtron will deploy the application and show:
- Deployment status
- Application health
- Kubernetes resource details
- Security vulnerabilities
- Rollback options in case of errors
Once the application is deployed, you will be able to see the application's health, deployment status, security vulnerabilities, the Kubernetes resources of the application, and more.
Method 2: Deploying Rails Applications Manually Using Kubernetes
Step 1: Create the Dockerfile
A Dockerfile is a set of instructions to build a container image. Below is the Dockerfile to containerize your Rails application:
# Stage 1: Build the Rails application
FROM ruby:3.0.0 AS build
# Set working directory
WORKDIR /app
# Install dependencies
RUN apt-get update -qq && apt-get install -y \
build-essential \
libpq-dev \
nodejs \
yarn \
&& rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
# Copy Gemfile and Gemfile.lock first to leverage Docker caching
COPY Gemfile Gemfile.lock ./
# Install Ruby gems
RUN bundle install --jobs 4 --retry 5
# Copy the Rails app code
COPY . .
# Precompile assets for production (optional)
RUN RAILS_ENV=production bundle exec rake assets:precompile
# Stage 2: Create the production image
FROM ruby:3.0.0-slim AS production
# Set working directory
WORKDIR /app
# Install only runtime dependencies
RUN apt-get update -qq && apt-get install -y \
libpq-dev \
&& rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
# Copy app from the build stage
COPY --from=build /app /app
# Set environment variables
ENV RAILS_ENV=production
ENV RACK_ENV=production
# Expose the port the app will run on
EXPOSE 3000
# Run database migrations and start the server
CMD ["sh", "-c", "bundle exec rake db:migrate && bundle exec rails server -b '0.0.0.0'"]
Step 2: Build and Push the Docker Image
Run the following command to build the Docker image:
- Run the following command to build the Docker image:
docker build -t devtron/Rails-app:v1 .
- Push the image to DockerHub:
docker push devtron/Rails-app:v1 .
Step 3: Creating the Kubernetes Deployment and Service Manifests
- Create a deployment.yaml file:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: Rails-deployment
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: Rails
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: Rails
spec:
containers:
- name: Rails-container
image: devtron/Rails-app
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
- Create a service.yaml file:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: Rails-service
spec:
selector:
app: Rails
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 8080
type: NodePort
Step 4: Deploy to Kubernetes
Run the following command to apply the manifests:
kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml service.yaml
Your Rails application is now deployed to Kubernetes!
Common Challenges and Solutions
1. Container Image Size Management
- Use Multi-Stage Builds to separate build and runtime environments.
- Use Lightweight Base Images like Alpine or Distroless to reduce size.
2. Handling Environment Configurations
- Use Kubernetes ConfigMaps & Secrets to inject environment variables dynamically.
- Avoid hardcoding configurations to enable seamless environment switching.
3. Secret Management
- Use Vault or External Secret Managers (e.g., HashiCorp Vault, AWS Secrets Manager) for secure secret handling.
4. Security and Vulnerability Management
- Regularly update dependencies using bundler-audit or dependabot.
- Scan container images with Trivy or Clair for vulnerabilities.
FAQ
What are the prerequisites for how to deploy ruby on rails applications to kubernetes effectively?
To deploy Ruby on Rails applications to Kubernetes effectively, you need a containerized Rails app (using Docker), a configured Kubernetes cluster, and a YAML manifest defining deployments, services, and config maps. Ensure proper database integration, environment variables, and scaling policies.
How can I troubleshoot issues during how to deploy ruby on rails applications to kubernetes effectively?
To troubleshoot deployment issues, use kubectl logs to check application and pod logs, kubectl describe for events and resource details, and ensure readiness/liveness probes are configured. Verify database connectivity, environment variables, and analyze any misconfigurations in the YAML manifests.
What tools are recommended for how to deploy ruby on rails applications to kubernetes effectively?
Recommended tools include Docker for containerizing the Rails app, Helm for managing Kubernetes resources, and kubectl for cluster interaction. Additionally, use CI/CD tools like ArgoCD or Jenkins for deployment automation and Prometheus/Grafana for monitoring.
What are the best practices for how to deploy ruby on rails applications to kubernetes effectively?
Best practices include containerizing your Rails app with multi-stage Docker builds, managing secrets securely with tools like Kubernetes Secrets or HashiCorp Vault, and using Horizontal Pod Autoscalers for scaling. Ensure proper health probes, monitor app performance, and use a CI/CD pipeline for seamless updates.
Conclusion
In this blog, we explored two approaches for deploying Rails applications on Kubernetes:
- Automated Devtron Deployment with built-in CI/CD pipelines and advanced configurations.
- Manual Kubernetes Deployment using Docker and YAML manifests.
Using Devtron simplifies Kubernetes deployments, reducing manual efforts and improving efficiency. Start deploying applications today using Devtron’s platform!