Spring Boot is a popular Java-based framework for building standalone, production-grade applications. It simplifies Java application development with auto-configuration and embedded servers. While Spring Boot streamlines Java application development and tools like Vagrant provide streamlined development environments, these alone aren't sufficient for production deployment. Production environments demand robust capabilities including automated failure handling, self-healing mechanisms, and dynamic scaling to meet varying workloads. These features are essential for maintaining reliable, high-performance applications in real-world scenarios.
Containerizing your Spring Boot applications makes them portable and infrastructure-agnostic. The containers package the application, its dependencies, and its runtime environment into standardized units. When combined with Kubernetes orchestration capabilities, this containerization approach enables efficient deployment, scaling, and management of Spring Boot applications in modern cloud infrastructure.
This blog will walk you through the journey of modernizing your Spring Boot applications for Kubernetes deployment. Whether you're running a high-traffic API service, a microservices architecture, or a traditional web application, you'll learn how to leverage Kubernetes to ensure your Spring Boot applications are scalable, reliable, and easy to maintain.
We will explore two methods for deploying Java Spring Boot applications:
- Using Devtron for Automated Deployment
- Using Kubernetes Manually
Deploying Java Spring Boot Applications on Kubernetes
Deploying a Java Spring Boot application to Kubernetes involves several steps. Let’s first review the overall process and then discuss the various steps in depth.
Steps for Deployment
- Write and build the Java Spring Boot Application
- Containerize the Java Spring Boot Application
- Push the container to a Container Registry such as DockerHub
- Create the required YAML Manifest for Kubernetes Resources
- Apply the YAML manifest to the Kubernetes clusters
Prerequisites
Before proceeding with the deployment process, please make sure that you have the following prerequisites
- A Java Spring Boot application (You can clone this repo)
- Docker
- Kubectl
- A Kubernetes Cluster such as kind
Method 1: Deploying Java Spring Boot Applications Using Devtron
Devtron is a Kubernetes management platform that simplifies the entire DevOps lifecycle. It automates the creation of Dockerfiles, and Kubernetes manifests, builds the application, and manages deployment through an intuitive UI.
Step 1: Create a Devtron Application and Add Git Repository
- From Devtron’s home page, create a new Devtron application.
- Add the Git Repository containing the Java Spring Boot application code.
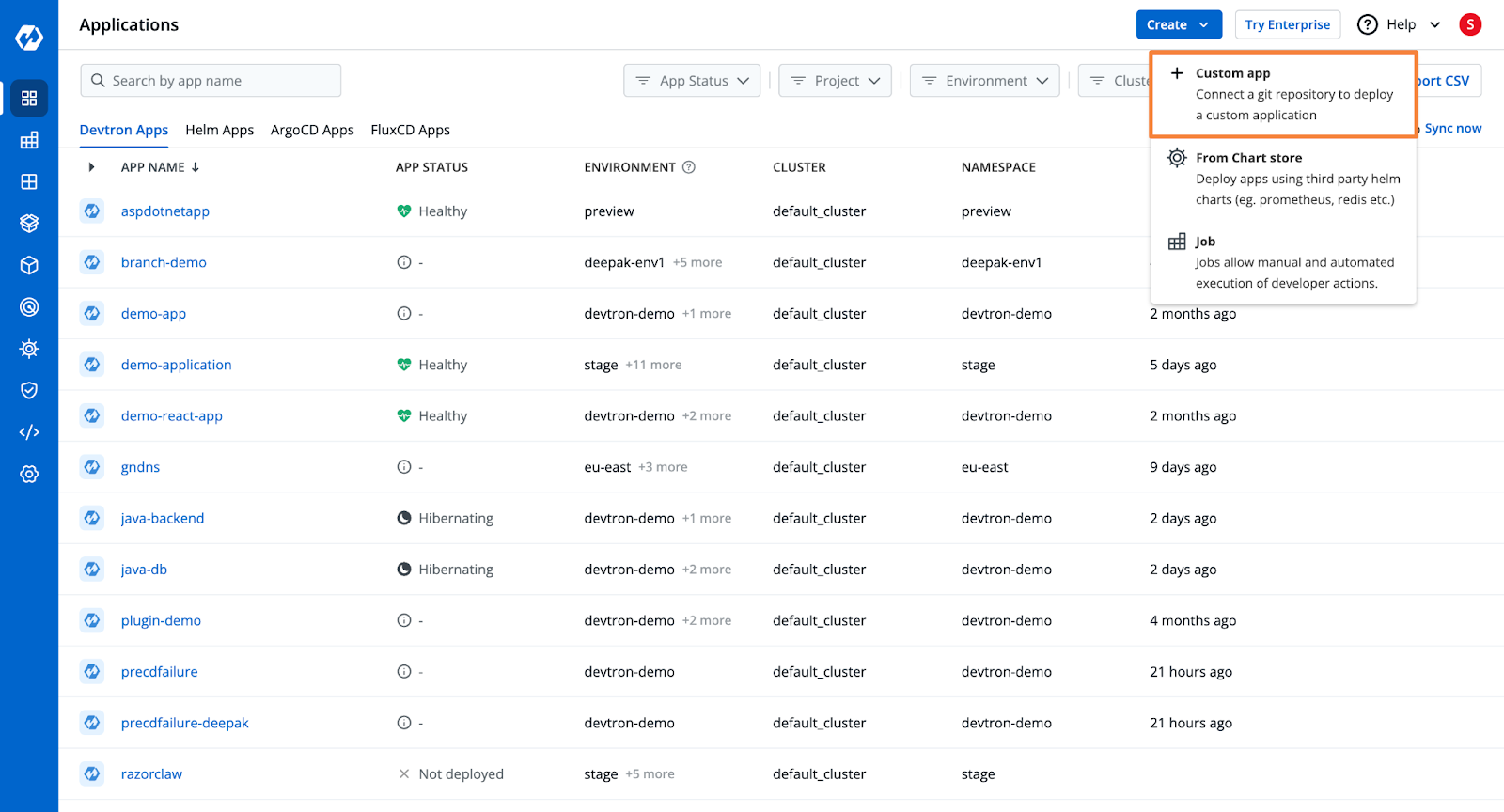
Check out the documentation to learn more about the application creation process.
Step 2: Configure the Build
- Devtron will pull code from the repository and build the Docker container.
- You need to configure an OCI Container Registry.
- Choose from three build options:
- Use an existing Dockerfile
- Create a Dockerfile (using Devtron's template for Express.js applications)
- Use Buildpacks
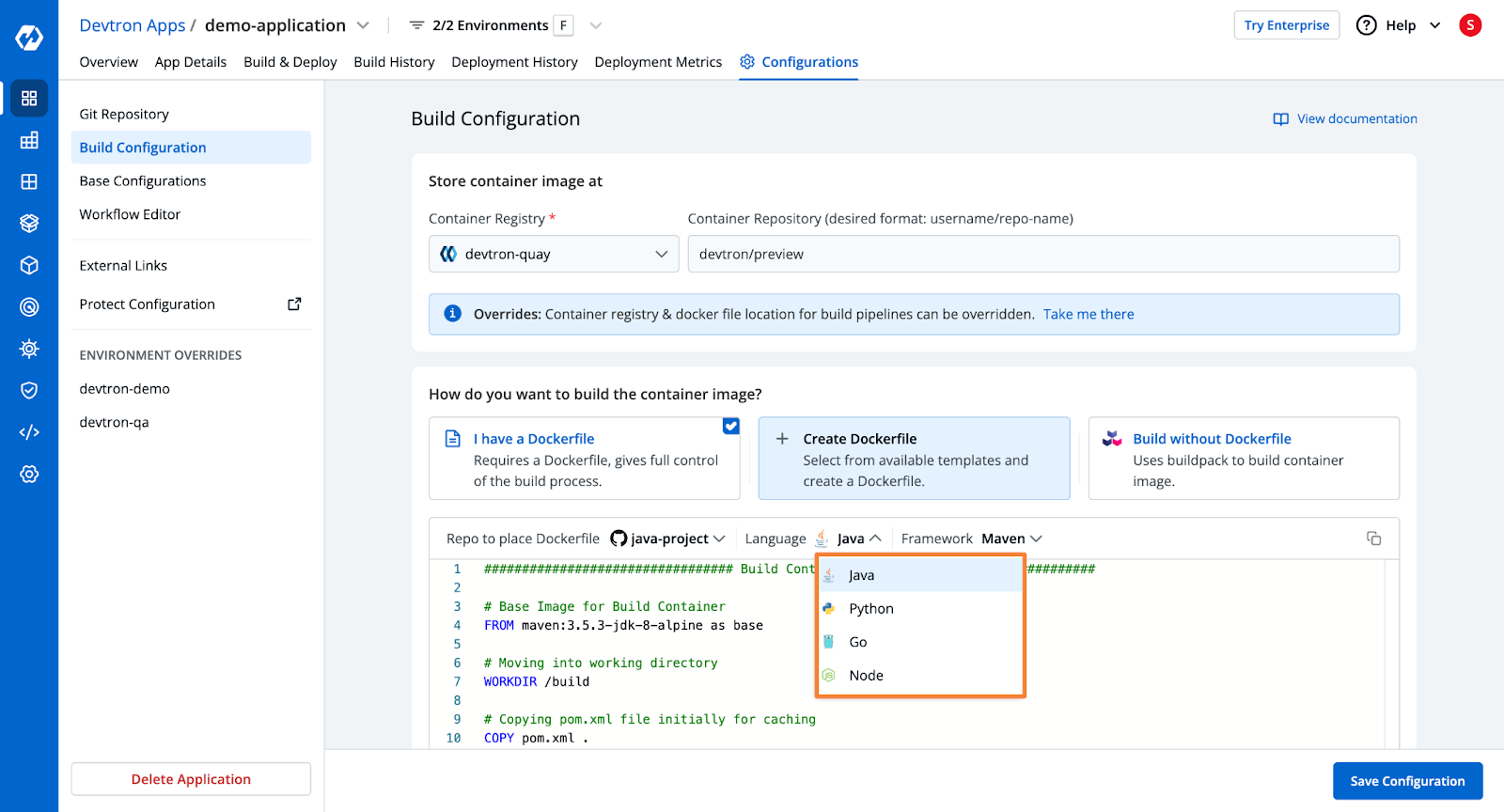
- Devtron provides a pre-configured YAML template for Kubernetes deployment.
- Configure ingress, autoscalers, and other deployment settings.
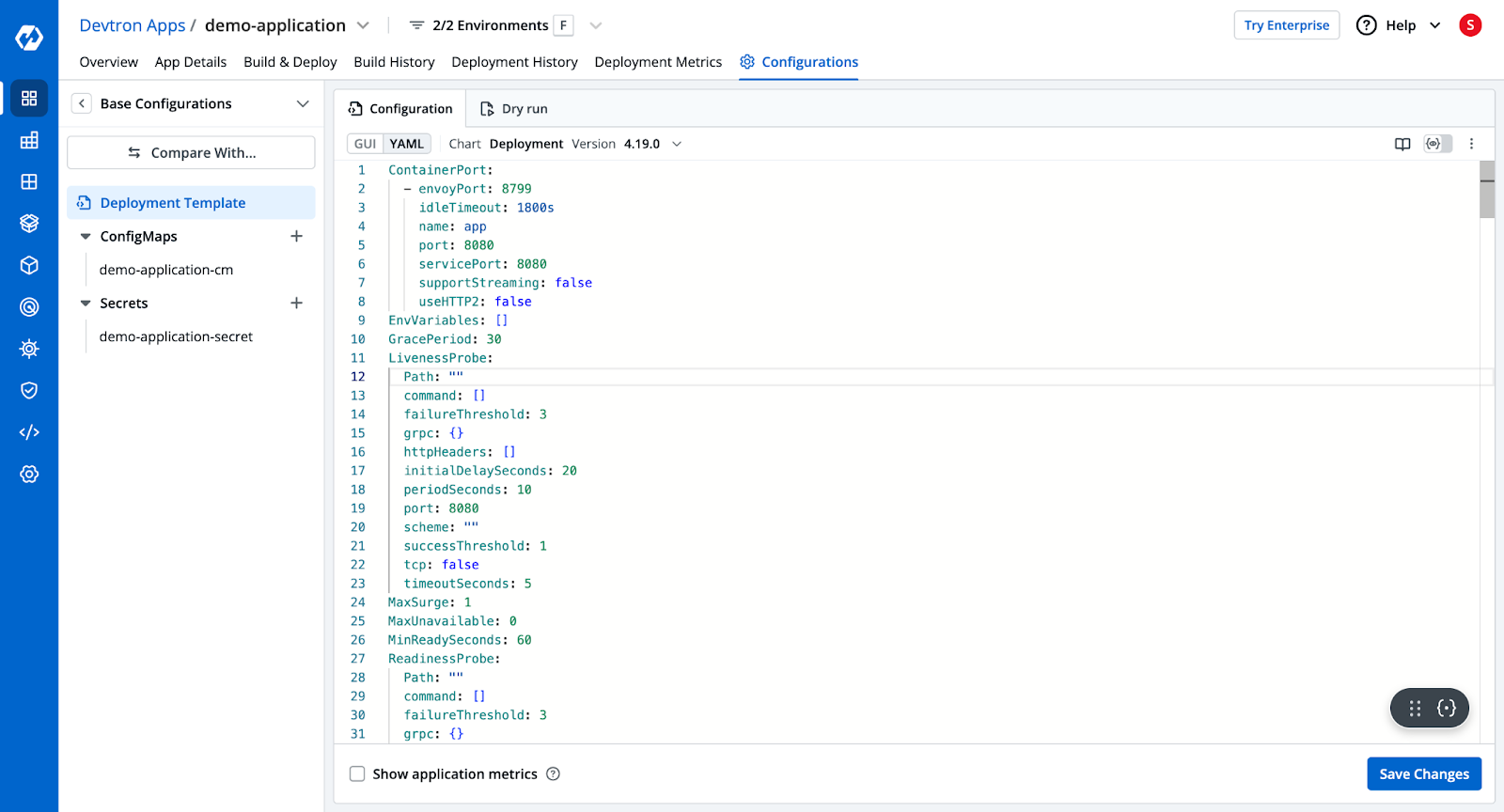
Step 4: Create the Build and Deploy Pipelines
- The CI pipeline will build the application and push the image to a registry.
- The CD pipeline will trigger deployments in the Kubernetes cluster.
- Configure Pre and Post Stages (e.g., security scanning, unit testing).
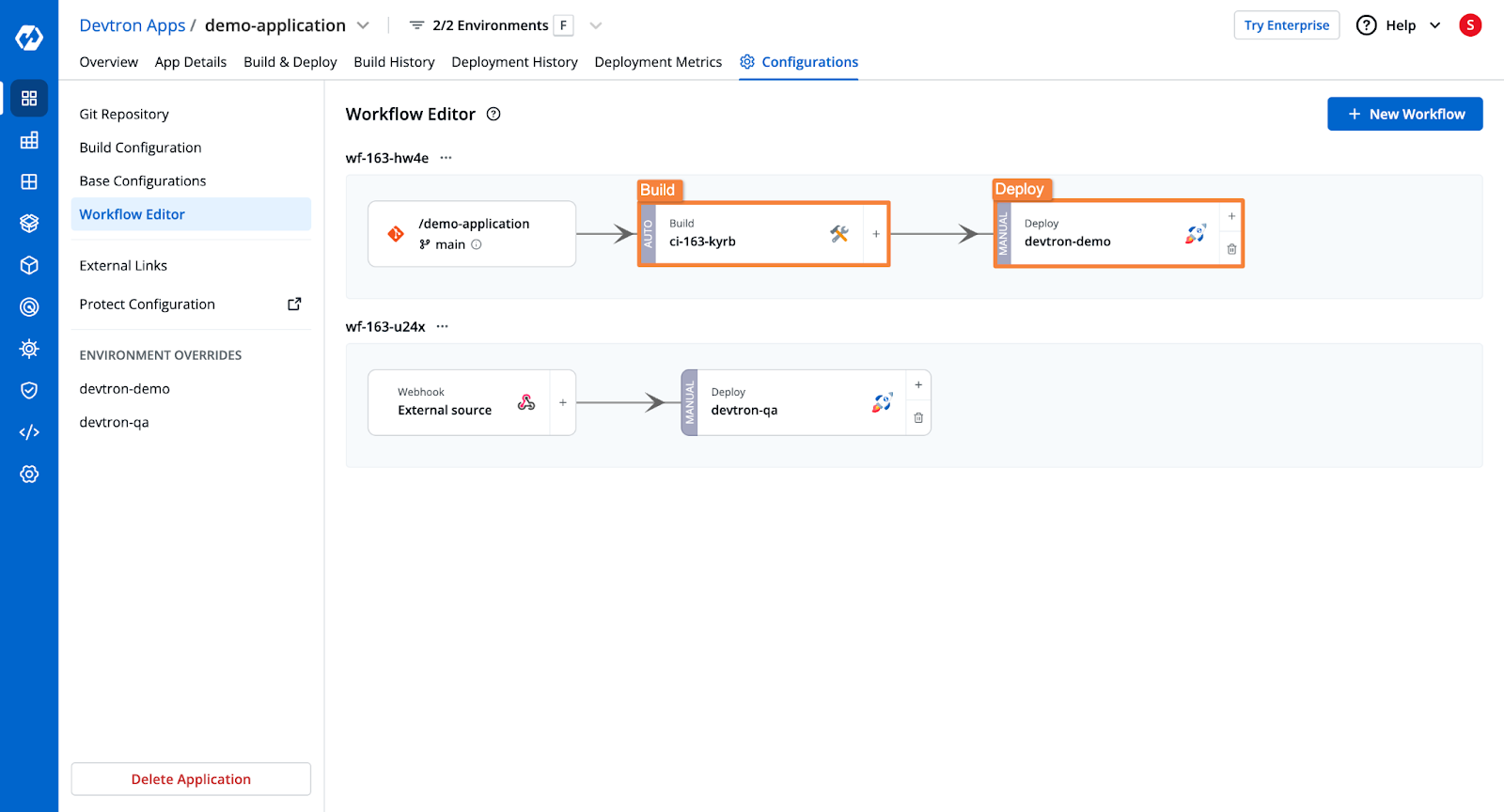
Step 5: Trigger the Build and Deployment Pipelines
- Select the Git branch and trigger the build stage.
- Once the build is complete, trigger the deployment stage.
- Devtron will deploy the application and show:
- Deployment status
- Application health
- Kubernetes resource details
- Security vulnerabilities
- Rollback options in case of errors
Once the application is deployed, you will be able to see the application's health, deployment status, security vulnerabilities, the Kubernetes resources of the application, and more.
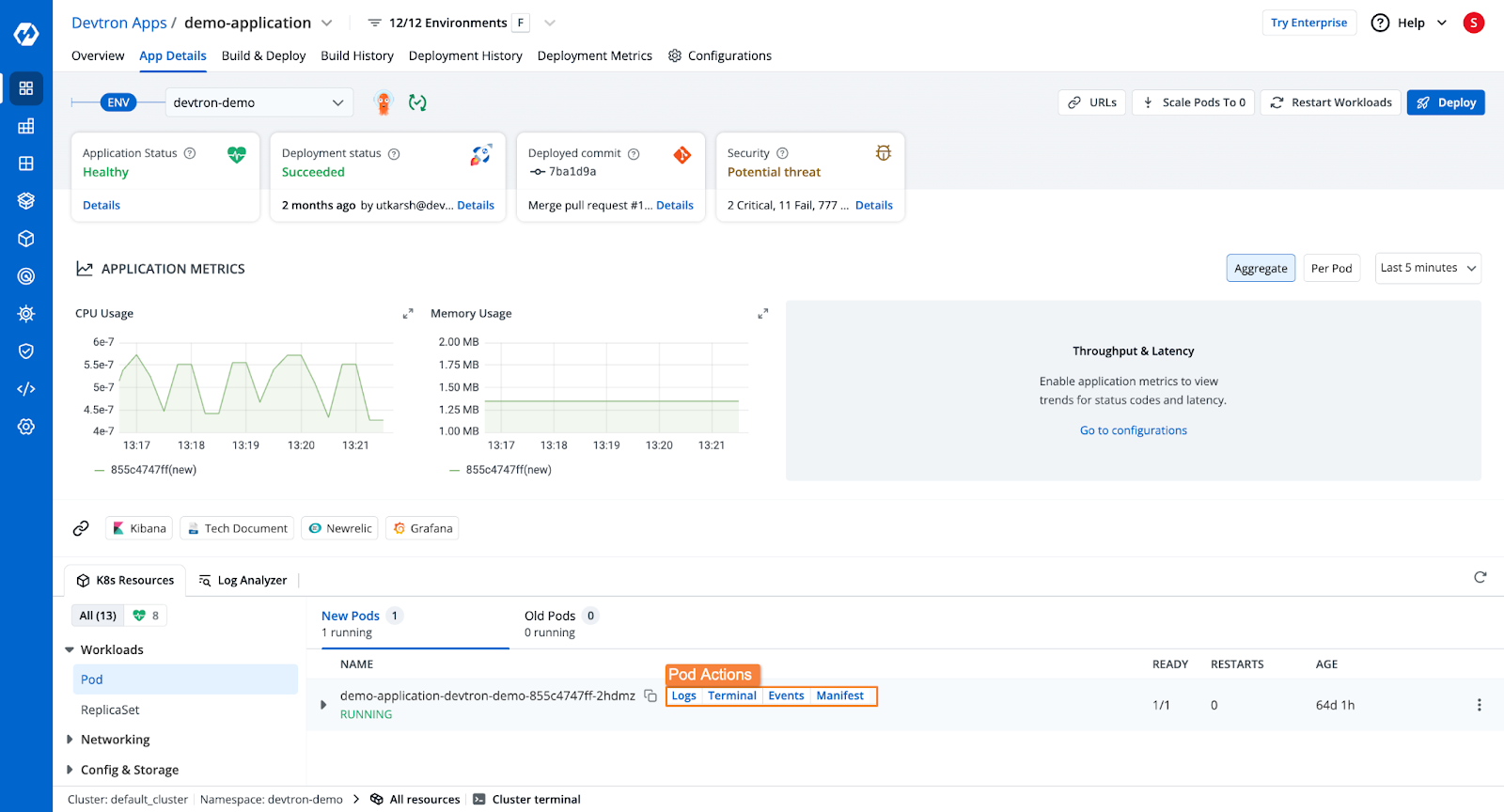
Method 2: Deploying Java Spring Boot Applications Manually to Kubernetes
Step 1: Create the Dockerfile
A Dockerfile is a set of instructions for building a container image. Below is the Dockerfile to containerize your Java Spring Boot application:
FROM adoptopenjdk/openjdk11:alpine-jre
# Refer to Maven build -> finalName
ARG JAR_FILE=target/spring-boot-web.jar
# cd /opt/app
WORKDIR /opt/app
# cp target/spring-boot-web.jar /opt/app/app.jar
COPY ${JAR_FILE} app.jar
# java -jar /opt/app/app.jar
ENTRYPOINT ["java","-jar","app.jar"]
Step 2: Build and Push the Docker Image
Run the following command to build the Docker image:
docker build -t devtron/spring-boot-app:v1 .
Push the image to DockerHub:
docker push devtron/spring-boot-app
Step 3: Creating the Kubernetes Deployment and Service Manifests
Create a deployment.yaml file:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: knote
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: knote
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: knote
spec:
containers:
- name: app
image: learnk8s/knote-java:1.0.0
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
env:
- name: MONGO_URL
value: mongodb://mongo:27017/dev
imagePullPolicy: Always
Create a service.yaml file:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: knote
spec:
selector:
app: knote
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 8080
type: LoadBalancer
Step 4: Deploy to Kubernetes
Run the following command to apply the manifests:
kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml service.yaml
Your Java Spring Boot application has now been deployed to Kubernetes.
Common Challenges and Solutions
1. Container Image Size Management
- Use Multi-Stage Builds to separate build and runtime environments.
- Use Lightweight Base Images like Alpine or Distroless to reduce size.
2. Resource Management
- Set Memory and CPU Limits to avoid overconsumption.
- Implement Autoscaling (HPA) to handle varying workloads.
3. Deployment Strategies
- Rolling Updates to ensure zero-downtime deployments.
- Graceful Shutdown Handling to avoid breaking live traffic.
Conclusion
In this blog, we explored two approaches for deploying Java Spring Boot applications on Kubernetes:
- Manual Kubernetes Deployment using Docker and YAML manifests.
- Automated Devtron Deployment with built-in CI/CD pipelines and advanced configurations.
Using Devtron simplifies Kubernetes deployments, reducing manual efforts and improving efficiency. Start deploying applications today using Devtron’s platform!
FAQ
What tools are required to deploy a Spring Boot application on Kubernetes?
To deploy Spring Boot application on Kubernetes you need, Docker for containerization, kubectl for interacting with Kubernetes, and a Kubernetes cluster (e.g., Kind, GKE, EKS, AKS).
How do I containerize a Spring Boot application?
Use Docker to create a container image by writing a Dockerfile that specifies the base image, copies application files, and sets the run command.
What are Kubernetes manifests used for?
Kubernetes manifests (YAML files) define resources like deployments and services, specifying how applications should be deployed and exposed within a Kubernetes cluster.
How do I automate the deployment of a Spring Boot application to Kubernetes?
Use CI/CD tools like Jenkins, GitHub Actions, or platforms like Devtron to automate building, testing, and deploying container images to Kubernetes.
What benefits does deploying a Spring Boot application on Kubernetes offer?
Deploying on Kubernetes provides scalability, reliability, and ease of management through features like automated scaling and self-healing.