Kubernetes CPU Manager enhances workload performance by allocating exclusive CPU cores to specific containers. This feature is crucial for latency-sensitive applications, providing predictable performance through CPU affinity and isolation while optimizing resource utilization across your cluster
Kubernetes
Learn how CPU limits in Kubernetes cause throttling, wasted resources, and poor performance. Use CPU requests instead of limits for efficient resource utilization. Best practices like reserving CPU requests and allowing burstable workloads can improve performance and optimize cost efficiency.
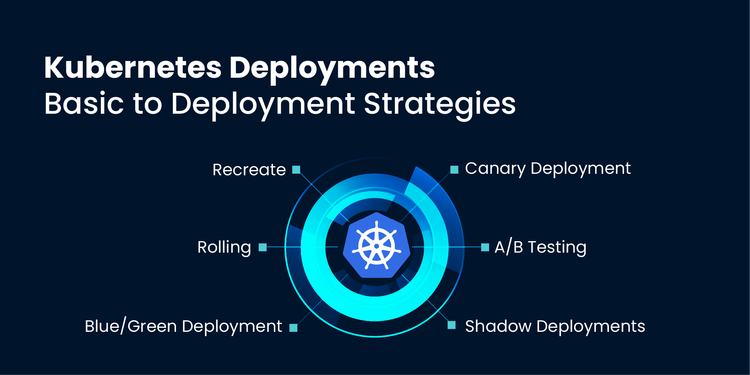
TL;DR: Master Kubernetes deployments with this guide to six essential strategies. Learn how to choose between Recreate, Rolling Update, Blue/Green, Canary, A/B Testing and Shadow Deployment to maximize reliability, minimize downtime, and improve your release process.
TL;DR: Learn Kubernetes Deployments, their role in managing pods and strategies like rolling updates, blue/green and canary for zero-downtime updates. Configure and apply these strategies in your Kubernetes environment to ensure high availability & smooth application rollouts.
TL;DR: Kubernetes v1.32 introduces key enhancements, including auto-removing PVCs, improved pod lifecycle and resource allocation and management, OpenTelemetry tracing and graceful shutdowns, ensuring a modern, secure and efficient infrastructure.
TLDR; Kubernetes Labels and Selectors are one of the Kubernetes fundamentals for identifying and relating resources to each other. Labels are the properties attached to each object. Selector helps us to filter the objects which have labels attached to them.
TL;DR: Developers do not need to operate Kubernetes Clusters with kubectl. Platforms help streamline the DX and provide them just the right information
TL;DR: Master Kubernetes node scheduling with Node Affinity. Learn how to attract pods to specific nodes based on labels, resources and more. Explore practical examples and use Devtron to manage Kubernetes deployments seamlessly.